Graduating high school with an associate’s degree is an ambitious but achievable goal. With careful planning and hard work, you can save time, money, and gain a competitive edge in higher education. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you along the journey:

Benefits of Earning an Associate’s Degree in High School
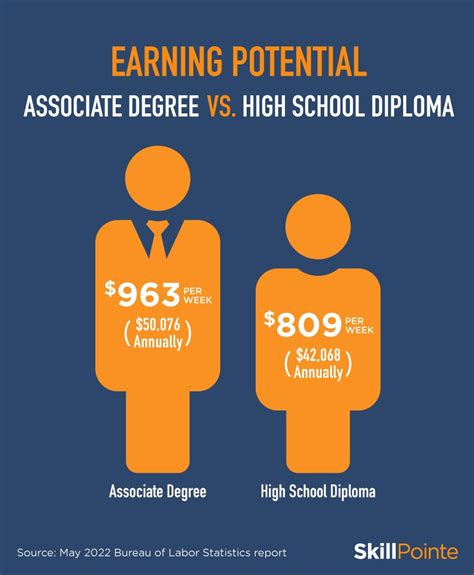
- Time savings: Graduate college in just 2-3 years instead of the typical 4 years.
- Cost savings: Earn college credits while still in high school, reducing future tuition expenses.
- Head start: Gain a competitive advantage in college with a strong academic foundation.
- Career advancement: Qualify for entry-level positions that typically require an associate’s degree.
- Enhanced marketability: Stand out in the job market with a valuable credential.
Requirements
1. Dual Enrollment Programs
Enroll in dual enrollment programs offered by your high school or local community college. These programs allow you to take college-level courses while still in high school, earning both high school and college credit.
2. College Prep Curriculum
Maintain a rigorous college preparatory curriculum with a strong emphasis on math, science, English, and social studies. Aim for a GPA of 3.0 or higher.
3. ACT/SAT Scores
Meet the college entrance exam requirements for your chosen community college. Typically, a score of 22 on the ACT or 1060 on the SAT is required for admission to an associate’s degree program.
4. Application Process
Apply to the community college of your choice and submit your high school transcript, ACT/SAT scores, and any other required materials.
Pain Points and Motivations
Pain Points:
- Balancing high school and college coursework
- Managing workload and extracurricular activities
- Financial constraints
Motivations:
- Desire to save time and money
- Ambition to gain a competitive edge in college
- Aspiration to pursue a specific career path
Effective Strategies
1. Time Management:
Create a schedule that allocates dedicated study time for both high school and college coursework. Prioritize tasks and break down assignments into smaller chunks.
2. Course Selection:
Choose college-level courses that align with your interests and future career goals. Consider taking courses during the summer or online to accelerate your progress.
3. Support System:
Build a support system of teachers, counselors, and family members who can provide guidance, encouragement, and motivation.
4. Financial Planning:
Explore scholarship opportunities and part-time job possibilities to offset the costs of college credits.
5. Dual Credit vs. AP/IB Credits:
Determine which type of college credit is more beneficial for your goals. Dual credit courses are typically more rigorous and provide a guaranteed transfer of credits, while AP/IB courses offer more flexibility and may not always transfer to all colleges.
Course Equivalencies
The following table lists common high school courses that may offer college equivalencies through dual enrollment programs:
| High School Course | College Equivalent |
|---|---|
| Algebra 2 | College Algebra |
| Geometry | College Geometry |
| English 4 | College Composition I |
| Biology | Biology 101 |
| History | History 101 |
Dual Enrollment Statistics
- According to the National Center for Education Statistics, 3.2 million high school students participated in dual enrollment programs in 2019-2020.
- Research shows that students who participate in dual enrollment programs are more likely to graduate from high school and college with higher GPAs.
- High-achieving students who participate in dual enrollment programs have a higher likelihood of earning a bachelor’s degree within four years.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can I graduate with an associate’s degree if I don’t do dual enrollment?
Yes, you can still graduate with an associate’s degree after high school. However, it will take longer and may require additional coursework.
2. What are the job opportunities for graduates with an associate’s degree?
Graduates with an associate’s degree qualify for various entry-level positions, including administrative assistants, medical assistants, and information technology technicians.
3. Can I transfer my associate’s degree credits to a four-year university?
Yes, most community colleges offer articulation agreements with four-year universities that allow for the transfer of associate’s degree credits towards a bachelor’s degree.
4. How much does it cost to earn an associate’s degree in high school?
The cost varies depending on the college and program. However, many high schools offer dual enrollment programs at a reduced cost or free of charge.
5. What are the benefits of earning an associate’s degree in high school?
Graduating with an associate’s degree in high school saves time, money, and provides a competitive edge in higher education.
6. What are some effective strategies for managing the workload of dual enrollment?
Time management, course selection, support system, and financial planning are key strategies for managing the workload of dual enrollment.
Conclusion
Earning an associate’s degree in high school is an ambitious yet achievable goal that can lead to significant benefits in both time and cost savings, as well as increased career opportunities. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can increase your chances of success and graduate high school with an associate’s degree in hand.