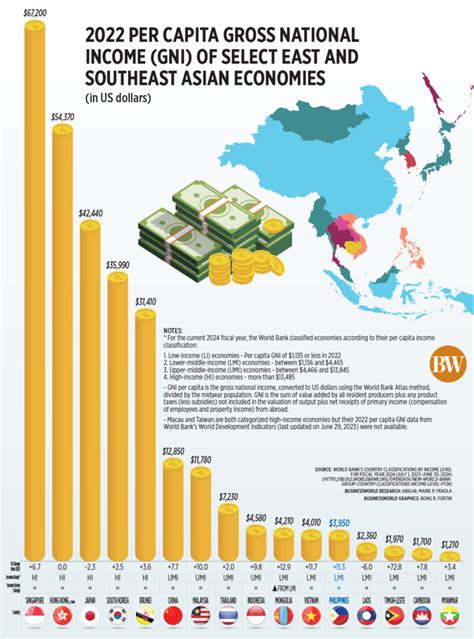
Gross National Income (GNI) per capita is a key indicator of a country’s economic well-being and is widely used by policymakers, economists, and development organizations to assess progress towards sustainable development goals. GNI measures the total income earned by a country’s citizens, regardless of where they live, and is calculated by adding up all the income earned by individuals within a country’s borders over a specific period, usually one year. GNI per capita is then calculated by dividing the total GNI by the country’s population.

GNI is a valuable tool for understanding global development and inequality because it provides a standardized measure of economic well-being that can be used to compare countries of different sizes and populations. By comparing GNI per capita across countries, we can gain insights into the relative economic development of different regions of the world and identify countries that are experiencing rapid economic growth or facing economic challenges.
GNI per capita can also be used to track progress towards sustainable development goals. The United Nations has set a target of eradicating extreme poverty by 2030, and GNI per capita is one of the key indicators used to measure progress towards this goal. By tracking changes in GNI per capita over time, we can assess the effectiveness of development interventions and identify countries that are falling behind in the fight against poverty.
However, it is important to note that GNI per capita is not a perfect measure of economic well-being. GNI per capita does not take into account the distribution of income within a country, so it is possible for a country to have a high GNI per capita but still have a large number of poor people. Additionally, GNI per capita does not take into account the quality of life in a country, so it is possible for a country to have a high GNI per capita but still have poor living conditions.
Despite its limitations, GNI per capita remains a valuable tool for understanding global development and inequality. By using GNI per capita in conjunction with other indicators of economic well-being and quality of life, we can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the challenges and opportunities facing countries around the world.
Global GNI per capita has been rising steadily over the past few decades. In 1990, the average GNI per capita was $3,400. By 2020, it had risen to $11,700. This growth has been driven by a number of factors, including:
- Globalization: Globalization has led to increased trade and investment, which has helped to boost economic growth in many countries.
- Technological change: Technological change has led to increased productivity and innovation, which has also contributed to economic growth.
- Education: Education is a key factor in economic development, and the number of people with access to education has increased significantly over the past few decades.
However, there are still large disparities in GNI per capita between countries. In 2020, the highest GNI per capita was $142,000 in Qatar, while the lowest GNI per capita was $200 in Burundi. These disparities are due to a number of factors, including:
- Natural resources: Countries with abundant natural resources tend to have higher GNI per capita than countries without natural resources.
- Political stability: Political stability is essential for economic growth, and countries with unstable political systems tend to have lower GNI per capita than countries with stable political systems.
- Government policies: Government policies can have a significant impact on economic growth, and countries with sound economic policies tend to have higher GNI per capita than countries with poor economic policies.
Reducing inequality is a major challenge for many countries around the world. In 2020, the top 1% of the world’s population owned 43% of the world’s wealth, while the bottom 50% of the world’s population owned just 1% of the world’s wealth. This inequality is due to a number of factors, including:
- Discrimination: Discrimination against certain groups of people, such as women and minorities, can limit their access to education, employment, and other opportunities.
- Lack of access to education and healthcare: Lack of access to education and healthcare can perpetuate poverty and inequality.
- Tax policies: Tax policies that favor the wealthy can exacerbate inequality.
Reducing inequality requires a multi-faceted approach that includes:
- Investing in education and healthcare: Investing in education and healthcare can help to improve the lives of the poor and reduce inequality.
- Promoting equal opportunities for women and minorities: Promoting equal opportunities for women and minorities can help to reduce discrimination and give them a fair chance to succeed.
- Implementing progressive tax policies: Implementing progressive tax policies can help to reduce inequality by taxing the wealthy more than the poor.
GNI per capita is likely to continue to rise in the coming years. However, the pace of growth is expected to slow as the global economy matures. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic is likely to have a negative impact on GNI per capita in many countries.
The future of GNI is also likely to be shaped by the following trends:
- The rise of the digital economy: The digital economy is growing rapidly, and this is likely to have a significant impact on GNI per capita in the coming years.
- Climate change: Climate change is a major threat to global development, and it is likely to have a negative impact on GNI per capita in many countries.
- Population growth: Population growth is slowing in many countries, and this is likely to have a positive impact on GNI per capita in the coming years.
GNI per capita is a valuable tool for understanding global development and inequality. By using GNI per capita in conjunction with other indicators of economic well-being and quality of life, we can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the challenges and opportunities facing countries around the world.
-
What is GNI per capita?
GNI per capita is a measure of a country’s economic well-being that is calculated by dividing the country’s total GNI by its population. -
Why is GNI per capita important?
GNI per capita is an important indicator of a country’s economic development and is used to track progress towards sustainable development goals. -
What are some of the factors that affect GNI per capita?
Some of the factors that affect GNI per capita include natural resources, political stability, government policies, and access to education and healthcare. -
What are some of the challenges of reducing inequality?
Some of the challenges of reducing inequality include discrimination, lack of access to education and healthcare, and tax policies that favor the wealthy. -
What is the future of GNI?
The future of GNI is likely to be shaped by the rise of the digital economy, climate change, and population growth. -
How can I use GNI per capita to understand global development?
GNI per capita can be used to compare the economic development of different countries and track progress towards sustainable development goals. -
What are some of the limitations of GNI per capita?
GNI per capita does not take into account the distribution of income within a country or the quality of life. -
What are some of the other indicators that can be used to measure economic well-being?
Other indicators that can be used to measure economic well-being include the Human Development Index, the Inequality-Adjusted Human Development Index, and the Genuine Progress Indicator.