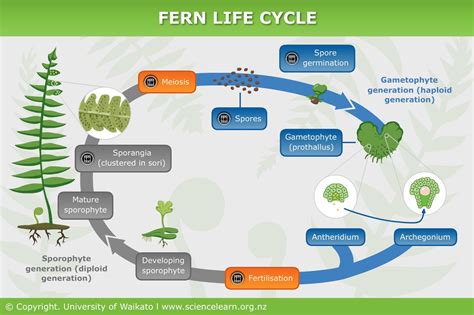
Ferns are a group of vascular plants that utilize a diploid-dominant life strategy. This means that the diploid (2n) phase of the fern life cycle is the dominant phase, and the haploid (n) phase is the shorter-lived phase.

The Fern Life Cycle
The fern life cycle begins with a haploid spore. The spore germinates and grows into a small, independent plant called a gametophyte. The gametophyte produces male and female gametes (sperm and eggs). When a sperm fertilizes an egg, a diploid zygote is formed. The zygote develops into a sporophyte, which is the dominant phase of the fern life cycle.
The sporophyte produces spores through meiosis. The spores are dispersed by the wind and can germinate to form new gametophytes, thus completing the life cycle.
Diploid Dominance
In most plants, the haploid phase of the life cycle is the dominant phase. However, in ferns, the diploid phase is the dominant phase. This means that the sporophyte is the larger and more complex phase of the life cycle. The gametophyte is a small and inconspicuous phase that is often short-lived.
Advantages of Diploid Dominance
The diploid-dominant life strategy provides several advantages for ferns. First, it allows ferns to grow larger and more complex than they would be able to if they were haploid-dominant. This is because diploid plants have two copies of each chromosome, which provides them with more genetic diversity and resilience.
Second, the diploid-dominant life strategy allows ferns to reproduce more efficiently. Diploid plants can produce spores through meiosis, which is a more efficient way to reproduce than mitosis. Mitosis is the process by which haploid plants reproduce.
Third, the diploid-dominant life strategy allows ferns to colonize new habitats more easily. Diploid plants are more tolerant of environmental stresses than haploid plants, which makes them more likely to survive in new and challenging habitats.
Examples of Ferns
There are over 10,000 species of ferns found all over the world. Some of the most common ferns include:
- Bracken fern (Pteridium aquilinum)
- Maidenhair fern (Adiantum capillus-veneris)
- Boston fern (Nephrolepis exaltata)
- Japanese painted fern (Athyrium niponicum)
- Sword fern (Polystichum munitum)
Uses of Ferns
Ferns have been used by humans for centuries for a variety of purposes. Some of the most common uses of ferns include:
- Food: The young fiddleheads of some ferns are edible and can be cooked and eaten.
- Medicine: Ferns have been used in traditional medicine to treat a variety of ailments, including wounds, burns, and digestive problems.
- Ornamentation: Ferns are often used as ornamental plants in gardens and homes.
- Erosion control: Ferns can be used to help control erosion on slopes and embankments.
- Air purification: Ferns can help to purify the air by removing pollutants.
Conclusion
Ferns are a group of vascular plants that utilize a diploid-dominant life strategy. This life strategy provides several advantages for ferns, including increased size and complexity, more efficient reproduction, and greater tolerance of environmental stresses. Ferns are found all over the world and are used by humans for a variety of purposes, including food, medicine, ornamentation, erosion control, and air purification.
Keywords
- Diploid-dominant life strategy
- Ferns
- Gametophyte
- Sporophyte
- Spores
FAQs
1. What is the difference between a haploid and a diploid cell?
A haploid cell has one set of chromosomes, while a diploid cell has two sets of chromosomes.
2. What is the dominant phase of the fern life cycle?
The diploid phase is the dominant phase of the fern life cycle.
3. What are the advantages of diploid dominance for ferns?
Diploid dominance allows ferns to grow larger and more complex, reproduce more efficiently, and colonize new habitats more easily.
4. What are some common uses of ferns?
Ferns are used for food, medicine, ornamentation, erosion control, and air purification.
Tips and Tricks
- Ferns prefer to grow in moist, shady areas.
- Ferns should be fertilized regularly with a balanced fertilizer.
- Ferns can be propagated by dividing the roots or by rooting cuttings.
- Ferns can be used to create a variety of garden designs, from formal to informal.
- Ferns can be used to add a touch of greenery to your home or office.
Useful Tables
| Fern Species | Height | Hardiness Zone | Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bracken fern | 2-4 ft | 3-9 | Food, medicine, erosion control |
| Maidenhair fern | 1-2 ft | 10-12 | Ornamentation, air purification |
| Boston fern | 3-4 ft | 10-12 | Ornamentation, air purification |
| Japanese painted fern | 2-3 ft | 5-8 | Ornamentation |
| Sword fern | 2-4 ft | 5-8 | Ornamentation, erosion control |
| Fern Uses | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Food | Edible fiddleheads |
| Medicine | Treats wounds, burns, and digestive problems |
| Ornamentation | Adds beauty to gardens and homes |
| Erosion control | Helps to control erosion on slopes and embankments |
| Air purification | Removes pollutants from the air |
| Fern Care Tips |
|---|
| Ferns prefer to grow in moist, shady areas. |
| Ferns should be fertilized regularly with a balanced fertilizer. |
| Ferns can be propagated by dividing the roots or by rooting cuttings. |
| Ferns can be used to create a variety of garden designs, from formal to informal. |
| Ferns can be used to add a touch of greenery to your home or office. |