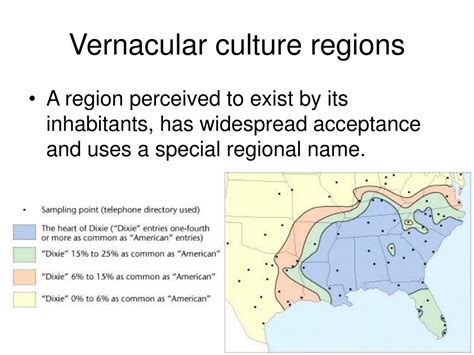
Vernacular regions are geographical areas characterized by a shared language, culture, and history that distinguishes them from surrounding regions. This concept plays a crucial role in understanding the diversity and richness of global societies. Here are some notable examples of vernacular regions:

Cultural Diversity and Vernacular Regions
-
Basque Country (Northern Spain and Southwestern France): The Basque Country is renowned for its unique language, Euskara, spoken by over 700,000 people. The region boasts a rich cultural heritage, including traditional dances, music, and a distinctive gastronomy centered around pintxos (tapas).
-
Appalachia (Eastern United States): Stretching from Maine to Alabama, Appalachia is a mountainous region with a distinct culture influenced by its isolation and rugged terrain. It is known for its folk music, storytelling traditions, and handcrafted goods such as quilts and pottery.
-
Okinawa (Japan): An archipelago in southern Japan, Okinawa has a culture influenced by both Japanese and Ryukyuan traditions. The region’s distinct language, Ryukyuan, and cultural practices, such as traditional festivals and martial arts like karate, set it apart from mainland Japan.
-
Cajun Country (Southern Louisiana, United States): The Cajun region is home to a French-speaking community descended from Acadian exiles. Cajun culture is vibrant and expressive, featuring unique music, cuisine, and storytelling traditions that blend French and Creole influences.
Vernacular Architecture and Landscape
-
Puebloan Pueblos (American Southwest): The Puebloan peoples of the American Southwest have a long history of building earthen dwellings called pueblos. These multi-story structures were designed for defense and communal living and often incorporated elements of the surrounding landscape.
-
Trulli of Apulia (Southern Italy): The conical-shaped trulli houses of Apulia are iconic structures built using local limestone. They feature thick walls, sloping roofs, and whitewashed exteriors, which help regulate temperature and resist wind.
-
Long Houses of the Great Plains (Central United States): Indigenous tribes of the Great Plains, such as the Lakota and Cheyenne, traditionally lived in long houses made of wooden frames covered with animal skins or woven mats. These houses were designed for extended family groups and provided shelter from the elements.
Vernacular Arts and Crafts
-
Batik Textiles of Java (Indonesia): Java is famous for its intricate batik textiles, a traditional form of fabric dyeing that uses wax and dye to create patterns on cloth. Batik motifs often draw inspiration from nature and cultural symbols, and the craft is passed down through generations.
-
Glassblowing in the Czech Republic: The Czech Republic has a long history of glassblowing, with renowned artisans in regions such as Bohemia and Moravia. Their techniques include free-blowing, casting, and engraving, creating beautiful glassware ranging from decorative objects to chandeliers.
-
Pottery of Mexico: Mexican pottery is celebrated for its vibrant colors and intricate designs. Artisans in states like Oaxaca and Jalisco use traditional methods passed down from ancient Mexican civilizations to create unique and functional pieces that reflect the region’s artistic heritage.
Vernacular Cuisine
-
Sushi of Japan: Sushi, a type of vinegared rice topped with seafood or other ingredients, is a staple of Japanese cuisine. Regional variations exist, such as Edomae sushi in Tokyo and Kansai sushi in Osaka, each with its distinctive styles and ingredients.
-
Pizza of Naples (Italy): Neapolitan pizza is known for its thin, chewy crust and simple yet flavorful toppings. The dish is recognized by UNESCO as an Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity, and its traditional preparation is strictly regulated.
-
Tacos of Mexico: Tacos are ubiquitous in Mexican cuisine, consisting of corn or wheat tortillas filled with various meats, seafood, or vegetables. Regional variations include tacos al pastor from central Mexico and tacos de camarón from the coastal regions.
Benefits of Understanding Vernacular Regions
-
Cultural Appreciation: Recognizing and preserving vernacular regions allows us to appreciate the diversity of human cultures and traditions. It fosters empathy and understanding among different peoples.
-
Cultural Heritage: Vernacular regions are often repositories of cultural heritage, embodying unique languages, customs, and art forms. Preserving these regions helps maintain cultural continuity and identity.
-
Economic Development: Vernacular regions can attract tourists and support local businesses that offer authentic cultural experiences. Tourism and cultural industries can contribute significantly to regional economies.
-
Environmental Conservation: Vernacular architecture and landscapes can be adapted to local conditions and contribute to sustainable development. Preserving traditional building practices and landscapes helps maintain ecological balance.
Effective Strategies for Preserving Vernacular Regions
-
Education and Awareness: Raising awareness about the importance of vernacular regions is crucial. Educational programs can foster appreciation for cultural diversity and encourage the preservation of local traditions.
-
Cultural Tourism: Promoting responsible and respectful cultural tourism supports vernacular regions by providing economic incentives for preserving traditional practices and cultural heritage.
-
Designated Heritage Areas: Creating designated heritage areas can provide legal protection for vernacular regions and restrict development that could harm their cultural integrity.
-
Government Support: Governments can allocate funding to support cultural preservation initiatives, provide tax incentives for vernacular architecture, and invest in community revitalization projects.
How to Appreciate and Support Vernacular Regions
-
Travel Responsibly: When visiting vernacular regions, respect local customs and traditions, engage with the community, and support local businesses that promote cultural preservation.
-
Learn the Local Language: Making an effort to learn basic phrases in the local language demonstrates respect and shows interest in the unique culture of the region.
-
Attend Cultural Events: Participate in local festivals, performances, or exhibitions to experience the vibrant cultural expressions of vernacular regions firsthand.
-
Support Local Artisans and Craftsmen: Purchasing handmade products from local artisans supports their livelihoods and helps preserve traditional arts and crafts.
-
Advocate for Cultural Preservation: Speak out against threats to vernacular regions and support organizations that advocate for their protection.
FAQs on Vernacular Regions
-
What is the difference between a region and a vernacular region?
– A region refers to a geographical area, whereas a vernacular region is defined by its shared language, culture, and history, which distinguishes it from surrounding regions. -
Why are vernacular regions important?
– Vernacular regions preserve cultural heritage, foster cultural appreciation, support economic development, and contribute to environmental conservation. -
How can I support vernacular regions?
– You can support vernacular regions by traveling responsibly, learning the local language, attending cultural events, supporting local artisans, and advocating for cultural preservation. -
What are some challenges facing vernacular regions today?
– Vernacular regions face challenges such as globalization, urbanization, mass tourism, and climate change, which can undermine their cultural integrity and sustainability. -
How can governments support vernacular regions?
– Governments can support vernacular regions by allocating funding for cultural preservation initiatives, providing tax incentives for vernacular architecture, and investing in community revitalization projects. -
What are some examples of vernacular architecture?
– Vernacular architecture includes traditional houses, public buildings, and religious structures that reflect the local culture, materials, and climate. Examples include the trulli of Apulia, the long houses of the Great Plains, and the earthen pueblos of the American Southwest.