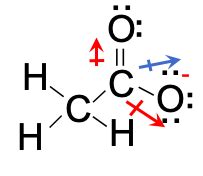
The C2H3O2 Lewis structure, also known as the acetic acid Lewis structure, is a representation of the arrangement of atoms and electrons in the molecule. It provides valuable insights into the bonding and properties of acetic acid.

Step-by-Step Approach to Draw the C2H3O2 Lewis Structure:
- Determine the Total Number of Valence Electrons: Carbon has 4 valence electrons, hydrogen has 1, and oxygen has 6. Therefore, the total number of valence electrons in C2H3O2 is 4 + (3 × 1) + (2 × 6) = 20.
- Connect the Atoms: Start by connecting the carbon atom to the two hydrogen atoms with single bonds. Then, connect the carbon atom to the oxygen atom with a double bond.
- Distribute the Remaining Electrons: Place the remaining 16 valence electrons around the atoms to satisfy the octet rule. Six electrons go to the two oxygen atoms, eight electrons go to the carbon atom, and the remaining two electrons go to the two hydrogen atoms.
- Check for Resonance: The double bond between the carbon and oxygen atoms can resonate with the single bond between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms. This means that the electrons in the double bond can delocalize and spread out over the three atoms, resulting in two equivalent resonance structures.
Resonance Structures of C2H3O2 Lewis Structure:
O O
|| ||
C==C C-C
|| ||
H H
Hybridization of C2H3O2:
The carbon atom in C2H3O2 is sp2 hybridized, meaning it has one s orbital and two p orbitals that overlap to form three equivalent sp2 hybrid orbitals. These orbitals form sigma bonds with the two hydrogen atoms and the oxygen atom. The oxygen atom is also sp2 hybridized and forms two sigma bonds with the carbon atom and one lone pair of electrons.
Bond Lengths and Bond Angles:
The C-H bond lengths are approximately 1.09 Å, and the C-O bond lengths are approximately 1.23 Å. The O-C-O bond angle is approximately 120°, consistent with the sp2 hybridization of the carbon atom.
Polarity and Dipole Moment:
The C2H3O2 molecule is polar due to the electronegativity difference between the carbon and oxygen atoms. The oxygen atoms have a higher electronegativity than the carbon atom, drawing electrons towards them and creating a partial negative charge on the oxygen atoms and a partial positive charge on the carbon atom. The dipole moment of C2H3O2 is approximately 1.84 D.
Applications of C2H3O2:
- Vinegar: C2H3O2 is the main component of vinegar, which is used as a food preservative, cleaning agent, and condiment.
- Acetic Anhydride: C2H3O2 is used to produce acetic anhydride, which is an important chemical intermediate in the production of other chemicals, such as aspirin and cellulose acetate.
- Pharmaceuticals: C2H3O2 is used in the production of a variety of pharmaceuticals, including aspirin, ibuprofen, and paracetamol.
- Cosmetics: C2H3O2 is used as an ingredient in some cosmetics, such as toners and astringents.
- Industrial Solvent: C2H3O2 is used as an industrial solvent for a variety of applications, such as the manufacture of paints, coatings, and adhesives.
Useful Tables:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 60.05 g/mol |
| Density | 1.049 g/cm³ |
| Boiling Point | 118.1 °C |
| Melting Point | 16.6 °C |
| Solubility in Water | Soluble |
| pKa | 4.76 |
Comparison of Pros and Cons of C2H3O2:
Pros:
- Versatile and widely used chemical
- Relatively inexpensive
- Non-toxic and biodegradable
- Environmentally friendly
Cons:
- Corrosive to metals
- Can cause skin irritation
- Flammable liquid
- Can react explosively with strong oxidizing agents
FAQs:
1. What is the hybridization of the carbon atom in C2H3O2?
A: sp2 hybridization
2. What is the dipole moment of C2H3O2?
A: Approximately 1.84 D
3. Is C2H3O2 toxic?
A: C2H3O2 is non-toxic in small amounts but can cause skin irritation and respiratory problems in high concentrations.
4. What is the main application of C2H3O2?
A: C2H3O2 is the main component of vinegar, which is used as a food preservative, cleaning agent, and condiment.
5. Is C2H3O2 flammable?
A: Yes, C2H3O2 is a flammable liquid.
6. Can C2H3O2 react explosively?
A: Yes, C2H3O2 can react explosively with strong oxidizing agents.
Innovation: “Aceto-Reactive” Materials
The unique chemical properties of C2H3O2 have inspired the development of a new class of materials known as “aceto-reactive” materials. These materials can undergo reversible chemical reactions with C2H3O2, enabling them to change their properties on demand. For example, aceto-reactive polymers can switch between stiff and flexible states when exposed to C2H3O2 vapor, creating new possibilities for adaptive materials and wearable devices.