Introduction

The caste system is a form of social stratification unique to India, where people are divided into different categories based on their birth. Its origins trace back thousands of years, shaping Indian society and influencing its cultural, economic, and religious fabric. This article provides a comprehensive guide to the caste system, its history, key concepts, and its relevance in the context of AP World History.
Defining the Caste System
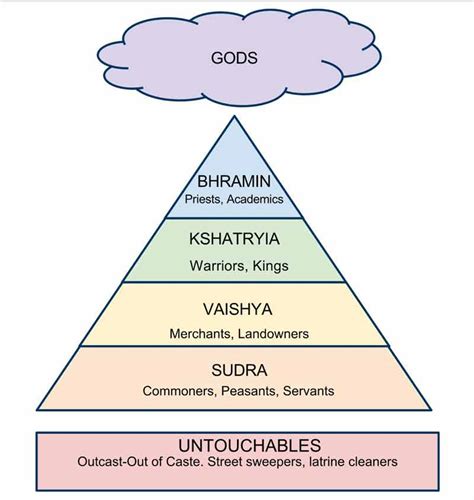
The caste system is a rigid hierarchical structure that divides society into distinct groups known as “castes.” Each caste is assigned a specific occupation, societal status, and set of rules governing daily life. Traditionally, there were four main castes: Brahmins (priests), Kshatriyas (warriors), Vaishyas (merchants), and Shudras (laborers). Outside these castes were the Dalits (formerly known as “untouchables”), who performed tasks considered impure and were marginalized from society.
Origins and Evolution
The origins of the caste system are contested, but it is believed to have emerged during the Vedic period (c. 1500-500 BCE). It is linked to the religious concept of “karma” and “dharma,” which prescribe one’s destiny based on past actions and one’s duty within society. Over time, the caste system became more complex, with hundreds of sub-castes emerging within the four main categories.
Key Principles
- Hierarchy: The caste system is organized into a vertical hierarchy, with Brahmins at the top and Dalits at the bottom.
- Endogamy: Members of different castes are expected to marry within their own caste.
- Occupational Specialization: Traditionally, each caste was assigned specific occupations, with little mobility across castes.
- Social Restrictions: Castes interact with one another according to prescribed rules, with varying degrees of separation and commensality.
- Purity and Pollution: The caste system assigns notions of purity and pollution to different castes, which influence social interactions and access to resources.
Social and Economic Impact
The caste system has had a profound impact on Indian society.
- Social Inequality: The caste system perpetuates social inequality, with higher castes enjoying privileges and lower castes facing discrimination and exclusion.
- Economic Disparities: Caste often determines economic opportunities, with higher castes dominating certain professions and lower castes relegated to menial jobs.
- Educational Barriers: Lower castes have historically faced barriers to education, limiting their social and economic mobility.
Challenges and Reforms
The caste system has faced challenges over the centuries.
- Religious Reform Movements: Movements like Buddhism and Sikhism rejected the caste system, emphasizing equality and merit.
- Colonial Era: British colonial rule introduced some reforms, such as banning untouchability and improving educational opportunities.
- Post-Independence India: The Indian constitution prohibits caste discrimination and promotes equal rights. However, caste continues to influence Indian society in various forms.
Caste System in AP World History
The caste system is a central topic in AP World History. Its study provides insights into:
- Social Stratification: The caste system offers a unique example of social hierarchy and its impact on society.
- Religion and Society: The caste system is closely tied to Hinduism and shaped by religious beliefs and practices.
- Change and Continuity: Despite efforts at reform, the caste system continues to play a role in contemporary Indian society, demonstrating the persistence of social structures over time.
Conclusion
The caste system is a complex and enduring feature of Indian society. Understanding its history, principles, and impact is essential for comprehending the social and cultural dynamics of India and its significance in AP World History. While the caste system has posed challenges to social equality and progress, it also represents a unique aspect of Indian civilization and continues to shape the lives of millions of people today.