Mucous membranes are thin, moist linings that cover the surfaces of body cavities and passages that are exposed to the external environment. They protect the underlying tissues from damage, infection, and dehydration.

Structure of a Mucous Membrane
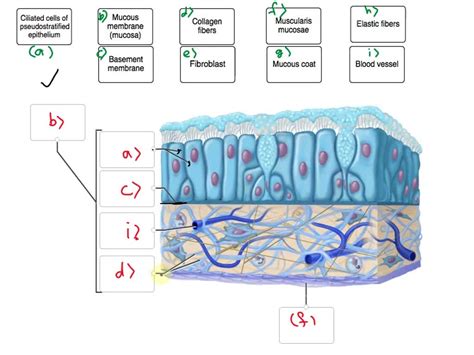
Mucous membranes consist of two main layers:
- Epithelium: The epithelium is the outermost layer of the mucous membrane. It is made up of closely packed cells that form a protective barrier against the external environment.
- Lamina propria: The lamina propria is the layer of connective tissue that lies beneath the epithelium. It contains blood vessels, nerves, and immune cells.
Epithelium
The epithelium of a mucous membrane can be classified as either stratified squamous, pseudostratified ciliated, or simple columnar.
- Stratified squamous epithelium is the most common type of epithelium in the body. It is made up of multiple layers of flattened cells.
- Pseudostratified ciliated epithelium is a type of epithelium that appears to be stratified but is actually made up of a single layer of cells. The cells are tall and narrow, and they have cilia on their apical surfaces.
- Simple columnar epithelium is a type of epithelium that is made up of a single layer of tall, column-shaped cells.
Lamina Propria
The lamina propria is the layer of connective tissue that lies beneath the epithelium. It contains blood vessels, nerves, and immune cells. The lamina propria provides support and nourishment to the epithelium.
Functions of a Mucous Membrane
Mucous membranes have a number of important functions, including:
- Protection: Mucous membranes protect the underlying tissues from damage, infection, and dehydration.
- Secretion: Mucous membranes secrete mucus, which is a thick, sticky fluid that traps foreign particles and helps to keep the surfaces of the body moist.
- Absorption: Mucous membranes absorb nutrients and other substances from the environment.
- Excretion: Mucous membranes excrete waste products from the body.
Clinical Significance of Mucous Membranes
Mucous membranes are involved in a number of diseases, including:
- Inflammation: Inflammation of a mucous membrane is called mucositis. Mucositis can be caused by a variety of factors, including infection, trauma, and radiation therapy.
- Infection: Mucous membranes are a common site of infection. Infections of the mucous membranes can be caused by bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
- Cancer: Mucous membranes can be the site of cancer. Cancers of the mucous membranes are called mucosal carcinomas.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
There are a number of common mistakes that people make when labeling the parts of a mucous membrane. These mistakes include:
- Mistaking the epithelium for the lamina propria: The epithelium is the outermost layer of the mucous membrane, while the lamina propria is the layer of connective tissue that lies beneath the epithelium.
- Mistaking pseudostratified ciliated epithelium for stratified squamous epithelium: Pseudostratified ciliated epithelium appears to be stratified but is actually made up of a single layer of cells, while stratified squamous epithelium is made up of multiple layers of cells.
- Mistaking simple columnar epithelium for pseudostratified ciliated epithelium: Simple columnar epithelium is made up of a single layer of tall, column-shaped cells, while pseudostratified ciliated epithelium is made up of a single layer of tall, narrow cells that have cilia on their apical surfaces.
FAQs
- What is the difference between a mucous membrane and a serous membrane?
A mucous membrane is a thin, moist lining that covers the surfaces of body cavities and passages that are exposed to the external environment, while a serous membrane is a thin, moist lining that covers the surfaces of internal organs and body cavities that are not exposed to the external environment.
- What is the function of mucus?
Mucus is a thick, sticky fluid that traps foreign particles and helps to keep the surfaces of the body moist.
- What are some of the diseases that can affect mucous membranes?
Mucous membranes can be affected by a number of diseases, including inflammation, infection, and cancer.
- How can I prevent diseases of the mucous membranes?
There are a number of things you can do to prevent diseases of the mucous membranes, including:
- Wash your hands frequently.
- Avoid touching your face.
- Get vaccinated against infections.
- Eat a healthy diet.
- Exercise regularly.
- Get enough sleep.