As humans, we intrinsically crave order and meaning in a chaotic world. This innate desire often leads us to simplify complex social situations by relying on superficial cues instead of delving into the complexities of individual behavior. One such cognitive shortcut, known as the halo effect, can significantly influence our evaluations and judgments of others.

Understanding the Halo Effect
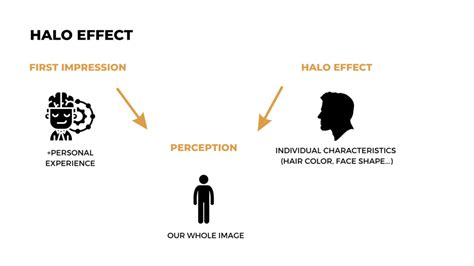
The halo effect refers to the tendency to form an overall impression of a person based on a single trait or characteristic, often leading to a biased and inaccurate perception. Like a halo that illuminates a saintly figure, positive traits can create a favorable overall impression, while negative traits can cast a shadow over our perception.
This cognitive bias can manifest in various social contexts, including interpersonal relationships, job interviews, and even court proceedings. For instance, an attractive individual may be perceived as more intelligent or trustworthy, while someone with messy hair may be seen as less competent or responsible.
Impact on Decision-Making
The halo effect has both positive and negative implications for our decision-making processes. On the positive side, it can expedite our evaluations, allowing us to make quick judgments in situations where time is limited. However, it can also lead to erroneous conclusions and biases, undermining the accuracy of our decisions.
Studies have shown that the halo effect can influence:
- Hiring decisions: Job candidates with physically attractive or well-dressed appearances may be favored over equally qualified candidates.
-
- Jury verdicts: Attractive defendants may receive lighter sentences than their less attractive counterparts.
- Medical diagnoses: Patients who display positive social behaviors may be perceived as having less severe illnesses.
Causes of the Halo Effect
The halo effect arises from several cognitive mechanisms, including:
- Cognitive schemas: Preexisting beliefs and expectations about people based on their superficial qualities.
- Confirmation bias: The tendency to seek information that confirms our existing impressions.
- Need for closure: The desire to form a coherent and complete understanding of others, even with limited information.
Strategies to Counteract the Halo Effect
Recognizing the potential influence of the halo effect is crucial for mitigating its impact on our judgments. Several strategies can help us counteract this cognitive bias:
- Be aware of your biases: Acknowledge that you may be susceptible to the halo effect.
-
- Focus on specific behaviors: Instead of relying on overall impressions, observe and evaluate specific actions and characteristics.
- Consider multiple perspectives: Seek input from others and gather diverse opinions before forming conclusions.
- Use objective criteria: Establish clear and impartial standards to assess performance or behavior.
Applications in Psychology
The concept of the halo effect has numerous applications in psychology, including:
- Person perception: Understanding how others form impressions of us can help us manage our self-presentation.
- Advertising: Companies may use attractive imagery or celebrity endorsements to create a positive halo effect around their products.
- Social influence: The halo effect can be harnessed to promote positive social behaviors by associating them with desirable traits.
Effective Strategies for Counteracting the Halo Effect
| Strategy | How it Works |
|---|---|
| Bias Awareness: | Recognize the potential influence of biases, including the halo effect. |
| Focused Observation: | Observe specific behaviors and characteristics rather than relying on overall impressions. |
| Multiple Perspectives: | Seek input from others and consider diverse opinions before forming conclusions. |
| Objective Criteria: | Use impartial standards to assess performance or behavior, minimizing the impact of subjective impressions. |
Tips and Tricks for Combating the Halo Effect
- Slow down: Give yourself ample time to make decisions and avoid relying on quick judgments.
- Pay attention to the specifics: Focus on the details of a person’s behavior and avoid jumping to conclusions.
- Challenge your assumptions: Question whether your overall impression is based on valid evidence.
- Seek feedback: Get feedback from others to gain a more balanced perspective.
Pros and Cons of the Halo Effect
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Expedited decision-making: Can make evaluations faster in time-sensitive situations. | Inaccurate judgments: Can lead to biased and incorrect conclusions. |
| Positive social interactions: May promote positive social behaviors by associating them with desirable traits. | Unfair treatment: Can result in discrimination or unequal treatment based on superficial qualities. |
| Simplified person perception: Helps us make sense of complex social situations by categorizing people based on their traits. | Overgeneralization: Can lead to inaccurate generalizations and stereotypes about people from certain groups. |