In the realm of statistics, correlation plays a fundamental role in investigating the relationships between variables. It measures the extent to which two variables vary together, providing insights into potential associations or patterns. However, a common question arises: does correlation necessarily require explanatory and response variables?

Understanding Correlation and Its Types
Correlation quantifies the degree of linear association between two variables. It ranges from -1 to 1, where:
- -1: Indicates a perfect negative correlation, meaning as one variable increases, the other decreases proportionally.
- 0: Indicates no correlation, meaning there is no linear relationship between the variables.
- 1: Indicates a perfect positive correlation, meaning as one variable increases, the other increases proportionally.
Explanatory and Response Variables in Regression Analysis
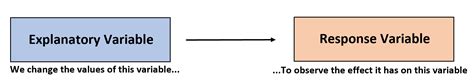
In regression analysis, a specific type of statistical modeling, explanatory variables (also known as independent variables) are used to predict the value of a response variable (also known as the dependent variable). By establishing a mathematical relationship between these variables, regression analysis aims to understand how changes in explanatory variables affect the response variable.
Correlation vs. Regression: Key Differences
While correlation measures the strength of the linear relationship between two variables, regression:
- Models the relationship: Regression creates a mathematical equation that describes how the explanatory variables influence the response variable.
- Predicts outcomes: Regression allows for the prediction of the response variable’s value based on the values of the explanatory variables.
- Estimates causal effects: By controlling for other factors, regression can help establish causality or determine if changes in explanatory variables cause changes in the response variable.
Correlation and Regression: Complementary Tools
In many situations, correlation can be a useful preliminary step to regression analysis. Correlation analysis can:
- Identify potential relationships: Correlation can highlight variables that have strong linear associations, suggesting the need for further exploration through regression.
- Provide insights about data: Correlation coefficients can indicate the direction and strength of relationships, offering valuable information about the nature of the data.
Applications of Correlation and Regression
Correlation and regression find applications in various fields, including:
- Medical research: Investigating the relationship between lifestyle factors and health outcomes.
- Economics: Modeling the impact of economic policies on growth and unemployment.
- Education: Assessing the correlation between teaching methods and student performance.
- Business: Predicting sales based on marketing campaigns or customer demographics.
Effective Use of Correlation and Regression
To effectively use correlation and regression, consider the following tips:
Tips for Using Correlation:
- Ensure data normality: Correlation assumes a linear relationship between variables, which may not always hold true for non-normal data.
- Consider sample size: Correlation coefficients can be misleading with small sample sizes. Use statistical tests to determine significance.
- Examine scatterplots: Visualizing the data in a scatterplot can reveal non-linear relationships or outliers that may affect correlation.
Tips for Using Regression:
- Identify appropriate explanatory variables: Select variables that are theoretically or logically related to the response variable.
- Ensure model fit: Validate the regression model using goodness-of-fit statistics to assess its accuracy in predicting the response variable.
- Interpret coefficients carefully: Regression coefficients provide insights into the direction and magnitude of the relationship between variables.
Conclusion
Correlation and regression are essential statistical tools that provide valuable insights into the relationships between variables. While correlation alone does not require explanatory and response variables, it can serve as a preliminary step to regression analysis. By understanding the differences and applications of these techniques, researchers and analysts can effectively investigate data and make informed conclusions.