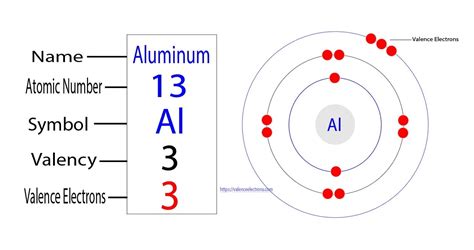
Aluminum, a versatile metal with a wide range of applications, has a unique electronic configuration that determines its chemical properties. Understanding the number of valence electrons in aluminum is crucial for comprehending its reactivity and behavior in chemical reactions.

Valence Electrons in Aluminum
Valence electrons refer to the outermost electrons of an atom, which are involved in chemical bonding. Aluminum has an atomic number of 13, indicating that it has 13 electrons. Its electron configuration can be represented as:
1s22s22p63s23p1
The superscripts indicate the number of electrons in each energy level. The outermost energy level (n=3) contains three electrons, with one electron in the 3p orbital. Therefore, aluminum has three valence electrons.
Reactivity of Aluminum
The number of valence electrons in aluminum impacts its reactivity. Elements with a high number of valence electrons are generally more reactive, as they are more likely to participate in chemical bonds. Aluminum’s three valence electrons are relatively low compared to other metals, contributing to its moderate reactivity.
Applications of Aluminum
Aluminum’s unique combination of properties, including its low density, high strength, and corrosion resistance, makes it a highly valuable material in various industries. Its uses span:
- Aerospace: Aluminum alloys are lightweight and durable, making them ideal for aircraft and spacecraft construction.
- Construction: Aluminum is used in building materials, such as siding, roofing, and windows, due to its strength and corrosion resistance.
- Transportation: Aluminum is utilized in car frames, body panels, and wheels to enhance fuel efficiency and performance.
- Packaging: Aluminum foil and cans protect food products from moisture and contamination.
- Electrical: Aluminum is a good conductor of electricity, making it suitable for electrical wiring and components.
Innovative Applications
The ongoing research and development efforts surrounding aluminum have led to the emergence of innovative applications, such as:
- Nanotechnology: Aluminum nanoparticles are being explored for use in biomedical applications and energy storage devices.
- Additive Manufacturing: Aluminum powders are utilized in 3D printing processes to create complex and lightweight structures.
- Metamaterials: Aluminum-based metamaterials with tailored electromagnetic properties offer promising applications in optics and telecommunications.
Conclusion
Aluminum’s three valence electrons play a significant role in determining its chemical properties and reactivity. The understanding of valence electrons is essential for exploring the diverse applications of this versatile metal, which continues to drive innovation across various industries.
Table 1: Valence Electrons of Group 13 Elements
| Element | Atomic Number | Valence Electrons |
|---|---|---|
| Boron | 5 | 3 |
| Aluminum | 13 | 3 |
| Gallium | 31 | 3 |
| Indium | 49 | 3 |
| Thallium | 81 | 3 |
Table 2: Electronegativity and Reactivity of Group 13 Elements
| Element | Electronegativity | Reactivity |
|---|---|---|
| Boron | 2.04 | High |
| Aluminum | 1.61 | Moderate |
| Gallium | 1.81 | Low |
| Indium | 1.78 | Very low |
| Thallium | 2.05 | Moderate |
Table 3: Applications of Aluminum
| Industry | Application |
|---|---|
| Aerospace | Aircraft and spacecraft |
| Construction | Siding, roofing, windows |
| Transportation | Car frames, body panels, wheels |
| Packaging | Foil, cans |
| Electrical | Wiring, components |
Table 4: Innovative Applications of Aluminum
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Nanotechnology | Nanoparticles for biomedical and energy storage |
| Additive Manufacturing | 3D printing of lightweight structures |
| Metamaterials | Tailored electromagnetic properties for optics and telecommunications |
- To determine the number of valence electrons in any element, look at its location in the periodic table. The valence electrons are equal to the group number (1-18).
- Remember that valence electrons are the ones that participate in chemical reactions.
- The number of valence electrons can influence the reactivity and bonding behavior of an element.
How to Calculate the Number of Valence Electrons in Aluminum
- Locate aluminum in the periodic table.
- Note the group number (13).
- The number of valence electrons is equal to the group number.
- Aluminum has three valence electrons.
Pros of Aluminum
- Lightweight
- Durable
- Corrosion resistant
- Malleable
- Good conductor of electricity and heat
Cons of Aluminum
- Can be expensive
- Relatively soft
- Can be susceptible to oxidation if not protected