Introduction
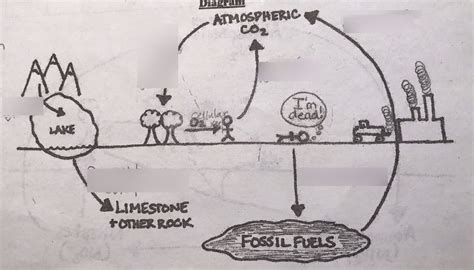
The carbon cycle, a complex planetary process, describes the continuous exchange of carbon between the atmosphere, oceans, biosphere, and geosphere. Humans, as part of the biosphere, play a pivotal role in this cycle. Our activities significantly influence the amount of carbon in the atmosphere and its distribution throughout the Earth’s systems. Understanding the carbon cycle apes is crucial for mitigating climate change and ensuring the planet’s long-term sustainability.

Human Impact on the Carbon Cycle
Human activities have substantially altered the carbon cycle since the onset of industrialization. The burning of fossil fuels (e.g., coal, oil, and natural gas) for energy and transportation has led to the release of vast quantities of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Additionally, deforestation, urban expansion, and agriculture contribute to increased carbon emissions.
Key Figures:
- Human activities have released an estimated 2,950 gigatons of carbon into the atmosphere since 1850. (IPCC, 2021)
- The burning of fossil fuels accounts for approximately 78% of global carbon emissions. (IEA, 2021)
- Deforestation contributes to 11% of global carbon emissions. (World Bank, 2020)
Absorption and Sequestration of Carbon
Humans also play a role in absorbing and sequestering carbon from the atmosphere. Forests, oceans, and soil act as carbon sinks, absorbing and storing carbon dioxide.
Key Figures:
- Forests absorb approximately 25% of the carbon emissions produced by human activities. (FAO, 2020)
- Oceans absorb an additional 20-25% of carbon emissions. (IPCC, 2021)
The Importance of Carbon Cycle Apes
Human understanding of carbon cycle apes is critical for several reasons:
- Climate Change Mitigation: By reducing carbon emissions and enhancing carbon absorption, we can mitigate climate change and minimize its impacts.
- Sustainable Development: The carbon cycle apes play a crucial role in ecosystem health, food security, and energy production. Understanding this cycle enables us to make informed decisions that promote sustainable development.
- Scientific Innovation: The study of carbon cycle apes drives scientific innovation in areas such as carbon capture and storage technologies, improved forestry practices, and the development of renewable energy sources.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Common mistakes to avoid when considering the carbon cycle apes include:
- Oversimplifying the Cycle: The carbon cycle is a complex process involving numerous interactions between different Earth systems. Oversimplifying it can lead to inaccurate conclusions and ineffective mitigation strategies.
- Ignoring the Role of Non-Human Factors: Although humans play a significant role in the carbon cycle, it is important to acknowledge the influence of natural factors such as volcanic eruptions and ocean currents.
- Focusing Solely on Carbon Dioxide: While carbon dioxide is a major greenhouse gas, other greenhouse gases such as methane and nitrous oxide also contribute to climate change.
FAQs
-
What is the most effective way to reduce human-induced carbon emissions? Renewable energy sources, improved energy efficiency, and sustainable forest management are crucial for reducing carbon emissions.
-
How can individuals contribute to the carbon cycle apes? Reducing energy consumption, planting trees, and supporting sustainable practices in local communities are effective ways to make a positive impact.
-
What are the consequences of ignoring the carbon cycle apes? Ignoring the carbon cycle apes can lead to accelerated climate change, biodiversity loss, and disruptions in the global food system.
-
How can we ensure that the carbon cycle apes are considered in policy decisions? Raising awareness about the carbon cycle apes, advocating for science-based policies, and promoting collaboration between scientists and policymakers are essential for incorporating climate change considerations into decision-making processes.
-
What is the potential for carbon capture and storage to mitigate climate change? Carbon capture and storage technologies have the potential to significantly reduce carbon emissions from industrial processes and power plants. However, their widespread implementation requires continued research, development, and policy support.
-
How can we adapt to the impacts of climate change caused by human-induced carbon emissions? Adaptation strategies include enhancing infrastructure resilience, improving agricultural practices, and developing early warning systems for extreme weather events.
Conclusion
The carbon cycle apes is a complex and dynamic process that plays a vital role in Earth’s climate system. Human activities have significantly altered this cycle, leading to increased carbon emissions and accelerated climate change. By understanding our role in the carbon cycle apes and taking proactive steps to reduce emissions and enhance carbon absorption, we can mitigate the impacts of climate change and ensure the planet’s long-term sustainability.