Understanding the Importance of a Degree
In today’s competitive job market, obtaining a college degree has become increasingly crucial. The Bureau of Labor Statistics projects that occupations requiring a bachelor’s degree or higher will grow by 11% between 2021 and 2031, significantly outpacing the growth of jobs requiring only a high school diploma or lower.

A degree unlocks a vast array of opportunities, providing individuals with advanced skills, knowledge, and credentials that are highly valued by employers. It empowers graduates to pursue their passions, contribute to their communities, and earn higher salaries throughout their careers.
Types of Degrees
Colleges and universities offer a wide range of degrees to meet the diverse needs of students:
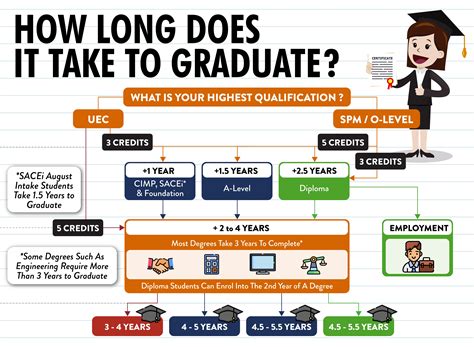
Associate Degree
- Typically requires two years of study
- Prepares individuals for entry-level positions in various fields
- Can serve as a pathway to a bachelor’s degree
Bachelor’s Degree
- Typically requires four years of study
- Provides a broad foundation in a chosen field
- Opens doors to a variety of career options
- Is the minimum requirement for many professional occupations
Master’s Degree
- Typically requires one or two years of study beyond a bachelor’s degree
- Focuses on advanced knowledge and skills in a specific field
- Enhances career opportunities and earning potential
Doctoral Degree
- The highest level of academic achievement
- Typically requires several years of study and research
- Prepares individuals for careers in academia, research, and advanced professional roles
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Degree
Selecting the right degree is crucial for a successful career. Individuals should consider the following factors:
- Interests and Passions: Choose a field that aligns with your passions and interests.
- Career Goals: Research the educational requirements for your desired career path.
- Job Market: Evaluate the availability of jobs in your chosen field and the salary potential.
- University Rankings: Research the reputation and rankings of universities offering your desired degree program.
- Program Length and Cost: Consider the time and financial investment required to complete the degree.
- Accreditation: Ensure that the degree program you choose is accredited by a reputable organization.
Benefits of Pursuing a Degree
In addition to career advancement, obtaining a degree offers numerous personal and societal benefits:
- Increased Earning Potential: Studies have consistently shown that individuals with bachelor’s degrees or higher earn significantly more throughout their careers compared to those with only a high school diploma.
- Improved Job Security: Degree holders are less likely to experience unemployment and have more stable careers.
- Greater Job Satisfaction: Individuals with higher education are more likely to find fulfillment and meaning in their work.
- Enhanced Critical Thinking Skills: Higher education develops critical thinking, problem-solving, and analytical skills that are essential for success in both personal and professional life.
- Increased Social Responsibility: Degree holders are more likely to engage in volunteerism and community service, contributing to a more equitable and just society.
Table 1: Salary Differences Based on Education Level
| Education Level | Median Annual Salary |
|---|---|
| Less than High School Diploma | $27,700 |
| High School Diploma or Equivalent | $39,210 |
| Associate Degree | $49,550 |
| Bachelor’s Degree | $67,520 |
| Master’s Degree | $91,900 |
| Doctoral Degree | $134,370 |
Table 2: Unemployment Rates by Education Level (2022)
| Education Level | Unemployment Rate |
|---|---|
| Less than High School Diploma | 6.3% |
| High School Diploma or Equivalent | 4.2% |
| Associate Degree | 3.1% |
| Bachelor’s Degree | 2.2% |
| Master’s Degree | 1.5% |
| Doctoral Degree | 0.8% |
Table 3: Return on Investment for Higher Education
| Degree Level | Average Earnings Over 40-year Career |
|---|---|
| Associate Degree | $1.6 million |
| Bachelor’s Degree | $2.3 million |
| Master’s Degree | $2.8 million |
| Doctoral Degree | $3.4 million |
Table 4: Percentage of Degree Holders Engaged in Civic Activities
| Education Level | Volunteering | Community Service |
|---|---|---|
| High School Diploma or Equivalent | 25% | 10% |
| Associate Degree | 32% | 15% |
| Bachelor’s Degree | 42% | 20% |
| Master’s Degree | 50% | 25% |
| Doctoral Degree | 58% | 30% |
Job Seeker’s Perspective: Why Seek a Degree?
For job seekers, obtaining a degree is an investment in their future. A degree:
- Increases Job Opportunities: Qualifies individuals for a wider range of jobs and opens doors to more lucrative careers.
- Enhances Credibility: Signals to potential employers that the candidate has the knowledge, skills, and commitment to excel in the role.
- Boosts Confidence: Gives job seekers the confidence to pursue their dream jobs and succeed in competitive job markets.
- Provides Continuing Education Opportunities: Degree holders have access to continuing education programs that enable them to stay current with industry trends and advance their careers.
Employer’s Perspective: Why Hire Degree Holders?
For employers, hiring degree holders offers numerous advantages:
- High Performance: Degree holders typically possess strong analytical, problem-solving, and communication skills, leading to higher productivity and efficiency.
- Innovation and Creativity: Higher education fosters critical thinking and innovation, equipping graduates with the ability to come up with creative solutions and contribute to team success.
- Improved Employee Retention: Employees with degrees are more likely to be engaged in their work and committed to the organization, reducing turnover costs.
- Increased Prestige: Hiring degree holders enhances the company’s reputation and attracts top talent.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between a degree and a certificate?
A degree is a comprehensive academic program that typically takes several years to complete and provides in-depth knowledge and skills in a specific field. A certificate is a short-term educational program that focuses on developing specific skills or competencies in a particular area.
2. Can I get a job without a degree?
While it is possible to obtain employment without a degree, certain career paths and higher-paying positions may require a college education. Additionally, individuals without a degree may face limited advancement opportunities within their careers.
3. Is it too late to go back to school for a degree?
It is never too late to pursue higher education. Many universities and colleges offer flexible programs for working adults who wish to complete their degree.
4. How much does it cost to get a degree?
The cost of a degree varies depending on factors such as the type of degree, the university, and the location. However, there are various financial aid options available to help students cover the expenses.
5. What is the best way to choose a degree program?
Consider your interests, career goals, and research different degree programs to find one that aligns with your aspirations. Consult with academic advisors and industry professionals for guidance.
6. How do I apply for a degree program?
Contact the admissions office of the university or college you wish to apply to for application requirements, deadlines, and instructions. Most applications include submitting transcripts, personal essays, and letters of recommendation.
7. What is the job outlook for degree holders?
The job outlook for degree holders is generally favorable, as higher education continues to be in high demand across various industries. However, the job prospects may vary depending on the specific field of study and economic conditions.
8. What are the different types of financial aid available for college?
Financial aid comes in various forms, including scholarships, grants, loans, and work-study programs. Students should explore all available options to minimize the cost of their education.