In educational and professional settings, grading scales serve as essential tools for evaluating performance, providing a structured and standardized approach to assess knowledge, skills, and abilities. For a 30-question assessment, the following grading scale offers a comprehensive framework for evaluating student or employee performance:

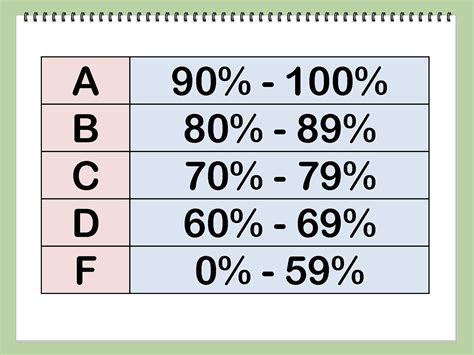
Percentage Range | Grade
—|—|
90-100% | A (Excellent)
80-89% | B (Very Good)
70-79% | C (Good)
60-69% | D (Passing)
Below 60% | F (Failing)
Criteria for Determining Grades
The grading scale for a 30-question assessment typically encompasses specific criteria that guide the evaluation process. These criteria may include:
- Accuracy: The number of correct answers out of the total questions.
- Comprehensiveness: The completeness and thoroughness of the responses.
- Clarity: The organization, coherence, and readability of the responses.
- Originality: The demonstration of unique ideas and perspectives in the responses.
- Timeliness: The ability to complete the assessment within the allotted time frame.
Interpreting the Results
The grading scale provides a clear and concise method for interpreting assessment results. By applying the percentage ranges to the student or employee’s score, educators and employers can determine the level of achievement and provide appropriate feedback.
- Excellent: A grade of A indicates a high level of understanding and proficiency, with minimal errors and a strong grasp of the concepts being assessed.
- Very Good: A grade of B represents a solid understanding of the material, with a few minor errors or inconsistencies.
- Good: A grade of C signifies a satisfactory level of performance, with a broader range of errors or omissions but still demonstrating a general understanding.
- Passing: A grade of D indicates a marginal level of achievement, with a significant number of errors or omissions but meeting the minimum requirements for passing.
- Failing: A grade of F represents an unsatisfactory performance, with a high number of errors or omissions, indicating a lack of understanding or insufficient preparation.
Implications of Grading Scales
Grading scales have several important implications for educational and professional settings:
- Objective Assessment: By providing standardized criteria, grading scales ensure that performance is evaluated objectively and consistently.
- Benchmark for Success: Grades establish clear expectations and benchmarks for students or employees to strive towards.
- Feedback and Improvement: Grading allows educators and employers to provide valuable feedback, highlighting areas for improvement and identifying strengths and weaknesses.
- Motivation and Engagement: A well-defined grading scale can motivate students or employees to perform better and engage fully in the learning or work environment.
- Communication and Transparency: Grades facilitate effective communication between educators/employers and students/employees, ensuring transparency and accountability in the assessment process.
Variations in Grading Scales
Grading scales can vary depending on factors such as the purpose of the assessment, the audience being evaluated, and the institution or organization administering the assessment. Some common variations include:
- Weighted Scales: Assigning different weights to different questions or sections of the assessment.
- Scaled Scores: Converting raw scores into a standardized scale, such as a z-score or percentile.
- Pass/Fail Grades: Using a binary system to indicate whether the student or employee has passed or failed the assessment.
- Holistic Scales: Evaluating the overall quality of the response rather than individual components.
Applications in Education and Business
Grading scales have wide-ranging applications in both educational and business settings:
- Educational Settings: In schools and universities, grading scales are used to assess students’ progress and achievement in various subjects, including mathematics, science, history, and literature.
- Business Settings: In the workplace, grading scales can be used to evaluate employee performance, set performance targets, and provide feedback for improvement.
- Customer Satisfaction Surveys: Grading scales can be incorporated into customer satisfaction surveys to gauge the effectiveness of products or services.
- Research and Evaluation: Grading scales can be used as a tool for evaluating the validity and reliability of research studies or surveys.
Tables for Reference
Table 1: Grading Scale for 30 Questions
| Percentage Range | Grade | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 90-100% | A | Excellent |
| 80-89% | B | Very Good |
| 70-79% | C | Good |
| 60-69% | D | Passing |
| Below 60% | F | Failing |
Table 2: Impact of Grading Scales on Motivation and Engagement
| Impact | Description |
|---|---|
| Positive Motivation | Encourages students/employees to strive for excellence. |
| Negative Motivation | May induce anxiety or discouragement if students/employees feel overwhelmed or pressured. |
| Goal Setting | Provides clear benchmarks for students/employees to set realistic goals. |
| Feedback and Improvement | Facilitates constructive feedback and helps identify areas for improvement. |
| Communication and Transparency | Enhances understanding and accountability between educators/employers and students/employees. |
Table 3: Variations in Grading Scales
| Type | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Weighted Scales | Assigns different weights to different questions or sections. | To emphasize the importance of certain topics or skills. |
| Scaled Scores | Converts raw scores into a standardized scale. | To compare performance across different assessments or populations. |
| Pass/Fail Grades | Indicates whether the student/employee has passed or failed the assessment. | Used in high-stakes assessments or when a specific level of competence is required. |
| Holistic Scales | Evaluates the overall quality of the response rather than individual components. | Suitable for assessments that emphasize global perspectives or creativity. |
Table 4: Applications of Grading Scales
| Setting | Purpose | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Education | Assess student achievement in various subjects. | Provides feedback, sets expectations, and motivates students. |
| Business | Evaluate employee performance. | Sets performance targets, provides feedback, and rewards exceptional performance. |
| Customer Satisfaction Surveys | Measure customer satisfaction levels. | Identifies areas of improvement and gauges the effectiveness of products or services. |
| Research and Evaluation | Evaluate the validity and reliability of studies or surveys. | Ensures data quality and facilitates comparisons across different research methods. |