Understanding Thyroid Function
The thyroid gland is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck. It plays a vital role in regulating metabolism, growth, and development. The thyroid produces two main hormones: thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3).

Thyroid Hormone Levels
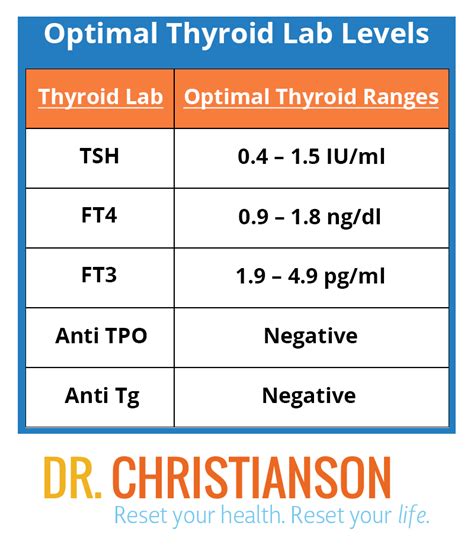
Thyroid hormone levels are measured through blood tests. The normal range for T3 levels in men is 1.54-3.37 nanograms per deciliter (ng/dL). A T3 level above the normal range is considered hyperthyroidism, while a level below the normal range is considered hypothyroidism.
T3 Levels and Men’s Health
T3 levels play a significant role in several aspects of men’s health, including:
- Metabolism: T3 regulates the body’s metabolic rate, influencing weight, energy expenditure, and appetite.
- Muscle Mass: Adequate T3 levels are essential for maintaining muscle mass and strength.
- Bone Health: T3 contributes to bone formation and mineralization.
- Cognitive Function: T3 is involved in cognitive function, memory, and attention.
- Libido: T3 levels may influence libido and sexual function in men.
Interpretation of a T3 Level of 3.54
A T3 level of 3.54 ng/dL is slightly above the upper limit of the normal range (3.37 ng/dL). This suggests that the individual may have mild hyperthyroidism.
Symptoms of Mild Hyperthyroidism
Individuals with mild hyperthyroidism may experience a range of symptoms, including:
- Increased heart rate and sweating
- Weight loss despite increased appetite
- Anxiety and irritability
- Difficulty sleeping
- Muscle weakness and tremors
Causes of Mild Hyperthyroidism
Several factors can contribute to mild hyperthyroidism, such as:
- Graves’ disease: An autoimmune disorder that causes the thyroid gland to produce excessive thyroid hormones
- Thyroiditis: Inflammation of the thyroid gland
- Certain medications: Certain medications, such as amiodarone, can interfere with thyroid function
- Iodine deficiency: Iodine is essential for thyroid hormone production
Treatment for Mild Hyperthyroidism
Treatment for mild hyperthyroidism typically involves medications to suppress thyroid hormone production. In some cases, radioactive iodine or surgery may be necessary.
Conclusion
A T3 level of 3.54 ng/dL in men suggests mild hyperthyroidism. This condition can cause a range of symptoms and requires proper evaluation and treatment to prevent potential complications. Regular thyroid hormone level monitoring and appropriate medical care are crucial for maintaining optimal health.