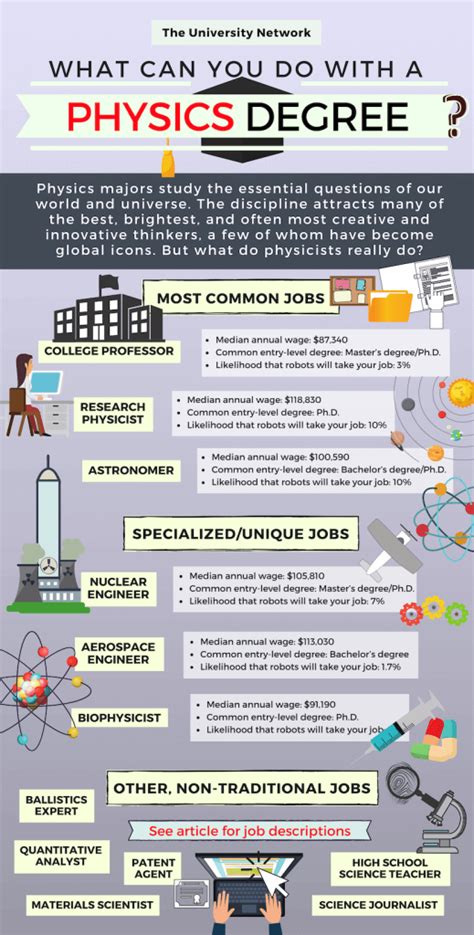
Introduction

Engineering physics, a transdisciplinary field that blends principles from physics with engineering design, has emerged as a highly sought-after career path. With its focus on developing innovative solutions for complex technological challenges, engineering physics professionals are in high demand across a wide spectrum of industries. This article delves into the expansive job opportunities available within the field of engineering physics, providing valuable insights into the skills, qualifications, and career paths for aspiring professionals.
Demand for Engineering Physicists
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the job outlook for materials scientists, a closely related field to engineering physics, is projected to grow 8% from 2020 to 2030, faster than the average for all occupations. This growth is attributed to increasing demand for advanced materials in various fields, including energy, transportation, and healthcare.
Industries Hiring Engineering Physicists
Engineering physicists find employment in a diverse array of industries, including:
- Aerospace and Defense
- Automotive
- Electronics
- Energy
- Healthcare
- Manufacturing
- Materials Science
- Nanotechnology
- Optics
- Pharmaceutical
Job Titles and Responsibilities
Within these industries, engineering physicists hold various job titles and perform a range of responsibilities:
- Research Engineer: Conducts fundamental research on materials, devices, and processes.
- Design Engineer: Develops and designs new products and systems.
- Materials Engineer: Characterizes and modifies materials properties for specific applications.
- Optics Engineer: Designs and develops optical devices and systems.
- Pharmaceutical Engineer: Applies engineering principles to the development and production of pharmaceuticals.
Skills and Qualifications
To succeed in the field of engineering physics, individuals typically possess:
- A Bachelor’s or Master’s degree in engineering physics, physics, or a related field.
- Strong analytical and problem-solving skills.
- Knowledge of materials science, optics, and thermodynamics.
- Proficiency in computer-aided design (CAD) software and programming languages.
- Excellent communication and interpersonal skills.
Career Paths
Engineering physics professionals can pursue various career paths, including:
- Research and Development
- Design and Development
- Manufacturing and Production
- Sales and Marketing
- Management and Administration
- Consulting
Innovative Applications
The interdisciplinary nature of engineering physics enables professionals to explore innovative applications in emerging fields such as:
- Quantum Computing: Developing materials and devices for quantum computing applications.
- Energy Storage: Designing and optimizing energy storage systems.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Integrating AI into engineering physics applications.
- Nanotechnology: Developing nanoscale devices and materials for various applications.
- Biophysics: Applying engineering principles to solve problems in biology and medicine.
Table 1: Industries Hiring Engineering Physicists and Average Salaries
| Industry | Average Salary |
|---|---|
| Aerospace and Defense | $114,510 |
| Automotive | $107,850 |
| Electronics | $118,730 |
| Energy | $118,510 |
| Healthcare | $120,360 |
| Manufacturing | $112,200 |
| Materials Science | $117,510 |
Table 2: Job Titles and Responsibilities of Engineering Physicists
| Job Title | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Research Engineer | Conducts fundamental research on materials, devices, and processes. |
| Design Engineer | Develops and designs new products and systems. |
| Materials Engineer | Characterizes and modifies materials properties for specific applications. |
| Optics Engineer | Designs and develops optical devices and systems. |
| Pharmaceutical Engineer | Applies engineering principles to the development and production of pharmaceuticals. |
Table 3: Skills and Qualifications for Engineering Physicists
| Skill | Qualification |
|---|---|
| Analytical and Problem-Solving Skills | Bachelor’s or Master’s degree in engineering physics, physics, or a related field. |
| Knowledge of Materials Science, Optics, and Thermodynamics | Strong analytical and problem-solving skills. |
| Proficiency in CAD Software and Programming Languages | Proficiency in computer-aided design (CAD) software and programming languages. |
| Excellent Communication and Interpersonal Skills | Excellent communication and interpersonal skills. |
Table 4: Career Paths for Engineering Physicists
| Career Path | Description |
|---|---|
| Research and Development | Conducts fundamental research on materials, devices, and processes. |
| Design and Development | Develops and designs new products and systems. |
| Manufacturing and Production | Manufactures and tests engineering physics products and systems. |
| Sales and Marketing | Markets and sells engineering physics products and services. |
| Management and Administration | Manages and administers engineering physics organizations. |
| Consulting | Provides consulting services to clients in the field of engineering physics. |
Conclusion
Engineering physics offers a wide range of rewarding career opportunities for individuals with a passion for solving complex technological challenges. By combining a strong foundation in physics with engineering design principles, engineering physics professionals play a vital role in the advancement of technology and the creation of innovative solutions that shape the future. With a growing demand for their expertise, engineering physicists continue to be highly sought after in various industries, ensuring a promising career path for those who embrace this field.