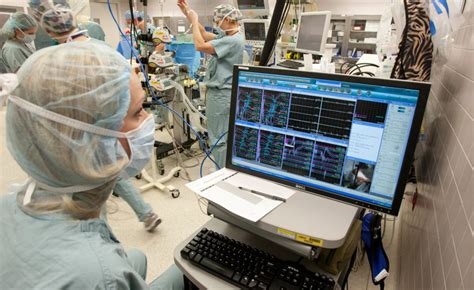
Intraoperative neuromonitoring (IONM) is a groundbreaking technology that has revolutionized surgical procedures by providing real-time monitoring of the nervous system during complex surgeries. This advanced technique safeguards delicate neural structures, minimizing the risk of neurological damage and ensuring optimal outcomes.

Benefits of IONM: Protecting the Nervous System
IONM offers numerous benefits in the surgical arena, including:
- Enhanced Precision: IONM allows surgeons to operate with greater confidence and precision, knowing that the nervous system is being closely monitored and protected.
- Reduced Risk of Neurological Damage: By providing continuous feedback on the integrity of neural structures, IONM alerts surgeons to potential risks during surgery, enabling timely interventions to minimize damage.
- Improved Patient Outcomes: The use of IONM has led to significantly improved patient outcomes, reducing the incidence of neurological complications and enhancing post-operative recovery.
Types of IONM Techniques
IONM encompasses a range of techniques, each tailored to monitor specific neural pathways:
- Motor Evoked Potentials (MEPs): Monitor the pathways that control muscle movement, ensuring proper function after spinal cord or brain surgery.
- Somatosensory Evoked Potentials (SEPs): Assess the pathways responsible for touch and sensory perception after spine or peripheral nerve surgeries.
- Electrocorticography (ECoG): Monitors brain activity during brain tumor surgeries, preserving critical neurological functions.
- Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS): Stimulates the motor cortex to assess brain function and connectivity, especially during awake brain surgeries.
Applications of IONM: Beyond Traditional Boundaries
IONM’s applications extend beyond traditional surgical specialties, opening up new frontiers in surgical monitoring:
- Spine Surgery: IONM plays a vital role in complex spinal surgeries, including spinal fusions, to protect the spinal cord and nerve roots from damage.
- Brain Tumor Surgery: IONM assists in preserving critical neural functions, such as speech and motor function, during brain tumor removal surgeries.
- Peripheral Nerve Surgery: IONM helps prevent nerve damage during peripheral nerve repairs and reconstructions, ensuring optimal nerve function.
- Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS): IONM ensures accurate electrode placement in DBS surgeries, maximizing therapeutic outcomes for patients with Parkinson’s disease and other neurological conditions.
Innovations in IONM: Pushing Boundaries
Technological advancements are driving continuous innovation in IONM:
- Wireless IONM: Eliminates cumbersome cables, providing greater mobility and enhanced patient comfort during surgery.
- Machine Learning Algorithms: Integrate AI algorithms into IONM systems, allowing for more sophisticated data analysis and improved detection of neural changes.
- Multimodal IONM: Combines multiple monitoring techniques to provide a comprehensive assessment of the nervous system, enhancing diagnostic accuracy and surgical safety.
Tips and Tricks for Effective IONM Utilization
To maximize the benefits of IONM, consider the following tips:
- Establish Clear Communication Protocols: Ensure proper communication between the surgeon, neurophysiologist, and anesthesia team throughout the surgery.
- Use Reliable Equipment: Invest in high-quality IONM equipment that is regularly calibrated and maintained.
- Train Staff Thoroughly: Provide comprehensive training to all surgical staff involved in IONM procedures.
Comparative Analysis of Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Enhanced surgical precision and safety
- Reduced risk of neurological complications
- Improved patient outcomes
- Wide range of applications in various surgical specialties
Cons:
- Can add to surgical costs
- Requires specialized equipment and trained personnel
- May not be feasible for all surgeries or patients
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What is the cost of IONM?
– The cost of IONM varies depending on the complexity of the surgery and the monitoring techniques used. -
Is IONM covered by insurance?
– Coverage varies by insurance provider. It is recommended to check with your insurance provider before the surgery. -
Can IONM guarantee no neurological damage?
– While IONM significantly reduces the risk of neurological damage, it cannot guarantee complete protection. -
Is IONM used in all surgeries?
– No, IONM is typically used in complex surgeries or when there is a high risk of neurological complications. -
How long does IONM monitoring last?
– The duration of IONM monitoring varies, depending on the type of surgery and the monitoring techniques used. -
Is IONM painful?
– IONM involves applying small electrodes to the scalp or spine, which is generally not painful. -
What are the potential risks of IONM?
– IONM is a safe procedure, but there is a small risk of skin irritation or infection at the electrode application sites. -
How can IONM be used in novel applications?
– The possibilities for IONM innovation are vast. One creative application is using IONM to monitor brain activity during non-surgical procedures, such as language therapy or rehabilitation, to optimize treatment outcomes.
Conclusion
Intraoperative neuromonitoring (IONM) is a revolutionary technology that empowers surgeons to operate with greater confidence and protect the delicate nervous system during complex procedures. By providing real-time feedback on neural function, IONM minimizes the risk of neurological damage and enhances patient outcomes. As the field continues to evolve with technological advancements and innovative applications, IONM will undoubtedly play an even more significant role in safeguarding the nervous system and improving surgical outcomes.