Understanding the Significance of Crude Birth Rate
The crude birth rate (CBR) is a fundamental demographic indicator that measures the fertility level within a population. It represents the number of live births per 1,000 people in a given year. Understanding CBR is crucial for geographers and policymakers, as it provides insights into population growth, age structure, and overall demographic trends.

Factors Influencing Crude Birth Rate
Numerous factors contribute to the variation in CBR across different regions and countries. These include:
- Cultural norms: Societal attitudes, family size ideals, and access to contraception significantly impact birth rates.
- Economic conditions: Economic stability and development often lead to lower CBRs as women delay childbearing or pursue higher education.
- Educational attainment: Higher levels of education, especially among women, are associated with lower fertility rates.
- Health and mortality: Improved healthcare and reduced infant mortality can increase CBR as families have fewer children to replace those who died.
- Government policies: Family planning programs, healthcare initiatives, and maternal leave policies influence birth rates directly or indirectly.
Global Patterns of Crude Birth Rate
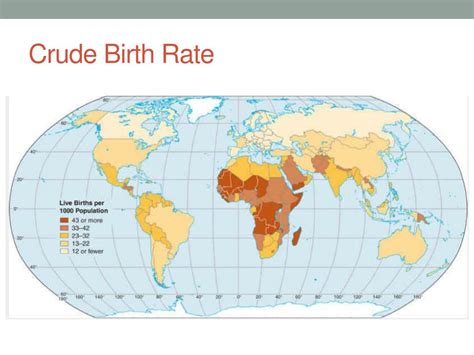
Globally, CBR has been declining in recent decades. According to the World Bank, the average CBR fell from 30.9 per 1,000 in 1950 to 17.9 in 2020. This decline is primarily attributed to urbanization, changing social norms, and improved access to contraceptives.
However, significant regional variations exist. CBRs are typically higher in developing countries and lower in developed countries. Sub-Saharan Africa has the highest regional CBR of 35.9, while Northern America and Europe have the lowest of 10.6 and 9.1, respectively.
Implications of Crude Birth Rate
Understanding CBR is essential for informed decision-making in various domains:
- Population planning: Accurate estimates of CBR are crucial for planning for housing, healthcare, and education.
- Economic development: High CBRs can strain economic resources, while low CBRs can lead to population aging.
- Social policy: CBR data informs policies related to family planning, maternal health, and child welfare.
- Environmental sustainability: High CBRs can contribute to overpopulation and stress on natural resources.
Strategies to Manage Crude Birth Rate
Managing CBR involves addressing the underlying factors that influence fertility. Effective strategies include:
- Investing in education: Promoting education, especially for girls, empowers women and reduces fertility.
- Expanding access to healthcare: Improving maternal and child health reduces infant mortality and encourages smaller family sizes.
- Supporting family planning: Providing access to contraceptives and family planning services enables individuals to control their fertility.
- Encouraging economic development: Economic growth improves living standards, which often leads to lower CBRs.
- Adopting population policies: Some governments implement policies that directly address birth rates, such as incentives for smaller families or penalties for large families.
Tips and Tricks for Analyzing Crude Birth Rate
- Consider the context: CBR should be interpreted in the context of other demographic indicators, such as mortality rates and population age structure.
- Examine trends: Analyze CBR over time to identify patterns and changes.
- Compare with other regions: Comparing CBRs across different regions can provide insights into cultural and socioeconomic factors.
- Use reliable sources: Ensure that data on CBR is obtained from credible sources, such as the World Bank or national statistical agencies.
- Consider data limitations: Recognize that CBR estimates may be affected by variations in data collection methods and underreporting.
Pros and Cons of Crude Birth Rate
Pros:
- Provides a straightforward measure of fertility at a population level.
- Easy to calculate and interpret.
- Useful for comparisons across regions and over time.
Cons:
- Does not capture variations in fertility within a population.
- Can be influenced by fluctuations in the number of deaths.
- May not reflect the actual number of births due to underreporting or data quality issues.
Conclusion
The crude birth rate is a pivotal concept in AP Human Geography. It provides valuable insights into population dynamics and helps us understand the factors that shape fertility. By delving deeper into the factors influencing CBR and exploring effective management strategies, we can contribute to informed decision-making that promotes sustainable human development.