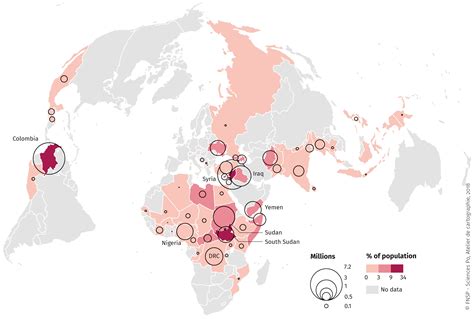
Introduction
Internally displaced persons (IDPs) are individuals who have been forced to flee their homes due to armed conflict, violence, natural disasters, or human-made disasters but have not crossed an internationally recognized border. According to the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR), an estimated 59.1 million people worldwide were internally displaced in 2022. This staggeringly large population faces immense challenges, including lack of shelter, food insecurity, and healthcare.

Causes of Internal Displacement
The primary causes of internal displacement are:
- Armed Conflict: The overwhelming majority of IDPs are displaced as a result of armed conflict. In 2022, approximately 53.2 million people were displaced due to war and violence.
- Natural Disasters: Natural disasters, such as earthquakes, floods, and hurricanes, can also trigger displacement, particularly in vulnerable communities. In 2022, an estimated 5.9 million people were displaced by natural disasters.
- Human-Made Disasters: Human-made disasters, such as industrial accidents, pollution, and forced evictions, can also lead to displacement. For example, the 2011 Fukushima nuclear disaster in Japan displaced approximately 160,000 people.
Challenges Faced by IDPs
IDPs face numerous challenges, including:
- Lack of Shelter: IDPs often lack adequate shelter, particularly in conflict zones where infrastructure is destroyed. They may live in temporary shelters, such as tents or makeshift camps, or seek refuge in overcrowded public spaces.
- Food Insecurity: IDPs frequently experience food insecurity due to disrupted food supplies and limited access to markets. In 2023, an estimated 48 million IDPs were food insecure and faced challenges obtaining sufficient food.
- Healthcare: IDPs often have limited access to healthcare services, including basic medical care, vaccinations, and specialized treatments. This lack of healthcare can lead to preventable diseases and fatalities.
- Education: IDPs face significant barriers to education, as schools may be damaged or inaccessible. Children who are displaced may miss out on critical years of schooling, which can have long-term consequences on their future prospects.
- Protection: IDPs are often vulnerable to violence, abuse, and exploitation. They may face discrimination and lack legal protection, which can exacerbate their vulnerability.
Strategies to Assist IDPs
Addressing the needs of IDPs requires a multi-faceted approach involving governments, international organizations, and humanitarian agencies. Effective strategies include:
- Emergency Relief: Providing immediate assistance to IDPs, such as food, shelter, and medical care, is critical. Humanitarian organizations play a vital role in delivering essential supplies and services to displaced populations.
- Protection: Strengthening the protection of IDPs through legal frameworks and law enforcement mechanisms is essential. Governments and international organizations must ensure that IDPs are safe and respected.
- Durable Solutions: Seeking durable solutions for IDPs, such as resettlement, local integration, or voluntary return, is crucial. This involves addressing the underlying causes of displacement and creating conditions that allow IDPs to rebuild their lives with dignity.
- Empowerment: Empowering IDPs through education, skills training, and income-generating opportunities is essential for their long-term well-being. This enables IDPs to become self-reliant and contribute to their communities.
The Future of IDPs
The number of IDPs worldwide is expected to rise in the coming years due to ongoing conflicts, natural disasters, and the effects of climate change. It is crucial that governments and international organizations prioritize the needs of IDPs and work towards sustainable solutions that address the root causes of displacement.
Data Tables
| Year | Number of IDPs Worldwide | Primary Cause |
|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 27.5 million | Armed conflict (78%) |
| 2015 | 40.3 million | Armed conflict (82%) |
| 2020 | 55.1 million | Armed conflict (82%) |
| 2022 | 59.1 million | Armed conflict (88%) |
| Region | Number of IDPs in 2022 | % of Global IDP Population |
|---|---|---|
| Africa | 32.2 million | 54.5% |
| Asia | 15.8 million | 26.7% |
| Latin America | 5.7 million | 9.7% |
| Europe | 4.3 million | 7.3% |
| North America | 0.9 million | 1.5% |
| Host Country | Number of IDPs in 2022 | % of Global IDP Population |
|---|---|---|
| Colombia | 5.4 million | 9.1% |
| Democratic Republic of the Congo | 5.5 million | 9.3% |
| Afghanistan | 3.9 million | 6.6% |
| Syria | 3.3 million | 5.6% |
| Ethiopia | 3.2 million | 5.4% |
| Cause of Displacement | Number of IDPs in 2022 | % of Global IDP Population |
|---|---|---|
| Armed conflict | 53.2 million | 89.7% |
| Natural disasters | 5.9 million | 10% |
| Human-made disasters | 0.01 million | 0.3% |