Introduction: Unveiling the Value of Education Credentials
In today’s competitive job market, a high school diploma or its equivalent is widely recognized as the minimum educational requirement for a wide range of employment opportunities. However, for those who may not have completed traditional high school due to various circumstances, the General Educational Development (GED) credential offers an alternative pathway to demonstrate their academic abilities and pursue higher education and career goals. This article will delve into a comprehensive analysis of the GED versus high school diploma debate, exploring the key advantages, disadvantages, and implications of each credential to help individuals make informed decisions about their education pathways.

Section 1: Delving into the GED Credential
Definition and Structure of the GED
The GED is a comprehensive academic assessment that measures an individual’s knowledge and skills in four core subject areas: mathematics, reading, writing, and science. It is offered by the American Council on Education and recognized by most postsecondary institutions and employers as equivalent to a high school diploma.
Advantages of Obtaining a GED
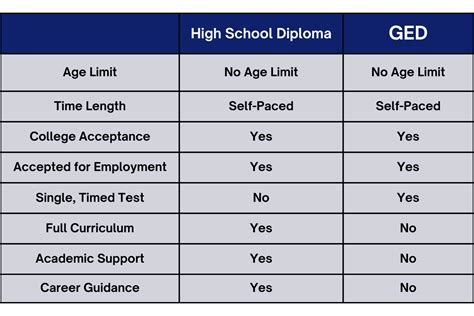
- Flexibility and Accessibility: The GED offers a flexible and convenient way to earn an equivalent high school credential, as it can be taken at testing centers at various times throughout the year. Individuals can also prepare for the GED at their own pace through self-study or by enrolling in approved GED preparation programs.
- Second Chance for Educational Attainment: For those who were unable to complete traditional high school due to personal, financial, or other challenges, the GED provides an opportunity to earn an equivalent credential and pursue higher education or career advancement.
- Affordability: The GED is a more affordable alternative to completing a traditional high school program, as it involves a one-time testing fee rather than ongoing tuition expenses.
Disadvantages of the GED
- Perceived Stigma: The GED may still carry a negative connotation in some circles, where it is perceived as inferior to a traditional high school diploma. This stigma can potentially limit employment opportunities for some individuals.
- Potential Challenges in College Admission: While the GED is recognized as equivalent to a high school diploma, it is important to note that some colleges and universities may have specific admission requirements that include a preference for traditional high school graduates.
- Limited Coursework and Extracurricular Activities: Unlike a traditional high school program, the GED focuses solely on the core academic subjects and does not include coursework in specialized areas such as foreign languages, fine arts, or vocational education. Additionally, GED preparation typically does not offer extracurricular activities or social opportunities that are commonly found in high school.
Section 2: Understanding the Value of a High School Diploma
The Traditional Path to Education
A high school diploma is the traditional credential earned by students who successfully complete a four-year academic program at an accredited high school. It signifies that the individual has met the state’s minimum educational requirements and is prepared for postsecondary education or employment.
Advantages of Earning a High School Diploma
- Comprehensive Education: A high school diploma provides a well-rounded education that includes coursework in a broad range of subjects, including core academic areas, electives, and career and technical education programs. This comprehensive education prepares students for a wide range of college majors and career paths.
- Access to Extracurricular Activities and Social Development: High school offers students the opportunity to participate in a variety of extracurricular activities, such as sports, clubs, and student government. These activities provide opportunities for personal growth, social development, and leadership skills.
- College and Career Preparation: A high school diploma opens doors to a wide range of postsecondary educational and career opportunities. Many employers require a high school diploma or equivalent as a minimum hiring requirement, and it is essential for admission to most colleges and universities.
Disadvantages of a High School Diploma
- Time and Cost: Completing a traditional high school program requires four years of full-time study and can involve significant expenses, including tuition, fees, and transportation.
- Attendance and Coursework Requirements: High school students are required to attend school regularly and complete all assigned coursework, which can be challenging for students who struggle academically or have other commitments outside of school.
- Limited Flexibility: Traditional high school programs typically offer less flexibility than GED preparation, as students are bound to a set schedule and curriculum.
Section 3: Comparing GED vs High School Diploma
Key Differences and Similarities
Key Differences:
- Flexibility vs. Structure: GED preparation offers greater flexibility, while traditional high school programs are more structured.
- Coursework and Activities: High school diplomas provide a more comprehensive education with a wider range of coursework and extracurricular activities.
- Perception and Stigma: High school diplomas are generally perceived as more prestigious than GEDs.
Similarities:
- Equivalence: Both the GED and a high school diploma are recognized as equivalent credentials for college admission and employment purposes.
- Academic Skills: Both credentials demonstrate an individual’s ability to meet basic academic standards in core subject areas.
- Pathways to Opportunity: Both the GED and a high school diploma provide pathways to pursue higher education, career advancement, and personal growth.
Making an Informed Decision
The choice between obtaining a GED or a high school diploma depends on an individual’s specific circumstances, needs, and aspirations. Here are some factors to consider:
- Educational Goals: If an individual plans to pursue higher education, a high school diploma may be a better choice due to its broader curriculum and acceptance at more colleges and universities.
- Career Goals: For individuals seeking immediate employment in fields that do not require a high school diploma, the GED may be a suitable option.
- Learning Style and Preferences: Individuals who prefer a flexible and self-paced learning environment may find the GED more accommodating, while those who thrive in a structured and traditional high school setting may prefer a high school diploma.
- Personal Circumstances: The GED offers a second chance for those who may not have completed traditional high school due to personal challenges or circumstances.
Section 4: The Future of Education Credentials: Emerging Trends
The landscape of education credentials is constantly evolving to meet the changing needs of society and the workforce. Here are some emerging trends to consider:
Personalized Learning Pathways
Education is becoming increasingly personalized, with individuals tailoring their learning experiences to their unique strengths, interests, and goals. This trend is leading to the development of alternative pathways to earning high school equivalency credentials, such as online learning programs and competency-based assessments.
Micro-Credentials and Stackable Credentials
The rise of micro-credentials and stackable credentials is another emerging trend in education. These smaller, specialized credentials allow individuals to acquire specific skills and knowledge that are in high demand in the workforce. Individuals can stack micro-credentials to create customized credentials that demonstrate their proficiency in a particular field.
Lifelong Learning and Credentialing
The concept of lifelong learning is gaining momentum, as individuals seek to continuously update their skills and knowledge throughout their careers. This trend is driving the development of new credentialing systems that recognize and reward lifelong learning and skill acquisition.
Conclusion: Empowering Individuals with Educational Choices
The decision between obtaining a GED or a high school diploma is a personal one that should be based on an individual’s specific needs, goals, and circumstances. Both credentials offer pathways to educational advancement, personal growth, and career opportunities. By understanding the advantages and disadvantages of each credential, individuals can make an informed decision that empowers them to achieve their full potential.
As the future of education evolves, new and innovative credentialing systems are emerging to meet the changing needs of society and the workforce. Personalized learning pathways, micro-credentials, and lifelong learning are shaping the future of education, providing individuals with greater flexibility, customization, and recognition for their skills and knowledge.
By embracing these emerging trends and continuing to invest in their education, individuals can unlock new opportunities for success and create a brighter future for themselves and their communities.