At the very core of all living organisms, from the tiniest bacteria to the majestic blue whale, lies a fundamental building block: the cell. This remarkable entity serves as the basic sub-unit of life, carrying out essential functions that sustain both individual organisms and the intricate ecosystems they inhabit.

Understanding Cells
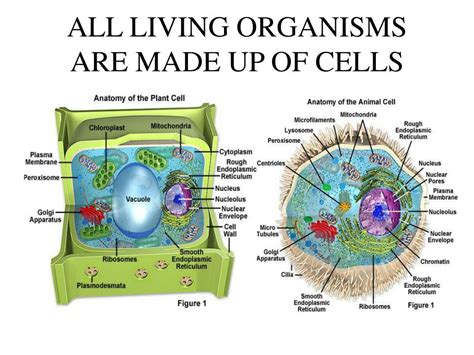
Cells are the smallest units capable of carrying out all the functions of life independently. They are typically microscopic, ranging in size from a mere 1 micrometer (μm) in some bacteria to a whopping 100 μm in certain plant cells. Despite their diminutive size, cells are incredibly complex structures, containing a vast array of specialized components that work together harmoniously.
Cell Structure and Functions
The structure and function of cells vary widely depending on the organism and its specific role. However, all cells share certain fundamental components:
- Cell Membrane: A thin, semipermeable barrier that encloses the cell and regulates the movement of substances in and out.
- Cytoplasm: The gel-like interior of the cell, containing organelles, molecules, and other cellular components.
- Nucleus: The control center of the cell, containing genetic material (DNA) and directing cell activities.
Cells perform a wide range of essential functions, including:
- Metabolism: Converting nutrients into energy and building new cellular components.
- Transport: Moving substances within and between cells.
- Communication: Sending and receiving signals to coordinate cellular activities.
- Reproduction: Creating new cells through cell division.
Types of Cells
There are two main types of cells:
- Prokaryotic Cells: These are simpler cells that lack a true nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Found in bacteria and blue-green algae, prokaryotic cells are typically smaller and less complex than eukaryotic cells.
- Eukaryotic Cells: These more complex cells have a true nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Found in all plants, animals, fungi, and protists, eukaryotic cells are larger and more structurally diverse than prokaryotic cells.
The Importance of Cells
Cells play a fundamental role in all aspects of life:
- Building Blocks of Life: Cells are the basic unit of all living organisms, providing the structural and functional foundation for life.
- Body Tissues and Organs: Cells combine to form tissues, which in turn form organs, such as muscles, bones, and organs.
- Cellular Processes: Cells carry out essential cellular processes, such as metabolism, transport, communication, and reproduction.
- Disease and Treatment: Understanding cells is crucial for diagnosing and treating diseases, as well as developing new therapies.
- Biotechnology: Cell-based technologies are revolutionizing medicine, agriculture, and other industries.
Special Applications of Cells
The study of cells has led to numerous innovative applications, including:
- Stem Cell Therapy: Stem cells have the potential to develop into any type of cell, making them promising candidates for treating diseases such as heart disease and Parkinson’s disease.
- Tissue Engineering: Scientists are using cells to create new tissues and organs for transplantation, providing hope for patients with organ failure.
- Gene Editing: CRISPR-Cas9 and other gene editing technologies allow scientists to modify cells and treat genetic diseases.
- Biofuels: Researchers are using cells to produce biofuels from renewable sources, offering a potential solution to the challenges of climate change.
Conclusion
Cells are the fundamental building blocks of life, carrying out essential functions that sustain all living organisms. From the smallest bacteria to the largest mammals, cells are the microscopic engines that drive the incredible diversity and complexity of the natural world. Understanding cells is not only a matter of scientific fascination; it is also critical for advancing medicine, biotechnology, and other fields that directly impact our health and well-being. By unraveling the secrets of cells, we open the door to new possibilities and a brighter future for humanity.