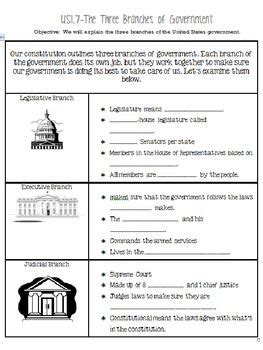
The United States government is a complex system of checks and balances designed to ensure that no one branch of government becomes too powerful. The three branches of government are the legislative branch, the executive branch, and the judicial branch.

The legislative branch is responsible for making laws. It is composed of the Senate and the House of Representatives. The Senate has 100 members, two from each state. The House of Representatives has 435 members, who are elected from districts based on population.
In 2021, the total federal budget was $6.8 trillion. Of this, $2.7 trillion was spent on Social Security, $1.2 trillion on Medicare, and $687 billion on defense.
The executive branch is responsible for carrying out the laws. It is headed by the president, who is also the commander-in-chief of the armed forces. The president is elected by the Electoral College, which is composed of electors from each state.
The judicial branch is responsible for interpreting the laws. It is composed of the Supreme Court, which has nine justices, and lower federal courts. The justices of the Supreme Court are appointed by the president and confirmed by the Senate.
The U.S. government is based on the principles of democracy and federalism. Democracy means that the government is elected by the people. Federalism means that there is a division of power between the national government and the state governments.
Answer the following questions:
- What are the three branches of government?
- What are the two houses of the legislative branch?
- Who is the commander-in-chief of the armed forces?
- How many justices are on the Supreme Court?
- What are the principles of democracy and federalism?
1. What are the main functions of the three branches of government?
The main functions of the three branches of government are as follows:
- Legislative branch: Make laws
- Executive branch: Carry out the laws
- Judicial branch: Interpret the laws
2. How are members of the House of Representatives elected?
Members of the House of Representatives are elected from districts based on population.
3. What is the role of the Electoral College?
The Electoral College is composed of electors from each state who are elected by the people. The electors then vote for the president and vice president.
4. How are justices of the Supreme Court appointed?
Justices of the Supreme Court are appointed by the president and confirmed by the Senate.
5. What is the difference between democracy and federalism?
Democracy means that the government is elected by the people, while federalism means that there is a division of power between the national government and the state governments.
6. What are some of the challenges facing the U.S. government?
Some of the challenges facing the U.S. government include:
- Economic inequality
- Political polarization
- Climate change
- National security threats
7. What can be done to address these challenges?
There are a number of things that can be done to address the challenges facing the U.S. government, including:
- Investing in education and job training
- Promoting economic growth
- Reducing political polarization
- Taking action on climate change
- Strengthening national security
Conclusion
The U.S. government is a complex and dynamic system that is constantly evolving to meet the challenges of a changing world. By understanding the principles of democracy, federalism, and the separation of powers, we can help to ensure that our government remains strong and responsive to the needs of the people.