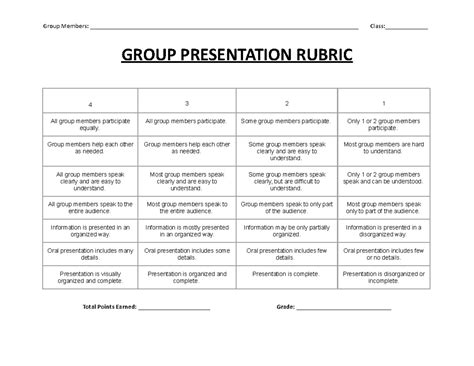
Effective group presentations are not merely a collection of slides; they are a collaborative effort that requires meticulous planning, preparation, and delivery. To ensure a successful presentation, it is essential to have a clear rubric that outlines the expectations and provides guidance for both presenters and audience members.

Key Elements of a Group Presentation Rubric
A comprehensive group presentation rubric should encompass the following key elements:
-
Content: This aspect evaluates the depth, accuracy, and organization of the information presented. The rubric should specify criteria for:
-
Knowledge and understanding of the topic
- Research and referencing
- Logical flow and coherence
-
Use of visual aids
-
Delivery: A well-delivered presentation engages the audience and ensures that the message is clearly conveyed. The rubric should assess:
-
Eye contact and engagement
- Verbal clarity and volume
- Nonverbal communication
-
Time management
-
Visuals: Effective visual aids enhance the presentation and reinforce the key points. The rubric should evaluate:
-
Relevance and appropriateness of visuals
- Design and clarity of slides
-
Usefulness of handouts (if applicable)
-
Group dynamics: Collaboration is crucial for a successful group presentation. The rubric should assess:
-
Role allocation and participation
- Communication and coordination
- Problem-solving and adaptability
Tips and Tricks for Using a Rubric
- Establish clear expectations upfront: Communicate the rubric to the group members at the start of the project to ensure everyone understands the expectations from the outset.
- Provide regular feedback: Use the rubric as a tool for formative feedback throughout the process. This helps groups identify areas for improvement before the final presentation.
- Be consistent and objective: Apply the rubric fairly and consistently to all groups to ensure a level playing field.
- Use the data to inform decision-making: The information gathered from the rubric can be used to make informed decisions about future group presentations and improve the overall quality of student work.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using a Rubric
- Lack of clarity: Ensure that the rubric is clear and easy to understand by both presenters and audience members. Avoid using vague or subjective language.
- Overemphasis on form over substance: While delivery and visuals are important, the rubric should not overshadow the content and depth of the presentation.
- Insufficient detail: Provide enough detail in the rubric to guide the groups and allow for fair assessment.
- Inconsistent application: The rubric should be applied consistently to all groups to ensure fairness and validity.
Tables for Rubric Creation
- Table 1: Content Evaluation
| Criteria | Excellent (4) | Good (3) | Fair (2) | Poor (1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Knowledge and understanding of the topic | Demonstrates a comprehensive understanding of the topic, including key concepts and theories | Shows a good understanding of the topic, but may lack depth | Demonstrates a basic understanding of the topic | Displays a limited understanding of the topic |
| Research and referencing | Provides thorough references to support the information presented | Provides some references, but could be more comprehensive | Cites limited references | Does not provide any references |
| Logical flow and coherence | Presents the information in a clear and logical order, with smooth transitions between slides | Presents the information in a logical order, but may have some minor gaps | Presents the information in a somewhat disjointed manner | Presents the information in a confusing and illogical way |
| Use of visual aids | Uses visuals to effectively reinforce the key points and enhance the presentation | Uses visuals, but they may be somewhat distracting or irrelevant | Uses few visuals, or visuals are not well-designed | Does not use any visuals |
- Table 2: Delivery Evaluation
| Criteria | Excellent (4) | Good (3) | Fair (2) | Poor (1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eye contact and engagement | Maintains eye contact with the audience and engages them actively throughout the presentation | Maintains eye contact with the audience most of the time | Makes occasional eye contact with the audience | Rarely makes eye contact with the audience |
| Verbal clarity and volume | Speaks clearly and at an appropriate volume, ensuring that the audience can hear and understand | Speaks clearly, but the volume may fluctuate | Speaks somewhat clearly, but the volume may be too soft or too loud | Speaks unclearly or at an inappropriate volume |
| Nonverbal communication | Uses appropriate body language and gestures to enhance the presentation | Uses some nonverbal communication, but it could be more effective | Uses limited nonverbal communication, or nonverbal communication is distracting | Does not use nonverbal communication |
| Time management | Manages time effectively, completing the presentation within the allotted time | Completes the presentation within the allotted time, but there may be some minor time constraints | Exceeds or falls short of the allotted time | Does not manage time effectively, leading to major time constraints |
- Table 3: Visuals Evaluation
| Criteria | Excellent (4) | Good (3) | Fair (2) | Poor (1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relevance and appropriateness of visuals | Uses visuals that are highly relevant to the content and enhance the presentation | Uses visuals that are mostly relevant to the content | Uses some visuals, but they may be somewhat irrelevant or distracting | Does not use visuals, or visuals are not relevant to the content |
| Design and clarity of slides | Uses slides that are well-designed, clear, and easy to read | Uses slides that are somewhat well-designed and clear | Uses slides that are somewhat cluttered or difficult to read | Uses slides that are poorly designed or illegible |
| Usefulness of handouts (if applicable) | Provides handouts that effectively summarize the key points and supplement the presentation | Provides handouts, but they may be somewhat lacking in content or organization | Provides handouts that are not particularly useful or relevant | Does not provide handouts |
- Table 4: Group Dynamics Evaluation
| Criteria | Excellent (4) | Good (3) | Fair (2) | Poor (1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Role allocation and participation | Clearly defines roles and responsibilities, and all members actively participate in the presentation | Defines roles and responsibilities, but some members may not participate equally | Defines roles, but not all members participate | Does not define roles or ensure equal participation |
| Communication and coordination | Communicates and coordinates effectively both within the group and with the audience | Communicates and coordinates somewhat effectively | Experiences some communication or coordination issues | Experiences significant communication or coordination issues |
| Problem-solving and adaptability | Demonstrates the ability to solve problems and adapt to unexpected situations | Can solve minor problems and adapt somewhat to unexpected situations | Has difficulty solving problems or adapting to unexpected situations | Unable to solve problems or adapt to unexpected situations |
Considerations for Using a Rubric
- Tailor the rubric to the specific presentation: The rubric should be tailored to the specific topic, audience, and learning objectives of the presentation.
- Provide opportunities for self-assessment: Encourage students to use the rubric to self-assess their own presentations and identify areas for improvement.
- Incorporate peer feedback: Allow students to provide feedback to their peers using the rubric. This can foster a collaborative learning environment and provide valuable insights.
- Revise and update the rubric as needed: Over time, it is likely that the content of the presentation, learning objectives, and audience may change. As such, the rubric should be revised and updated accordingly.
Pros and Cons of a Group Presentation Rubric
Pros
- Provides clear expectations: A rubric outlines the specific criteria for a successful presentation, ensuring that all groups are aware of the standards.
- Promotes fairness: By using a consistent evaluation tool, the rubric ensures that all groups are assessed fairly, reducing biases and subjectivity.
- Facilitates self-assessment and improvement: The rubric can be used by students to self-assess their presentations and identify areas for improvement.
- Enhances collaboration: A rubric helps group members understand their individual roles and responsibilities, fostering collaboration and shared accountability.
Cons
- Can be time-consuming to create: Developing a comprehensive and effective rubric can be time-consuming, particularly if it needs to be tailored to specific presentations.
- May limit creativity: A rubric can sometimes restrict creativity by focusing on specific criteria.
- Difficult to assess in a large class setting: Assessing group presentations using a rubric can be challenging in large classes due to time constraints.
- Potential for disagreement: Different individuals may have varying interpretations of the rubric’s criteria, leading to potential disagreements over assessment.
Conclusion
A well-designed group presentation rubric is a valuable tool that can enhance the quality of group presentations and provide valuable feedback to students. By establishing clear expectations, promoting fairness, and facilitating self-assessment, a rubric can foster collaboration, improve delivery and content, and ultimately help students achieve their learning goals.