Chemical kinetics delves into the intricacies of chemical reactions, exploring their rates, mechanisms, and the factors that govern them. This field of study holds immense significance in understanding a vast array of chemical processes, from the combustion of fuels to the intricate reactions occurring within biological systems.

Understanding Reaction Rates
The rate of a chemical reaction refers to the speed at which products are formed or reactants are consumed. Measuring reaction rates provides valuable insights into the efficiency and feasibility of chemical processes. The rate law, a mathematical expression, encompasses the dependence of the reaction rate on the concentrations of reactants and the influence of temperature and other external factors.
Activation Energy: The Energy Barrier to Reactions
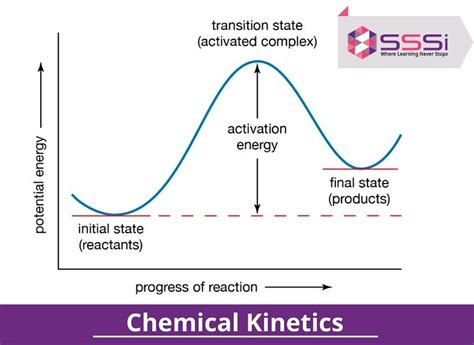
For a chemical reaction to occur, the reactants must overcome an energy barrier known as the activation energy. This energy represents the minimum amount of energy required for reactants to transform into products. The greater the activation energy, the slower the reaction rate. Catalysts, substances that participate in a reaction but are not consumed, can lower the activation energy and accelerate reaction rates.
The Arrhenius Equation: Quantifying Temperature Dependence
The Arrhenius equation establishes a quantitative relationship between the reaction rate constant, temperature, and activation energy. According to this equation, the reaction rate constant increases exponentially with increasing temperature and decreases exponentially with increasing activation energy. This equation serves as a cornerstone for understanding the impact of temperature on chemical reactions.
Applications of Chemical Kinetics: Transforming Industries
Chemical kinetics finds applications in diverse industries, including:
- Industrial Chemistry: Optimizing reaction conditions for efficient chemical production and minimizing waste.
- Environmental Science: Assessing the rates of pollutant degradation and developing strategies for environmental remediation.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Designing drug delivery systems and predicting drug efficacy and side effects.
- Energy Sector: Studying the kinetics of combustion reactions to improve energy efficiency and reduce emissions.
Future Prospects: Exploring New Frontiers
The field of chemical kinetics continues to evolve, with researchers exploring novel applications and technologies. Some promising areas of research include:
- Microfluidics: Miniaturizing chemical reactions to enhance reaction rates and control reaction conditions precisely.
- Quantum Chemistry: Applying quantum mechanical principles to understand the fundamental mechanisms of chemical reactions at the atomic and molecular levels.
- Machine Learning: Utilizing artificial intelligence to predict reaction rates, identify optimal reaction conditions, and develop new catalytic materials.
Conclusion
Chemical kinetics is a vital discipline that unravels the dynamics of chemical reactions. Understanding reaction rates, mechanisms, and influencing factors enables scientists and engineers to tailor chemical processes for optimal performance, minimize waste, and innovate groundbreaking technologies. As research continues to push the boundaries of this field, we can anticipate even more transformative applications that will shape the future of chemistry and its impact on society.