Introduction
Studio art, encompassing a wide spectrum of visual art forms, has enriched human expression for centuries. It encapsulates the creation of tangible artworks within a designated studio or workspace, encompassing various artistic disciplines. This article delves into the multifaceted world of studio art, shedding light on its history, key elements, and diverse applications.

A Journey Through the History of Studio Art
The origins of studio art can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where artisans and artists worked in designated spaces to produce functional and decorative objects. In the Renaissance era, the concept of the studio as a creative sanctuary gained prominence, with renowned artists establishing independent workshops. As time progressed, the studio became an integral part of the artistic process, fostering experimentation, collaboration, and the development of innovative techniques.
The Core Elements of Studio Art
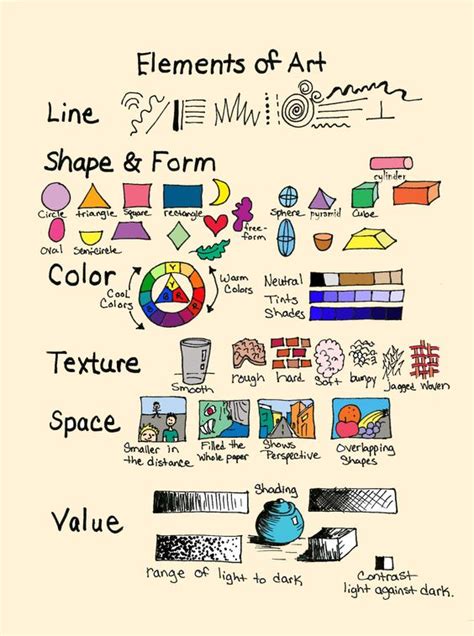
Studio art encompasses a diverse range of artistic mediums and approaches, each contributing to the unique character of an artwork. Key elements include:
- Concept: The underlying idea or message conveyed through the artwork.
- Form: The physical structure and composition of the artwork, including shape, color, texture, and scale.
- Materials: The tangible substances used to create the artwork, such as paint, clay, metal, or found objects.
- Techniques: The methods and processes employed to apply materials and achieve desired effects.
- Presentation: The manner in which the artwork is displayed, framed, or installed.
Exploring the Applications of Studio Art
Studio art finds myriad applications across various domains:
1. Fine Art
Painting, sculpture, drawing, and printmaking are traditional fine art forms that often prioritize aesthetic considerations and personal expression.
2. Commercial Art
Studio art is extensively used in commercial contexts, including graphic design, illustration, advertising, and packaging.
3. Applied Art
Studio art encompasses functional objects imbued with artistic value, such as furniture, textiles, ceramics, and jewelry.
4. Digital Art
With the advent of digital technology, studio art has expanded into the realm of digital media, embracing computer-generated imagery, video art, and interactive installations.
The Evolution of Studio Art in the Digital Age
Digital technology has significantly transformed studio art, opening up new possibilities for artistic expression and expanding its accessibility.
- Increased Accessibility: Digital tools and software enable individuals with limited traditional art skills to create digital artworks.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Online platforms facilitate collaboration between artists from different geographical locations.
- Innovative Techniques: Digital technology introduces novel techniques and effects that were previously unavailable in traditional mediums.
A Creative Future: Studio Art and Idea Generation
To generate innovative studio art ideas, artists can leverage a host of creative techniques:
- Brainstorming: Collaboratively generating a wide range of ideas without judgment.
- Mind Mapping: Visually organizing ideas and connecting them to related concepts.
- Freewriting: Stream-of-consciousness writing to explore thoughts and ideas.
- Research: Investigating existing artworks, materials, and techniques for inspiration.
Tables for Comprehensive Understanding
Table 1: Types of Studio Art Mediums
| Medium | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Painting | Applying pigments to a surface | Acrylic, oil, watercolor |
| Sculpture | Creating three-dimensional forms | Clay, wood, metal |
| Drawing | Creating marks on paper or other surfaces | Charcoal, graphite, ink |
| Printmaking | Transferring images to paper or other surfaces | Etchings, lithographs, screen prints |
| Digital Art | Creating artworks using digital tools and software | Computer-generated imagery, video art |
Table 2: Applications of Studio Art
| Application | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Fine Art | Personal expression and aesthetic exploration | Paintings, sculptures, drawings |
| Commercial Art | Creating visual content for businesses | Logos, advertisements, packaging |
| Applied Art | Functional objects with artistic value | Furniture, ceramics, textiles |
| Digital Art | Art created using digital tools and software | Video art, interactive installations |
Table 3: Advantages and Disadvantages of Digital Studio Art
| Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|
| Increased accessibility | Potential loss of tactile experience |
| Enhanced collaboration | Requires technical proficiency |
| Innovative techniques | Can be hardware and software dependent |
FAQs about Studio Art
1. What are the qualifications to become a studio artist?
Formal qualifications are not always necessary, but a bachelor’s degree or specialized training in art can provide a strong foundation.
2. How can I find inspiration for my studio art?
Draw inspiration from existing artworks, nature, personal experiences, or current events.
3. What are the different career paths for studio artists?
Artists can pursue careers in fine art, commercial art, applied art, or digital art, among others.
4. How can I market my studio art?
Establish an online presence, participate in art exhibitions, and utilize social media to promote your work.
5. What are the ethical considerations in studio art?
Respect copyright laws, avoid plagiarism, and consider the environmental impact of your materials and practices.
6. How can I stay updated on the latest trends in studio art?
attend art exhibitions, visit art magazines, and engage with artists and art enthusiasts online.
Conclusion
Studio art, with its rich history, diverse elements, and wide-ranging applications, remains a vibrant and essential part of the human experience. As technology continues to shape the art world, new forms and possibilities emerge, ensuring that studio art will continue to inspire, engage, and challenge audiences for generations to come. By understanding the multifaceted nature of studio art and embracing its potential, contemporary artists and enthusiasts can unlock a world of creativity, expression, and innovation.