Introduction

AP Human Geography is a rigorous college-level course that delves into the complex interactions between humans and their environment. Understanding the core definitions in this subject is crucial for students aspiring to excel in the AP exam and develop a comprehensive understanding of global human geography. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of the key concepts that define the field, enabling readers to grasp their significance and apply them to real-world scenarios.
Definition of Core Concepts
1. Culture
Culture encompasses the shared beliefs, values, customs, and behaviors that shape the identity of a society. It manifests itself through language, art, religion, political systems, and economic practices. Understanding culture is essential for comprehending the diversity of human societies and their interactions with their surroundings.
2. Economic Development
Economic development refers to the process by which a society’s economic well-being improves over time. It involves factors such as GDP, industrialization, urbanization, and technological advancements. Economic development plays a pivotal role in shaping the living conditions, opportunities, and challenges faced by different societies.
3. Environmental Impacts of Human Activities
Human activities have a profound impact on the environment, both positive and negative. These impacts include air and water pollution, deforestation, climate change, and loss of biodiversity. Understanding the environmental consequences of human actions is critical for developing sustainable practices and mitigating environmental degradation.
4. Globalization
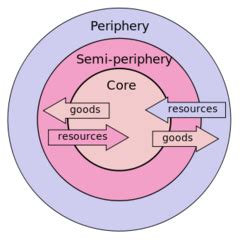
Globalization describes the increasing interconnectedness and interdependence of the world’s economies, cultures, and societies. It involves the flow of goods, services, capital, and ideas across national borders. Globalization has both advantages, such as increased trade, economic growth, and cultural exchange, and disadvantages, such as inequality, cultural erosion, and environmental degradation.
5. Population
Population refers to the total number of individuals residing in a particular area or society. Population growth, density, and distribution have a significant impact on the environment, resources, and social structures. Understanding population dynamics is crucial for planning and addressing societal challenges.
6. Political Organization
Political organization encompasses the structures and processes by which power is distributed and exercised within a society. It includes types of government, electoral systems, and political ideologies. Political organization plays a crucial role in shaping the policies and decisions that affect human lives and the environment.
7. Space and Place
Space refers to the abstract physical environment, while place refers to the specific location or area with its unique characteristics. Understanding the relationship between space and place is essential for analyzing human activities and the distribution of resources and populations.
8. Technology
Technology is the application of scientific knowledge to create tools, machines, and systems that solve problems or meet human needs. Technological advancements have a profound impact on the way humans interact with their environment, solve challenges, and transform societies.
How Core Definitions Matter
Understanding the core definitions in AP Human Geography is not just an academic exercise. These concepts have real-world significance and practical applications:
- Boosts Global Awareness: Understanding core definitions enhances students’ awareness of the diverse cultures, societies, and environmental challenges facing the world.
- Sharpens Critical Thinking: Analyzing core concepts develops students’ critical thinking skills by enabling them to evaluate evidence, identify biases, and draw informed conclusions.
- Empowers Responsible Citizenship: Grasping core definitions equips students with the knowledge and skills to engage in informed discussions and make responsible decisions about human-environment interactions.
- Career Readiness: Many careers in fields such as urban planning, international relations, and environmental science require a solid foundation in human geography core concepts.
Benefits of Understanding Core Definitions
Numerous benefits stem from understanding core definitions in AP Human Geography:
- Enhanced AP Exam Performance: A solid grasp of core definitions is essential for success on the AP Human Geography exam.
- Improved Understanding of Global Issues: Core definitions provide a framework for understanding complex global issues such as climate change, poverty, and inequality.
- Informed Decision-Making: Understanding core definitions empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their own actions and the impact they have on the world.
- Appreciation of Diversity: Core definitions foster an appreciation for the cultural diversity of human societies and their unique perspectives.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How can I memorize core definitions effectively?
- Use flashcards or create a concept map.
- Practice using core definitions in context.
- Review regularly and test your understanding.
2. What are some real-world examples of core definitions in action?
- Culture: The unique customs and tradiciones of different ethnic groups.
- Economic Development: Industrialization leading to increased GDP and improved living standards.
- Environmental Impacts: Deforestation resulting in loss of biodiversity and soil erosion.
3. How can I apply core definitions to my own life?
- Consider the cultural influences that shape your values and behaviors.
- Evaluate the impact of your consumption on the environment.
- Engage in civic activities that address global issues.
4. What are some challenges in understanding core definitions?
- Terms may have multiple meanings or nuanced interpretations.
- Concepts can be abstract and complex.
- Bias and stereotypes can influence our understanding.
5. How do core definitions relate to other social science disciplines?
- Core definitions provide a bridge between human geography and fields such as sociology, economics, and political science.
- Interdisciplinary perspectives enhance our understanding of complex social and environmental issues.
6. What are some emerging trends and applications of core definitions in human geography?
- The rise of GIS technology for mapping and spatial analysis.
- The use of big data to study human behavior and spatial patterns.
- The development of sustainable practices to mitigate environmental impacts.
Tables
| Table 1: Key Core Definitions in AP Human Geography |
|—|—|
| Concept | Definition |
| Culture | Shared beliefs, values, customs, and behaviors that shape society’s identity |
| Economic Development | Process of improving a society’s economic well-being |
| Environmental Impacts of Human Activities | Positive and negative effects of human actions on the environment |
| Globalization | Increasing interconnectedness and interdependence of the world’s economies, cultures, and societies |
| Table 2: Benefits of Understanding Core Definitions |
|—|—|
| Benefit | Explanation |
| Enhanced AP Exam Performance | Increased success on the AP Human Geography exam |
| Improved Understanding of Global Issues | Deeper comprehension of complex global challenges |
| Informed Decision-Making | Empowers individuals to make well-informed decisions |
| Appreciation of Diversity | Fosters respect for the cultural diversity of human societies |
| Table 3: Real-World Examples of Core Definitions |
|—|—|
| Concept | Example |
| Culture | Traditional festivals and rituals in different cultures |
| Economic Development | Technological advancements leading to increased productivity |
| Environmental Impacts of Human Activities | Air pollution from vehicle emissions |
| Globalization | International trade agreements and cultural exchanges |
| Table 4: Challenges in Understanding Core Definitions |
|—|—|
| Challenge | Explanation |
| Multiple Meanings | Terms may have varied interpretations |
| Abstract Concepts | Some concepts are complex and difficult to grasp |
| Bias and Stereotypes | Preconceived notions can influence understanding |