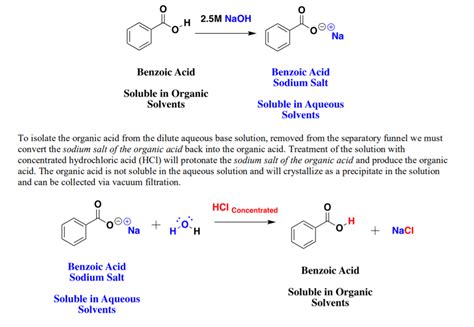
Benzoic acid and sodium hydroxide (NaOH), two versatile and widely-used chemicals, play pivotal roles in a myriad of industrial applications. From preserving food and beverages to manufacturing plastics and pharmaceuticals, their combined properties offer an effective and economical solution to numerous challenges.

Benzoic Acid: A Natural Antibacterial and Preservative
Benzoic acid, a naturally occurring compound found in various fruits and berries, is widely used as a preservative in food and beverage products. Its antibacterial and antifungal properties inhibit the growth of harmful microorganisms, extending the shelf life and maintaining the quality of perishable goods.
Key Points:
- Benzoic acid is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
- It is particularly effective against bacteria and yeast, making it an ideal preservative for acidic foods and beverages.
- Benzoic acid is typically used in concentrations ranging from 0.05% to 0.1% by weight.
NaOH: A Versatile Base with Wide-Ranging Applications
NaOH, also known as caustic soda or lye, is a strong base with numerous industrial applications. Its ability to neutralize acids and dissolve organic matter makes it essential in processes such as:
Key Points:
- NaOH is highly corrosive and requires careful handling.
- It is primarily produced by the electrolysis of brine (sodium chloride solution).
- NaOH is widely used in the manufacture of paper, soap, textiles, and detergents.
Benzoic Acid and NaOH: A Synergistic Combination
When combined, benzoic acid and NaOH form a powerful duo with enhanced properties.
Soap and Detergent Production:
In the manufacturing of soap and detergents, NaOH is used to saponify fats and oils, converting them into fatty acids and glycerol. Benzoic acid acts as a preservative, preventing the growth of bacteria that can spoil the finished product.
Paints and Coatings:
Benzoic acid is used as an additive in paints and coatings to improve adhesion, prevent corrosion, and stabilize the pigments. NaOH helps to neutralize acidic contaminants and improve the dispersion of pigments in the paint.
Pharmaceuticals:
In the pharmaceutical industry, NaOH is used to neutralize acids and adjust the pH of medications. Benzoic acid is employed as a preservative in various pharmaceutical formulations, ensuring their stability and efficacy over time.
Pain Points, Motivations, and Benefits
Pain Points:
- Spoilage and contamination of food and beverages
- Corrosion and degradation of materials
- Inefficient and costly manufacturing processes
Motivations:
- Extend the shelf life of perishable goods
- Improve the quality and durability of materials
- Optimize manufacturing processes and reduce costs
Benefits:
- Effective preservation against bacteria and fungi
- Enhanced adhesion, corrosion resistance, and stability
- Streamlined and cost-effective manufacturing
New Applications and Future Prospects
The combination of benzoic acid and NaOH continues to inspire new applications and solutions. The development of “biocomposites,” materials that combine natural fibers with synthetic polymers, has opened up potential applications in automotive, construction, and aerospace industries. Researchers are also exploring the use of benzoic acid and NaOH in the production of biofuels and green chemicals.
Conclusion
Benzoic acid and NaOH are indispensable chemicals that offer a wide range of benefits in industries ranging from food production to pharmaceuticals. Their synergistic properties provide effective solutions to pain points, improve product quality and longevity, and optimize manufacturing processes. As research continues, new applications for this versatile duo are emerging, driving innovation and shaping the future of various sectors.