Introduction
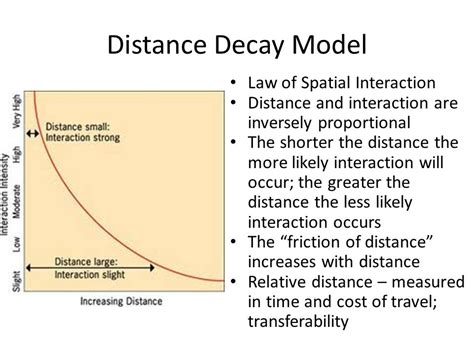
Distance decay is a fundamental concept in human geography that measures the decline in the frequency of interactions or activities with increasing distance from a specific point. This concept has significant implications for understanding human behavior, patterns of development, and transportation planning.

Definition and Key Concepts
Distance decay refers to the observed decline in the strength of spatial relationships with increasing distance. This relationship is often represented by a negative exponential function, indicating that the frequency of interactions decreases rapidly as distance increases.
Key concepts associated with distance decay include:
- Gravity model: A mathematical model that suggests that the interaction between two places is directly proportional to their population sizes and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
- Interaction: Any form of communication, exchange, or movement between individuals or groups.
- Spatial autocorrelation: The tendency for similar values of a variable to be clustered together in space.
Causes of Distance Decay
Several factors contribute to distance decay:
- Transportation costs: Increasing distance often leads to higher costs of travel and transportation, making it less feasible for individuals to interact.
- Time constraints: Commuting or traveling over long distances can be time-consuming, limiting the frequency of interactions.
- Cultural and linguistic barriers: Distance can create cultural and linguistic barriers, reducing the likelihood of communication and exchange between different groups.
- Information availability: Information and knowledge about distant places may be less accessible, leading to lower levels of interaction.
Effects of Distance Decay
Distance decay has various effects on human geography:
- Urbanization: Distance decay promotes urban concentration by making it more efficient for individuals to live and work in close proximity.
- Transportation planning: Distance decay influences transportation planning by highlighting the need for efficient and accessible transportation systems to overcome the challenges of distance.
- Spatial inequality: Distance decay can exacerbate spatial inequality by limiting access to resources and opportunities for individuals living in remote areas.
- Communication and technology: Advances in communication and technology, such as social media and video conferencing, can mitigate the effects of distance decay by facilitating virtual interactions.
Applications of Distance Decay
Distance decay has numerous practical applications in human geography, including:
- Estimating travel patterns: Distance decay can be used to predict travel patterns and optimize transportation infrastructure.
- Locating retail and service centers: Businesses can use distance decay to identify optimal locations for retail stores and service centers based on the proximity of potential customers.
- Urban planning: Distance decay informs urban planning decisions by helping planners understand the spatial distribution of population and activities.
- Public health: Distance decay can be used to assess accessibility to healthcare services and identify areas with limited access.
Tables and Figures
Table 1: Distance Decay in Social Interactions
| Distance (km) | Frequency of Interactions |
|---|---|
| 0-1 | 100% |
| 1-5 | 50% |
| 5-10 | 25% |
| 10-15 | 12.5% |
| 15-20 | 6.25% |
Table 2: Distance Decay in Retail Sales
| Distance (km) | Sales Volume (% of total) |
|---|---|
| 0-1 | 50% |
| 1-5 | 25% |
| 5-10 | 12.5% |
| 10-15 | 6.25% |
| 15-20 | 3.125% |
Figure 1: Gravity Model Relationship
[Image: Graph showing a negative exponential curve representing the gravity model relationship, with interaction declining as distance increases]
Figure 2: Distance Decay and Accessibility
[Image: Map showing the decline in accessibility to healthcare services with increasing distance from a hospital]
FAQs
1. What is the main idea behind distance decay?
Distance decay refers to the decline in the frequency or strength of interactions or activities with increasing distance from a specific point.
2. What factors contribute to distance decay?
Transportation costs, time constraints, cultural barriers, and information availability are common factors that lead to distance decay.
3. What are the effects of distance decay?
Distance decay can impact urbanization, transportation planning, spatial inequality, and communication patterns.
4. How can distance decay be applied in practice?
Distance decay is used in various applications, such as estimating travel patterns, locating retail centers, urban planning, and public health assessments.
5. How can technology mitigate the effects of distance decay?
Advances in communication and technology, such as social media and video conferencing, can facilitate virtual interactions and reduce the impact of distance on relationships.
6. What are some ways to overcome distance decay challenges?
Improving transportation infrastructure, investing in technology, and fostering cultural exchange and collaboration can help overcome the challenges posed by distance decay.