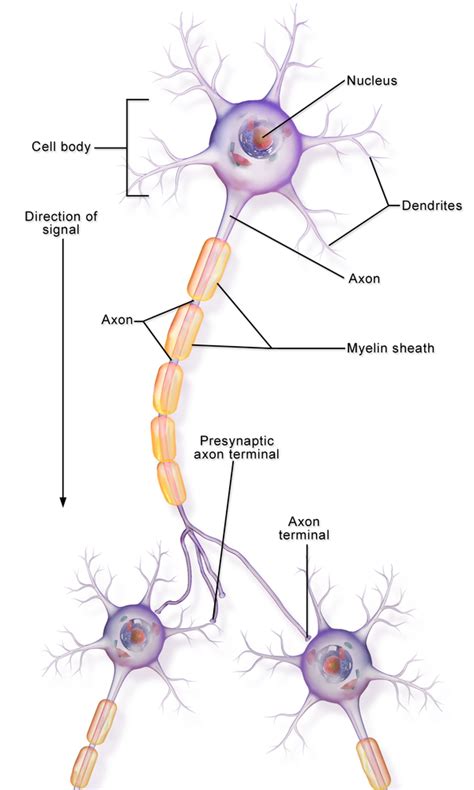
What are Interneurons?
Interneurons, also known as association neurons, are a type of neuron found in the central nervous system (CNS) responsible for connecting other neurons within the same region of the brain or spinal cord. They transmit signals between sensory neurons, which receive information from the outside world, and motor neurons, which control muscle movement. Interneurons play a crucial role in processing, integrating, and coordinating neural signals, shaping our thoughts, emotions, and actions.

Structure of Interneurons
Interneurons vary greatly in size, shape, and complexity. They typically have short axons and dendrites, enabling them to form intricate local connections within specific brain regions. Unlike sensory and motor neurons, interneurons do not extend axons beyond the CNS.
Types of Interneurons
Interneurons can be classified into several types based on their function and location within the CNS:
-
Excitatory Interneurons: Release neurotransmitters that increase the likelihood of postsynaptic neurons firing.
-
Inhibitory Interneurons: Release neurotransmitters that decrease the likelihood of postsynaptic neurons firing.
-
Local Interneurons: Connect neighboring neurons within the same brain or spinal cord region.
-
Projection Interneurons: Connect neurons over longer distances, often across different brain regions.
Functions of Interneurons
Interneurons perform a wide range of functions in the CNS, including:
-
Signal Processing: Integrate and modulate incoming sensory information, allowing for sophisticated analysis and decision-making.
-
Circuit Formation: Form connections that create neural pathways, enabling complex patterns of neural activity.
-
Motor Control: Coordinate motor neuron activity to produce precise and controlled movements.
-
Cognitive Function: Support higher-order cognitive functions such as attention, memory, and learning.
Importance of Interneurons
Interneurons are essential for the proper functioning of the nervous system. Their ability to modulate and integrate neural signals allows for:
-
Efficient Information Processing: Interneurons filter and channel information, preventing sensory overload and ensuring only relevant signals reach decision-making centers.
-
Complex Behavior: Interneurons enable the coordination of multiple motor and sensory functions, allowing for complex and adaptive behavior.
-
Higher Cognitive Function: Interneurons support cognitive processes by linking different brain regions involved in memory, attention, and planning.
Research and Applications
Research on interneurons is ongoing, with scientists exploring their role in various neurological disorders such as epilepsy, autism, and schizophrenia. Understanding interneuron function could lead to new therapeutic approaches for these conditions.
Conclusion
Interneurons are the unsung heroes of neural communication, playing a crucial role in shaping our thoughts, emotions, and actions. Their intricate connections and diverse functions make them a fascinating and important area of study in neuroscience. Ongoing research promises to shed further light on their role in health and disease, with the potential for novel therapeutic applications.