Introduction
The Hoyt Sector Model, proposed by Homer Hoyt in 1939, is a classic urban land use model that describes the patterns of land utilization within a city. This model has been widely used to understand the spatial distribution of different urban functions and has served as a basis for urban planning and development.

Assumptions of the Model
The Hoyt Sector Model assumes:
- Cities expand outward from a central business district (CBD).
- Land use patterns are influenced by transportation routes.
- Different land uses have specific requirements and compete for space.
Key Features
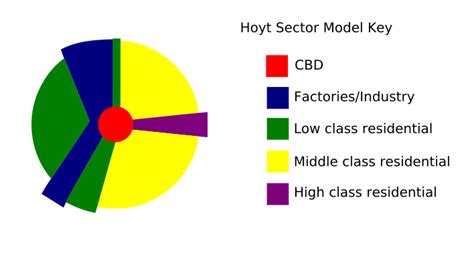
The Hoyt Sector Model divides a city into six concentric zones, each with distinct land use characteristics:
1. Central Business District (CBD)
- Center of commercial, financial, and administrative activities.
- High land values and building densities.
2. Wholesale and Light Manufacturing Zone
- Surrounds the CBD.
- Warehouses, factories, and distribution centers.
- Transition zone between CBD and residential areas.
3. Low-Density Residential Zone
- First residential zone, closest to the CBD.
- Single-family homes and apartments.
- Progressive increase in land values as distance from the CBD increases.
4. High-Density Residential Zone
- Inner-city area characterized by high population densities.
- Multi-family dwellings, low-income housing, and small businesses.
5. Suburban Residential Zone
- Outermost residential zone.
- Single-family homes with yards and lower population densities.
- Commuting distance from the CBD.
6. Commuter Zone
- Surrounds the city.
- Rural areas with farms, open space, and some suburban development.
Criticisms and Modifications
The Hoyt Sector Model has been criticized for its oversimplification of urban land use patterns. Subsequent models, such as the Burgess Concentric Zone Model, have attempted to refine the model by incorporating additional factors like topography and migration patterns.
Applications
The Hoyt Sector Model has been applied in various urban planning contexts:
- Land Use Zoning: Delineating areas for different land uses.
- Transportation Planning: Optimizing transportation networks to support land use patterns.
- Urban Renewal: Identifying blighted areas and planning for their redevelopment.
- Environmental Planning: Managing urban sprawl and promoting sustainable land use practices.
Tips and Tricks
- Use the model as a starting point for understanding urban land use, but consider local variations and additional factors.
- Combine the Hoyt Sector Model with other urban models to gain a more comprehensive perspective.
- Apply the model to real-world case studies to test its validity and make informed decisions.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Assuming universal applicability: The Hoyt Sector Model may not be equally applicable to all cities.
- Overlooking historical and cultural influences: Land use patterns can be shaped by historical events and cultural preferences.
- Ignoring transportation advancements: Technological advancements in transportation can alter land use patterns over time.
FAQs
-
What is the main principle of the Hoyt Sector Model?
– Land use patterns in cities follow a concentric pattern, expanding outward from the CBD. -
How does the model account for transportation?
– Transportation routes influence the location of different land uses, with major roads and railways acting as boundaries between zones. -
What are the limitations of the Hoyt Sector Model?
– It oversimplifies urban land use patterns and does not consider many factors that can affect development. -
How can the model be used in urban planning?
– It can guide zoning decisions, transportation planning, and redevelopment efforts. -
What is a creative new word to generate ideas for new applications?
– “Urbanography” – Exploring urban development through a combination of data analysis, mapping, and storytelling. - Table 1: Land Use Zones in the Hoyt Sector Model
| Zone | Land Use |
|---|---|
| CBD | Commercial, financial, administrative |
| Wholesale and Light Manufacturing | Warehouses, factories, distribution centers |
| Low-Density Residential | Single-family homes, apartments |
| High-Density Residential | Multi-family dwellings, low-income housing |
| Suburban Residential | Single-family homes, yards, lower density |
| Commuter Zone | Farms, open space, suburban development |
- Table 2: Factors Influencing Land Use Patterns
| Factor | Influence |
|---|---|
| Transportation | Roads and railways shape boundaries between zones |
| Topography | Hills, rivers, and other physical features affect development |
| Economic Conditions | Job opportunities and income levels influence residential choices |
| Cultural Preferences | Ethnic enclaves and religious institutions can concentrate certain land uses |
| Historical Events | Wars, disasters, and migrations can alter land use patterns |
- Table 3: Applications of the Hoyt Sector Model in Urban Planning
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Land Use Zoning | Delineating areas for different land uses based on model principles |
| Transportation Planning | Optimizing roads, railways, and public transit to support land use distribution |
| Urban Renewal | Identifying blighted areas and planning for redevelopment using the model as a guide |
| Environmental Planning | Managing urban sprawl and promoting sustainable land use practices through model-based analysis |
- Table 4: Common Criticisms of the Hoyt Sector Model
| Criticism | Reason |
|---|---|
| Oversimplification | Ignores variations in urban land use patterns |
| Static Nature | Does not account for changes over time |
| Lack of Cultural Considerations | Does not address the influence of culture on land use |
| Limited Applicability | May not apply equally to all cities |