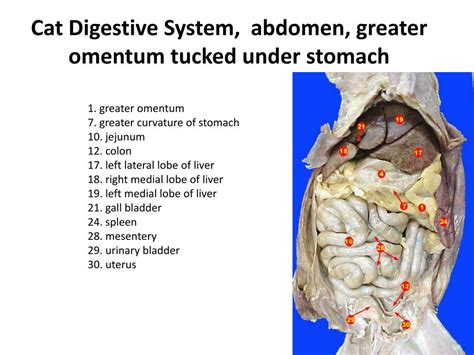
Nestled within the digestive tract of cats, the cecum is an intriguing organ that plays a vital role in their overall well-being. This blind pouch serves as a crucial site for microbial fermentation and immune function, providing insights into the fascinating world of feline physiology.

Anatomy and Function of the Cecum
The cecum is located at the junction of the small and large intestines in cats. It assumes the form of a small, sac-like structure with a distinct blind end. The cecum’s primary function is to facilitate fermentation, a process where bacteria break down complex carbohydrates, such as plant fibers, into simpler molecules that can be utilized by the feline body. Additionally, the cecum also plays a significant role in water absorption and immune surveillance.
Cecal Fermentation: A Vital Process
Fermentation within the cecum is essential for cats, as they lack the necessary enzymes to digest plant material effectively. Bacteria residing in the cecum break down fibers, releasing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), such as butyrate, propionate, and acetate. These SCFAs serve as a primary source of energy for the colonocytes, the cells lining the colon. Furthermore, SCFAs contribute to the maintenance of intestinal pH, stimulating water absorption and inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria.
Immune Function of the Cecum
The cecum also plays a critical role in the immune system of cats. It houses specialized immune cells, including Peyer’s patches, which are responsible for sampling and monitoring the luminal contents for potential pathogens. The cecum acts as a protective barrier, preventing harmful microorganisms from entering the bloodstream and causing systemic infections.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Understanding the crucial nature of the cecum in cats helps avoid common mistakes that could compromise their well-being. Some key pitfalls to avoid include:
- Ignoring Dietary Fiber: Cats require a balanced diet that includes adequate fiber to promote healthy cecal fermentation. Avoid feeding your feline companion diets that are devoid of fiber, as it can lead to digestive issues and a compromised immune system.
- Overfeeding: Overfeeding cats can result in excessive fermentation within the cecum, potentially leading to gas buildup, abdominal discomfort, and diarrhea.
- Abrupt Dietary Changes: Sudden alterations in a cat’s diet can disrupt the delicate microbial balance within the cecum, causing digestive upsets. Gradually introduce new foods over time to allow the microbiota to adapt and maintain homeostasis.
Step-by-Step Approach to Healthy Cecum
Maintaining a healthy cecum in cats requires a holistic approach that encompasses several key steps:
- Provide a Fiber-Rich Diet: Offer your feline friend a balanced diet that incorporates adequate dietary fiber. Commercial cat foods specifically designed for their digestive needs are readily available.
- Avoid Overfeeding: Ensure you feed your cat according to the recommended daily amounts provided on the pet food packaging.
- Introduce Dietary Changes Gradually: When making changes to your cat’s diet, do so gradually over a period of several days to minimize any potential digestive disturbances.
- Consult a Veterinarian: If your cat experiences persistent digestive issues, such as diarrhea, gas, or constipation, consult your veterinarian promptly for a thorough evaluation and appropriate treatment.
Why Cat Cecum Matters
The cecum is not merely an anatomical curiosity but rather a vital organ contributing to the overall health and well-being of cats. Its role in fermentation, immune function, and water absorption makes it an essential component of their digestive and immune systems. Preserving the health of the cecum is paramount to ensuring a long and healthy life for our feline companions.
Benefits of a Healthy Cecum
Cats with healthy ceca experience numerous benefits, including:
- Regular Digestion: Proper cecal function facilitates the smooth passage of food through the digestive tract, preventing issues such as constipation or diarrhea.
- Strong Immune System: A healthy cecum bolsters the immune system, protecting cats from harmful bacteria and pathogens that can cause infections.
- Optimal Energy Levels: The SCFAs produced during fermentation provide a significant energy source for the colonocytes, promoting overall energy levels in cats.
- Improved Water Absorption: The cecum plays a crucial role in water absorption, ensuring proper hydration and preventing dehydration, especially in environments with limited water availability.
Future Innovations: Microbiota Manipulation
The tantalizing possibility of manipulating the microbiota within the cat cecum opens up novel avenues for feline health advancements. Research is actively exploring the potential of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics to modulate the cecal microbiota, with promising implications for optimizing digestion, bolstering the immune system, and preventing or treating various health conditions.
Conclusion
The cat cecum is an enigmatic yet vital organ that orchestrates fermentation, immune function, and water absorption within the feline digestive tract. Understanding its significance and adhering to recommended practices ensure the well-being of these enigmatic creatures, allowing them to thrive and enrich our lives with their companionship and unwavering affection.
Table 1: Composition of the Cecal Microbiota in Cats
| Bacterial Group | Percentage of Total Microbiota |
|---|---|
| Firmicutes | 90-95% |
| Bacteroidetes | 3-8% |
| Proteobacteria | 1-3% |
| Actinobacteria | 1-2% |
| Fusobacteria | 0.5-1.5% |
Table 2: Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs) Produced by Cecal Fermentation
| SCFA | Function |
|---|---|
| Butyrate | Energy source for colonocytes, maintains intestinal pH, anti-inflammatory |
| Propionate | Energy source, regulates blood glucose levels |
| Acetate | Energy source, anti-inflammatory |
Table 3: Benefits of a Healthy Cecum in Cats
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Regular Digestion | Facilitates smooth passage of food through the digestive tract, preventing constipation or diarrhea |
| Strong Immune System | Bolsters the immune system, protecting cats from harmful bacteria and pathogens |
| Optimal Energy Levels | SCFAs produced during fermentation provide a significant energy source for colonocytes |
| Improved Water Absorption | Ensures proper hydration and prevents dehydration |
Table 4: Common Mistakes to Avoid for Cecal Health in Cats
| Mistake | Consequence |
|---|---|
| Ignoring Dietary Fiber | Digestive issues, compromised immune system |
| Overfeeding | Excessive fermentation, gas buildup, abdominal discomfort, diarrhea |
| Abrupt Dietary Changes | Disrupted microbial balance, digestive upsets |