Introduction

Environmental chemistry is a rapidly growing field that combines principles of chemistry with environmental science to address pressing ecological challenges. It involves studying the chemical composition of the environment, the fate and transport of pollutants, and developing solutions to mitigate environmental damage.
With increasing public awareness about environmental issues, the demand for skilled professionals in environmental chemistry is surging. This article provides a comprehensive overview of environmental chemistry jobs, their responsibilities, and career prospects.
Job Responsibilities
Environmental chemists play a crucial role in various environmental sectors, performing responsibilities such as:
1. Environmental Monitoring and Analysis:
- Collect and analyze environmental samples (e.g., air, water, soil) to identify and quantify pollutants
- Monitor environmental compliance and enforce regulations
- Assess the impact of human activities on the environment
2. Pollution Control and Remediation:
- Develop and implement strategies to reduce pollution from industrial processes and other sources
- Design and operate pollution control devices (e.g., scrubbers, filters)
- Conduct environmental remediation projects to clean up contaminated sites
3. Risk Assessment and Management:
- Evaluate the potential risks of chemicals to human health and the environment
- Develop risk management plans to minimize exposure and mitigate adverse effects
- Conduct environmental impact assessments prior to development projects
4. Environmental Policy and Regulation:
- Advise policymakers on environmental issues and develop environmental regulations
- Provide scientific support for environmental litigation
- Participate in public outreach and education initiatives
Industries and Employment Outlook
Environmental chemists are employed in a wide range of industries, including:
- Environmental consulting firms
- Government agencies (e.g., EPA, NOAA)
- Research institutions (e.g., universities, laboratories)
- Chemical manufacturing companies
- Waste management companies
- Environmental nonprofits
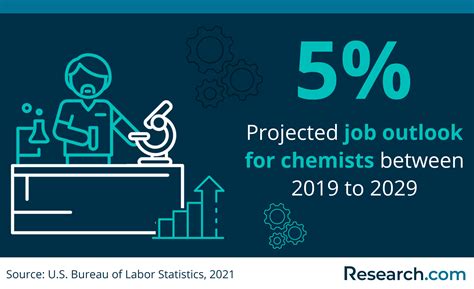
The US Bureau of Labor Statistics projects a 6% growth in employment for environmental scientists, which include environmental chemists, over the next decade. As environmental concerns continue to rise, the demand for skilled professionals is expected to increase significantly.
Education and Experience Requirements
Most environmental chemistry jobs require at least a bachelor’s degree in environmental chemistry, chemistry, or a related field. Some positions may also require a master’s degree or doctorate.
Additional experience in environmental consulting, research, or government agencies can enhance one’s competitiveness in the job market. Certifications in environmental management or specific environmental disciplines can also be beneficial.
Career Prospects
Environmental chemists have a wide range of career options, including:
1. Environmental Consultant: Provide environmental advice to clients, conduct environmental assessments, and develop pollution control plans.
2. Government Scientist: Conduct environmental research, regulate pollution, and enforce environmental laws.
3. Environmental Researcher: Investigate environmental problems and develop new technologies to address them.
4. Environmental Manager: Supervise environmental programs and ensure compliance with regulations.
5. Environmental Educator: Educate the public about environmental issues and promote sustainable practices.
Tips and Tricks for a Successful Career
- Develop strong analytical skills: Environmental chemistry involves extensive data analysis and interpretation.
- Gain practical experience: Internships, research projects, and fieldwork provide valuable hands-on experience.
- Keep up with industry trends: Attend conferences, read scientific journals, and engage in professional development activities.
- Cultivate strong communication skills: Environmental chemists must be able to communicate their findings effectively to a wide range of audiences.
- Embrace eco-innovation: Explore new and innovative approaches to environmental problems.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Underestimating the importance of field experience: Practical experience is essential for success in environmental chemistry.
- Focusing solely on technical skills: Strong communication and problem-solving skills are equally important.
- Neglecting regulatory knowledge: Environmental chemists must have a good understanding of environmental laws and regulations.
- Lacking a sense of urgency: Environmental problems are urgent and require timely solutions.
- Overspecialization: While specialization can be beneficial, it is important to have a broad understanding of environmental chemistry.
Environmental Chemistry in the Future: “Eco-innovation”
As environmental challenges become increasingly complex, environmental chemists are playing a pivotal role in developing innovative solutions. Eco-innovation, a term coined by the European Union, refers to the development of new products, processes, and technologies that minimize environmental impact and maximize resource efficiency.
Environmental chemists are actively involved in eco-innovation, exploring areas such as:
- Green chemistry: Developing environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional industrial processes
- Sustainable materials: Designing and manufacturing materials with reduced environmental footprints
- Bioremediation: Utilizing microorganisms to clean up contaminated sites
- Environmental sensor technology: Developing advanced sensors for real-time environmental monitoring
- Climate change mitigation: Developing technologies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and adapt to climate change impacts
Tables
Table 1: Environmental Chemistry Job Titles and Responsibilities
| Job Title | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Environmental Consultant | Provide environmental advice, conduct assessments, and develop pollution control plans |
| Government Scientist | Conduct environmental research, regulate pollution, and enforce environmental laws |
| Environmental Researcher | Investigate environmental problems and develop new technologies to address them |
| Environmental Manager | Supervise environmental programs and ensure compliance with regulations |
| Environmental Educator | Educate the public about environmental issues and promote sustainable practices |
Table 2: Industries Employing Environmental Chemists
| Industry | Percentage of Environmental Chemists Employed |
|---|---|
| Environmental Consulting Firms | 35% |
| Government Agencies | 25% |
| Research Institutions | 15% |
| Chemical Manufacturing Companies | 10% |
| Waste Management Companies | 10% |
| Other Industries | 5% |
Table 3: Effective Strategies for Environmental Chemists
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Collaboration | Partner with other professionals to tackle complex environmental problems |
| Research and Innovation | Stay up-to-date with industry trends and explore new technologies |
| Communication | Effectively communicate environmental findings to a wide range of audiences |
| Regulation | Advocate for strong environmental regulations and enforce compliance |
| Education | Educate the public about environmental issues and promote sustainable practices |
Table 4: Common Mistakes to Avoid in Environmental Chemistry
| Mistake | Consequences |
|---|---|
| Underestimating Field Experience | Limits practical knowledge and career advancement |
| Neglecting Regulatory Knowledge | Hinders compliance and ethical decision-making |
| Overspecialization | Restricts career opportunities and hinders adaptability |
| Lack of a Sense of Urgency | Delays implementation of solutions to pressing environmental problems |
| Poor Communication Skills | Limits effectiveness in conveying environmental findings and advocating for change |