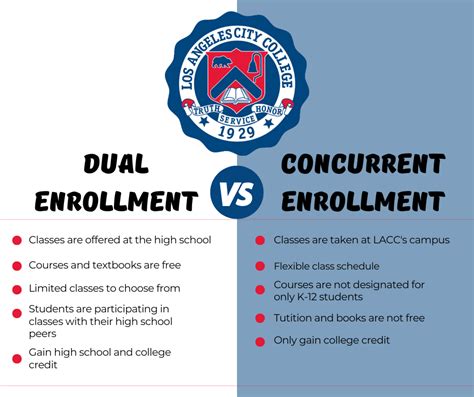
As a high school student, you’re likely eager to explore your options for pursuing higher education. You may have heard of dual enrollment, a program that allows high school students to take college-level courses while earning high school and college credit simultaneously. While dual enrollment offers various benefits, it’s essential to understand its distinctions from traditional college courses before making an informed decision.

Key Differences between Dual Enrollment and College Courses
| Feature | Dual Enrollment | College Courses |
|---|---|---|
| Available to | High school students | College students |
| Location | Typically at high school or satellite campuses | College campuses |
| Cost | Varies by school district or college; may be free or low-cost | Higher tuition and fees |
| Flexibility | Limited course selection and scheduling may differ from high school curriculum | Wide range of courses and scheduling options |
| Credit | Earns both high school and college credit | Earns only college credit |
| Instructor | High school teachers or adjunct college professors | College professors |
| Class Size | May be smaller or comparable to high school classes | Typically larger, with more diverse students |
| Grading | May be graded on a high school or college scale | Graded on a college scale |
| Prerequisites | May have fewer or different prerequisites compared to traditional college courses | Often require specific prerequisites and higher academic standards |
Benefits of Dual Enrollment
- Accelerated College Degree Completion: Students can save time and money by earning college credits while in high school, potentially shortening their college journey.
- Enhanced Academic Preparedness: Dual enrollment courses challenge students academically, preparing them for the rigors of college-level work.
- Exploration of Interests: Students can explore various academic disciplines and career paths by taking college-level courses in subjects they enjoy.
- Scholarship Eligibility: Dual enrollment can boost a student’s academic profile, making them more competitive for scholarships and college admission.
Benefits of College Courses
- Wider Selection and Flexibility: College offers a broader range of courses and scheduling options tailored to students’ interests and availability.
- Higher Academic Standards: College courses adhere to stricter academic standards, ensuring a rigorous learning experience.
- Exposure to Diverse Perspectives: College classrooms bring together students from diverse backgrounds and perspectives, fostering intellectual growth.
- Preparation for College Life: College courses simulate the academic, social, and extracurricular aspects of college life, allowing students to adapt before entering higher education.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Choosing the Wrong Courses: It’s essential to carefully consider your interests, academic goals, and the transferability of courses before enrolling in dual enrollment or college courses.
- Overloading Your Schedule: Don’t attempt to take too many college courses while still pursuing high school coursework. Balance your academic load to avoid burnout and maintain your grades.
- Ignoring Prerequisites: Ensure you meet all the prerequisites for the college course you wish to take. Failure to do so can hinder your progress and impact your grades.
- Neglecting High School Requirements: While dual enrollment offers valuable opportunities, don’t neglect your high school requirements and graduation credits.
- Assuming College Courses Are Easier: Don’t underestimate the difficulty of college courses. They require a higher level of academic rigor and independent learning than high school courses.
Step-by-Step Approach to Dual Enrollment or College Courses
- Research and Plan: Explore your options, consult with your counselor, and determine which dual enrollment or college courses align with your academic goals and interests.
- Meet Prerequisites: Ensure you have the necessary prerequisites and academic standing to enroll in the desired courses.
- Apply and Enroll: Follow the application and enrollment procedures outlined by the school or institution offering the courses.
- Prepare and Succeed: Attend classes regularly, participate actively, and seek support when needed.
- Monitor Progress: Track your grades, stay organized, and seek guidance from instructors or advisors if necessary.
- Request Transcript: Upon course completion, request an official transcript of your dual enrollment or college credits for future use in college applications and transfer.
Why It Matters: The Impact of Dual Enrollment and College Courses
Dual enrollment and college courses offer transformative educational experiences that positively impact high school students. Studies have shown that students enrolled in dual enrollment programs:
- Have higher high school GPAs and college entrance exam scores.
- Are more likely to enroll in college, pursue further education, and earn a bachelor’s degree.
- Develop stronger critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
- Enhance their college readiness and academic confidence.
Conclusion
Deciding between dual enrollment and college courses is a personal choice that depends on your academic goals, abilities, and circumstances. Carefully consider the benefits and challenges of both options before making a decision. By exploring your options, preparing adequately, and approaching the experience with dedication, you can unlock the full potential of dual enrollment or college courses and gain valuable knowledge and skills that will benefit you throughout your educational journey.
Additional Information
Useful Tables
| Table 1: Dual Enrollment Participation Rates by State |
|—|—|
| State | Percentage of High School Students Enrolled in Dual Enrollment |
| California | 18% |
| Florida | 13% |
| Texas | 10% |
| New York | 8% |
| Table 2: College Course Success Rates for Dual Enrollment Students |
|—|—|
| Study | Success Rate of Dual Enrollment Students in College Courses |
| National Center for Education Statistics | 85% |
| College Board | 90% |
| Table 3: Common Prerequisites for College Courses |
|—|—|
| Course | Common Prerequisites |
| Mathematics | Algebra I, Geometry, Algebra II |
| English | English I, English II, English III |
| Science | Biology, Chemistry, Physics |
| History | World History, US History |
| Table 4: Benefits of Dual Enrollment and College Courses |
|—|—|
| Educational Benefits | Personal Benefits |
| Accelerated college degree completion | Enhanced academic preparedness |
| Enhanced academic preparedness | Exploration of interests |
| Exploration of interests | Scholarship eligibility |
| Scholarship eligibility | Preparation for college life |