Navigating the Path to College Success

Every college student yearns for the day they finally become a junior. It marks a significant milestone in their academic journey, unlocking new opportunities and signaling their progress toward graduation. But before you can don the mantle of a junior, you must first understand the requirements that stand between you and this coveted status.
The Credit Hour Conundrum: Unraveling the Mysteries
The higher education landscape operates on a system of credit hours, which serve as the building blocks of your academic progress. Each course you take carries a certain number of credit hours, typically ranging from 3 to 5. These credit hours represent the amount of time you’re expected to dedicate to that course, both inside and outside the classroom.
The accumulation of credit hours is crucial for determining your academic standing. Colleges and universities use them to calculate your GPA, assess your eligibility for scholarships and financial aid, and ultimately, determine whether you’ve met the requirements for graduation.
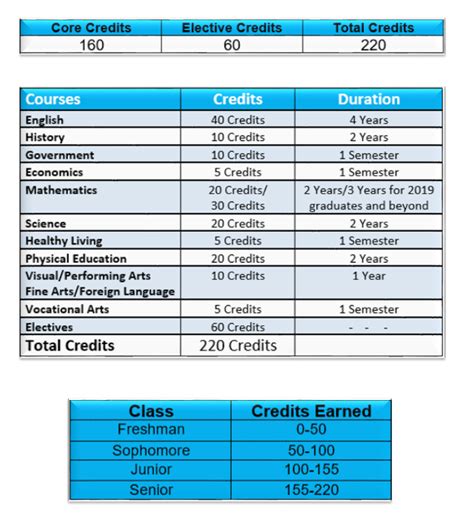
Junior Status: Unlocking the Gateway to New Horizons
The transition from sophomore to junior status typically occurs when students have earned a predefined number of credit hours. These requirements vary from institution to institution, but the general consensus is that most colleges require between 54 and 84 credit hours for junior standing.
Some colleges may adopt the Quarter System, which divides the academic year into quarters instead of semesters. In this case, the credit hour requirements for junior status may differ slightly. For instance, the University of California system requires students to complete 120 quarter units to achieve junior standing.
Breaking Down the Credit Hour Thresholds
To provide a more comprehensive understanding of the credit hour thresholds, we’ve compiled a table outlining the requirements for various universities:
| University | Credit Hour Requirement for Junior Status |
|---|---|
| Harvard University | 84 credit hours |
| Stanford University | 81 credit hours |
| Yale University | 72 credit hours |
| University of California, Berkeley | 120 quarter units |
| Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) | 54 credit hours |
| University of Pennsylvania | 72 credit hours |
| Princeton University | 72 credit hours |
| Georgia Institute of Technology | 60 credit hours |
| University of Michigan | 56 credit hours |
| University of Florida | 54 credit hours |
The Importance of Meeting the Credit Hour Requirements
Reaching junior status is not merely a numerical milestone; it carries significant implications for your academic and personal growth.
Enhanced Course Selection: As a junior, you gain access to a wider range of upper-level courses that delve deeper into your chosen field of study.
Increased Research Opportunities: Junior status opens doors to research opportunities, allowing you to collaborate with professors and engage in meaningful scholarly pursuits.
Career Preparedness: Many internships and entry-level jobs require candidates to have junior standing, demonstrating their commitment to their field and their progress toward graduation.
Scholarship and Financial Aid: Junior status may make you eligible for additional scholarships and financial aid opportunities, providing financial support for your continued education.
Personal Growth: Transitioning to junior status represents a time of significant personal growth. You’ll develop increased confidence, critical thinking skills, and a deeper understanding of your academic interests.
Frequently Asked Questions About Junior Status
Q: What if I transfer from another college?
A: The credit hours you’ve earned at your previous institution will typically transfer to your new college, but the specific requirements for junior status may vary.
Q: What if I fall short of the credit hour requirement?
A: Contact your academic advisor to discuss your options. They may recommend taking additional courses or adjusting your course load in future semesters.
Q: Can I take graduate-level courses as a junior?
A: It’s possible, but only in certain circumstances. Check with your academic advisor and the graduate school to determine if you qualify.
Q: What are the benefits of reaching junior status early?
A: The sooner you achieve junior status, the more time you have to explore your academic interests, pursue research, and prepare for your future career.
Q: What if I’m a part-time student?
A: The credit hour requirements for junior status may be adjusted for part-time students. Contact your academic advisor for specific details.
Q: Can I skip a year of college and become a junior?
A: While it’s possible to accelerate your studies, it’s not recommended. Taking a full course load each semester will provide you with a stronger foundation for your future academic and career endeavors.
Conclusion
Achieving junior status is a testament to your hard work, dedication, and pursuit of higher education. By understanding the credit hour requirements and