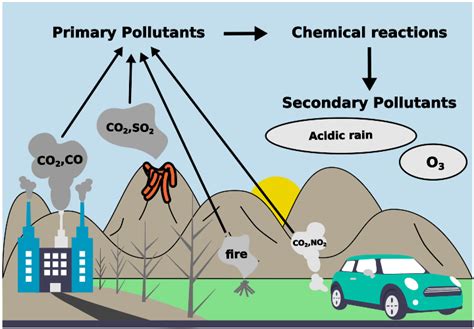
What are Secondary Pollutants?
Secondary pollutants are chemical compounds that are formed in the atmosphere as a result of chemical reactions between primary pollutants. Primary pollutants are pollutants that are directly emitted into the atmosphere from sources such as power plants, factories, and vehicles.

Secondary pollutants can be more harmful than primary pollutants because they can be more toxic and can have a greater impact on human health and the environment. Some of the most common secondary pollutants include ozone, particulate matter, and sulfuric acid.
Examples of Secondary Pollutants
Ozone
Ozone is a secondary pollutant that is formed when nitrogen oxides (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) react in the presence of sunlight. Ozone is a gas that is harmful to human health. It can cause respiratory problems, such as asthma and bronchitis, and it can also damage crops and vegetation.
Particulate Matter
Particulate matter is a secondary pollutant that is formed when small particles of solid or liquid matter are suspended in the atmosphere. Particulate matter can be harmful to human health. It can cause respiratory problems, such as asthma and bronchitis, and it can also increase the risk of heart disease and cancer.
Sulfuric Acid
Sulfuric acid is a secondary pollutant that is formed when sulfur dioxide (SO2) reacts with water vapor in the atmosphere. Sulfuric acid is a highly corrosive liquid that can cause damage to buildings, vegetation, and human health. It can also contribute to acid rain.
Impacts of Secondary Pollutants
Secondary pollutants can have a significant impact on human health and the environment. Some of the most common impacts of secondary pollutants include:
- Respiratory problems: Secondary pollutants can cause respiratory problems, such as asthma and bronchitis.
- Cardiovascular disease: Secondary pollutants can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, such as heart disease and stroke.
- Cancer: Secondary pollutants can increase the risk of cancer, such as lung cancer and bladder cancer.
- Crop damage: Secondary pollutants can damage crops and vegetation.
- Acid rain: Secondary pollutants can contribute to acid rain, which can damage buildings, vegetation, and aquatic ecosystems.
Reducing Secondary Pollutants
There are a number of things that can be done to reduce secondary pollutants. Some of the most effective measures include:
- Reducing emissions of primary pollutants: The most effective way to reduce secondary pollutants is to reduce emissions of primary pollutants. This can be done by implementing measures such as using cleaner fuels, improving energy efficiency, and reducing industrial emissions.
- Controlling emissions of VOCs: VOCs are a major precursor to ozone formation. Controlling emissions of VOCs can help to reduce ozone levels. Some of the most effective measures for controlling VOC emissions include using low-VOC paints and solvents, and improving vehicle emissions controls.
- Controlling emissions of NOx: NOx is a major precursor to ozone formation. Controlling emissions of NOx can help to reduce ozone levels. Some of the most effective measures for controlling NOx emissions include using cleaner fuels, improving energy efficiency, and reducing industrial emissions.
Conclusion
Secondary pollutants are a major threat to human health and the environment. Reducing secondary pollutants is essential for protecting public health and the environment. There are a number of things that can be done to reduce secondary pollutants, including reducing emissions of primary pollutants, controlling emissions of VOCs, and controlling emissions of NOx.
Additional Resources
- Environmental Protection Agency: Secondary Pollutants
- World Health Organization: Ambient Air Pollution
- American Lung Association: Air Pollution and Your Health