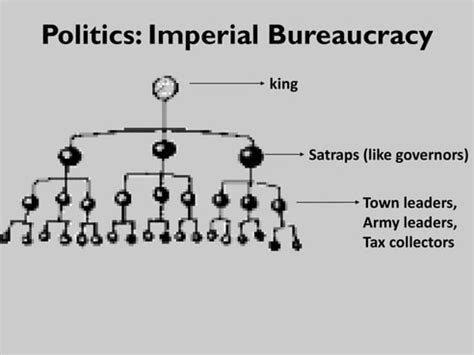
Defining Imperial Bureaucracy

In the context of AP World History, an imperial bureaucracy refers to a complex administrative system established by an imperial power to govern its vast territories. Its primary role is to implement and maintain the laws, policies, and directives of the empire, ensuring the smooth functioning of the government and the well-being of its subjects.
Imperial bureaucracies are typically characterized by:
- Hierarchy: Officials are arranged in a hierarchical structure, with each level reporting to and being responsible to the level above.
- Division of Labor: Tasks are divided and assigned to specialized departments or offices, resulting in increased efficiency.
- Meritocracy: In theory, officials are selected and promoted based on their qualifications and abilities, rather than their social status or connections.
- Professionalization: Bureaucrats are trained and educated in the principles of administration and governance, ensuring their competence and impartiality.
Examples of Imperial Bureaucracies
- Roman Empire: The Roman bureaucracy was highly developed and influential, with a vast network of officials responsible for various administrative, financial, and judicial functions.
- Han Dynasty China: The Han Dynasty established a centralized bureaucracy that played a crucial role in governing the empire’s extensive territories.
- British Empire: The British Empire relied heavily on its bureaucracy to manage its colonies and overseas possessions.
- Ottoman Empire: The Ottoman bureaucracy was a complex and diverse system that administered the empire’s multi-ethnic and religious population.
Functions of an Imperial Bureaucracy
Imperial bureaucracies perform a wide range of functions, including:
- Taxation and Revenue Collection: Collect taxes and other revenues from citizens, ensuring the financial stability of the empire.
- Administration of Justice: Adjudicate legal disputes, enforce laws, and maintain order throughout the empire.
- Public Works: Plan, construct, and maintain infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, and irrigation systems.
- Military Administration: Manage military affairs, including recruitment, training, and deployment of troops.
- Diplomatic Relations: Conduct diplomatic activities with other empires and foreign powers, safeguarding the empire’s interests abroad.
Importance of Imperial Bureaucracies
Imperial bureaucracies are vital to the functioning and stability of empires due to several reasons:
- Centralized Authority: They allow the imperial government to exercise centralized control over its vast territories, ensuring the consistent implementation of policies and laws.
- Efficiency and Productivity: By dividing tasks and assigning them to specialized departments, imperial bureaucracies improve administrative efficiency and productivity.
- Impartiality and Rule of Law: In theory, bureaucracies operate impartially based on meritocracy, which helps prevent nepotism and corruption.
- Legitimacy and Stability: Well-functioning bureaucracies contribute to the legitimacy of the imperial government and promote social stability by providing predictable and fair administration.
Challenges to Imperial Bureaucracies
Despite their importance, imperial bureaucracies faced several challenges:
- Corruption: Bureaucrats may be susceptible to bribery, extortion, and other forms of corruption, undermining the integrity and effectiveness of the administration.
- Inefficiency and Bureaucracy: Large bureaucracies can become cumbersome and inefficient, leading to delays, red tape, and poor decision-making.
- Lack of Accountability: Bureaucrats may be shielded from accountability due to their hierarchical structure and bureaucratic processes.
- Resistance and Rebellions: Imperial bureaucracies could sometimes alienate local populations due to their perceived elitism or oppressive policies, leading to resistance or even revolts.
Tips and Tricks
- Understand the hierarchical structure and the division of labor within the imperial bureaucracy being studied.
- Recognize the importance of meritocracy and professionalism in bureaucratic selection and promotion.
- Analyze the various functions and challenges faced by imperial bureaucracies, and their impact on the empire.
- Consider the impact of corruption, inefficiency, and lack of accountability on the effectiveness of imperial bureaucracies.
- Compare and contrast the imperial bureaucracies of different empires to identify similarities and differences.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Do not confuse imperial bureaucracy with feudalism or other forms of political organization.
- Do not assume that all imperial bureaucracies were equally efficient or impartial.
- Do not oversimplify the challenges faced by imperial bureaucracies, which were often complex and multifaceted.
Why It Matters
Imperial bureaucracies played a crucial role in shaping the course of history by:
- Establishing and maintaining order and stability within vast empires.
- Facilitating economic growth and trade through infrastructure development and administration.
- Promoting cultural exchange and the spread of knowledge through diplomacy and communication.
- Providing a foundation for the development of modern bureaucracy and administrative systems.
How It Benefits
Imperial bureaucracies have numerous benefits for empires, including:
- Increased revenue through efficient taxation and financial management.
- Improved public services and infrastructure, enhancing the well-being of subjects.
- Strengthened military capabilities and defense strategies.
- Enhanced diplomatic relations and international influence.
Tables
Table 1: Functions of an Imperial Bureaucracy
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Taxation and Revenue Collection | Collecting taxes and other revenues to finance the empire |
| Administration of Justice | Adjudicating legal disputes, enforcing laws, and maintaining order |
| Public Works | Planning, constructing, and maintaining infrastructure |
| Military Administration | Managing military affairs, including recruitment, training, and deployment |
| Diplomatic Relations | Conducting diplomatic activities with other empires and foreign powers |
Table 2: Challenges to Imperial Bureaucracies
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Corruption | Bribery, extortion, and other forms of corruption among bureaucrats |
| Inefficiency and Bureaucracy | Cumbersome and inefficient administrative processes |
| Lack of Accountability | Bureaucrats shielded from accountability due to hierarchical structure |
| Resistance and Rebellions | Alienation of local populations due to perceived elitism or oppressive policies |
Table 3: Comparison of Imperial Bureaucracies of Different Empires
| Empire | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Roman Empire | Highly developed and influential bureaucracy |
| Han Dynasty China | Centralized bureaucracy playing a crucial role in governing the empire |
| British Empire | Relied heavily on its bureaucracy to manage colonies and overseas possessions |
| Ottoman Empire | Complex and diverse bureaucratic system administering a multi-ethnic and religious population |
Table 4: Benefits of Imperial Bureaucracies
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased Revenue | Efficient taxation and financial management generates increased revenue |
| Improved Public Services | Enhanced well-being of subjects through improved public services and infrastructure |
| Strengthened Military Capabilities | Efficient military administration leads to strengthened military capabilities |
| Enhanced Diplomatic Relations | Skilled diplomatic corps promotes enhanced diplomatic relations and international influence |