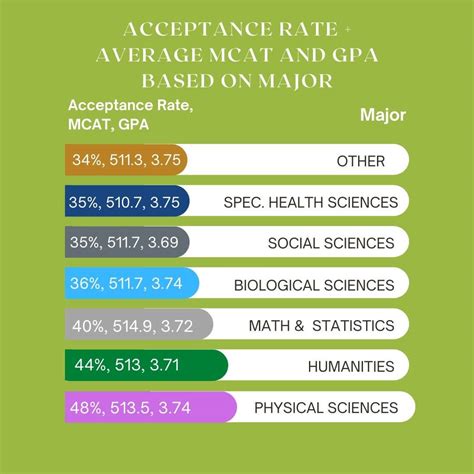
Aspiring medical students face a crucial decision when selecting their undergraduate major. While there is no single “best” premed major, certain disciplines provide a solid foundation for the rigors of medical school and future medical practice. This comprehensive guide explores the most suitable premed majors, their advantages, potential career paths, and common mistakes to avoid.

#1. Biology
- Advantages: Biology majors acquire a profound understanding of living organisms, their structure, function, and interactions. This knowledge forms an indispensable foundation for understanding human physiology, disease processes, and medical interventions.
- Potential Career Paths: Medical Doctor (MD), Physician Assistant (PA), Research Scientist, Biomedical Engineer
#2. Chemistry
- Advantages: Chemistry majors develop expertise in the composition, structure, and properties of matter. This knowledge is essential for understanding the biochemical processes that govern human health and disease.
- Potential Career Paths: MD, PA, Pharmacist, Medical Researcher
#3. Biochemistry
- Advantages: Biochemistry combines elements of biology and chemistry to study the chemical processes that occur within living organisms. This knowledge is highly relevant to understanding metabolism, drug mechanisms, and various disease states.
- Potential Career Paths: MD, PA, Research Scientist, Pharmaceutical Scientist
#4. Physics
- Advantages: Physics majors gain a deep understanding of the fundamental laws of nature and how they govern physical phenomena. This knowledge can be applied to medical imaging techniques, radiation therapy, and the development of medical devices.
- Potential Career Paths: MD, Radiation Therapist, Medical Physicist, Biomedical Engineer
#5. Biomedical Engineering
- Advantages: Biomedical engineering combines engineering principles with medical knowledge to design and develop innovative medical technologies, devices, and treatments.
- Potential Career Paths: Biomedical Engineer, Clinical Engineer, Medical Device Sales Representative, Researcher
#6. Neuroscience
- Advantages: Neuroscience majors explore the structure, function, and development of the nervous system. This knowledge is essential for understanding neurological disorders, mental health conditions, and the brain-body connection.
- Potential Career Paths: MD, Neurologist, Psychiatrist, Research Scientist
#7. Psychology
- Advantages: Psychology majors gain insights into human behavior, cognition, and mental processes. This knowledge can be beneficial for understanding patient interactions, managing stress, and providing effective medical care.
- Potential Career Paths: MD, Psychiatrist, Clinical Psychologist, Health Psychologist
#8. Mathematics
- Advantages: Mathematics majors develop strong analytical, problem-solving, and critical thinking skills. These skills are transferable to medical research, data analysis, and clinical reasoning.
- Potential Career Paths: MD, Biostatistician, Medical Researcher, Operations Research Analyst
#9. Computer Science
- Advantages: Computer science majors acquire expertise in programming, data analysis, and software development. These skills can be applied to medical informatics, electronic health records management, and the development of medical software.
- Potential Career Paths: MD, Clinical Informaticist, Medical Software Engineer, Health Data Analyst
#10. Kinesiology
- Advantages: Kinesiology majors study human movement, exercise physiology, and biomechanics. This knowledge can be applied to injury prevention, rehabilitation, and promoting physical health and well-being.
- Potential Career Paths: MD, Physical Therapist, Athletic Trainer, Exercise Physiologist
Comparative Table of Premed Majors
| Major | Focus | Skills Developed | Potential Career Paths |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biology | Living organisms | Research, lab techniques, critical thinking | MD, PA, Research Scientist |
| Chemistry | Matter | Problem-solving, analytical chemistry, lab techniques | MD, PA, Pharmacist |
| Biochemistry | Chemical processes in living organisms | Metabolism, drug mechanisms, research | MD, PA, Research Scientist |
| Physics | Fundamental laws of nature | Analytical reasoning, problem-solving, data analysis | MD, Radiation Therapist, Medical Physicist |
| Biomedical Engineering | Medical technologies | Design, innovation, engineering principles | Biomedical Engineer, Clinical Engineer |
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Not considering your interests: Choose a major that aligns with your passions and career goals.
- Ignoring the prerequisites: Ensure you meet all required prerequisites for medical school, including coursework in science, math, and English.
- Focusing solely on GPA: While a high GPA is important, it is not the sole determinant of medical school admission. Gain experience through research, clinical volunteering, and extracurricular activities.
- Neglecting research: Get involved in research projects to gain hands-on experience, develop analytical skills, and explore potential career paths.
- Not seeking mentorship: Connect with professors, pre-health advisors, and medical professionals for guidance and support.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the most popular premed major?
A: Biology is the most commonly selected premed major.
Q: Is it possible to get into medical school with a non-science major?
A: Yes, but it is important to complete all required science prerequisites and demonstrate a strong academic record.
Q: What is the average GPA of students accepted into medical school?
A: The median GPA for students accepted into medical school for the 2023-2024 application cycle was 3.82.
Q: Is it necessary to take the MCAT?
A: Yes, the MCAT is a standardized exam required for admission to all U.S. medical schools.
Q: How long does it take to become a doctor?
A: The traditional path to becoming a doctor includes four years of undergraduate study, four years of medical school, and three to seven years of residency training.
Q: How can I make my premed application stand out?
A: Engage in research, volunteer in clinical settings, shadow physicians, and demonstrate a passion for medicine.