Introduction
Lewis structures are a powerful tool for understanding the electronic structure of molecules. They can be used to predict the shape of a molecule, its polarity, and its reactivity. In this article, we will discuss how to choose the Lewis structure that best represents CH3CO2H (acetic acid).

Step-by-Step Approach
- Count the total number of valence electrons. For CH3CO2H, there are 20 valence electrons.
- Determine the central atom. The central atom is the atom that is bonded to the most other atoms. In CH3CO2H, the central atom is carbon.
- Connect the atoms with single bonds. Start by connecting the central atom to each of the other atoms with a single bond. This will use up 12 of the valence electrons.
- Distribute the remaining valence electrons as lone pairs. The remaining 8 valence electrons can be distributed as lone pairs on the oxygen and hydrogen atoms.
- Check the octet rule. Each atom should have a full valence shell of 8 electrons. If an atom does not have a full valence shell, then the Lewis structure is not correct.
The Three Lewis Structures of CH3CO2H
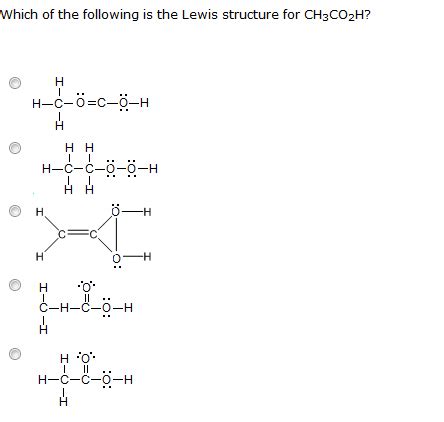
There are three possible Lewis structures for CH3CO2H:
- Structure A: In this structure, the carbon atom is bonded to the oxygen atom with a double bond and to the hydrogen atoms with single bonds. The oxygen atom has two lone pairs of electrons.
- Structure B: In this structure, the carbon atom is bonded to the oxygen atom with a single bond and to the hydrogen atoms with single bonds. The oxygen atom has three lone pairs of electrons.
- Structure C: In this structure, the carbon atom is bonded to the oxygen atom with a single bond and to the hydrogen atoms with single bonds. The oxygen atom has one lone pair of electrons and the carbon atom has one lone pair of electrons.
Which Lewis Structure is Best?
The best Lewis structure is the one that has the lowest formal charge. Formal charge is a measure of the charge that an atom would have if all of the electrons in its bonds were shared equally. The formal charge of an atom is calculated as follows:
Formal charge = valence electrons - non-bonding electrons - 1/2 bonding electrons
For the three Lewis structures of CH3CO2H, the formal charges are as follows:
- Structure A: C = 0, O = 0, H = 0
- Structure B: C = 0, O = -1, H = 0
- Structure C: C = 1, O = -2, H = 0
As you can see, Structure A has the lowest formal charge. Therefore, it is the best Lewis structure for CH3CO2H.
Applications of CH3CO2H
CH3CO2H is a versatile compound with a wide range of applications. It is used in the food industry as a food additive, in the pharmaceutical industry as a drug precursor, and in the chemical industry as a solvent.
Conclusion
Lewis structures are a powerful tool for understanding the electronic structure of molecules. In this article, we have discussed how to choose the Lewis structure that best represents CH3CO2H. We have also explored the applications of CH3CO2H.
Tables
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | CH3CO2H |
| Molecular weight | 60.05 g/mol |
| Density | 1.05 g/mL |
| Melting point | 16.6 °C |
| Boiling point | 118.1 °C |
| Application | Industry |
|---|---|
| Food additive | Food |
| Drug precursor | Pharmaceutical |
| Solvent | Chemical |
| Formal Charge | Atom | Structure A | Structure B | Structure C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | C | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | O | 0 | -1 | -2 |
| 0 | H | 0 | 0 | 0 |