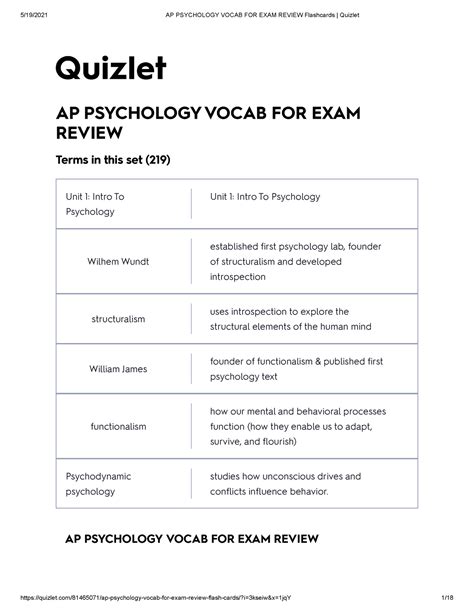
AP Psychology Quizlet: Ace Your Exam with Confidence
Are you preparing for the AP Psychology exam and looking for a reliable and comprehensive study resource? Quizlet, an online learning platform, offers an extensive collection of AP Psychology materials to cater to your needs. This article delves into how you can leverage Quizlet to enhance your exam preparation and maximize your chances of success.

-
Personalized Study Plans: Quizlet allows you to create customized study plans that cater to your individual learning style and pace. You can set study goals, track your progress, and receive tailored recommendations based on your performance.
-
Variety of Study Formats: Quizlet offers multiple study formats, including flashcards, practice tests, games, and written summaries. This variety helps keep your studies engaging and improves your retention of key concepts.
-
Extensive Content Library: The Quizlet community has created a vast collection of AP Psychology materials, including study sets, practice questions, and notes. You can access these resources for free, providing you with a wide range of learning materials to choose from.
-
Create Your Own Study Sets: Engage actively with the material by creating your study sets. This process forces you to synthesize information and strengthens your understanding of the concepts.
-
Use Spaced Repetition: Quizlet employs spaced repetition, a scientifically proven technique that helps improve long-term memory. By reviewing the material at increasing intervals, you reinforce your learning and prevent forgetting.
-
Collaborate with Classmates: Join study groups within Quizlet to collaborate with classmates. By sharing study sets, discussing key concepts, and quizzing each other, you can enhance your understanding and prepare more effectively.
-
Step 1: Create an Account: Visit the Quizlet website or download the mobile app and create an account to access the platform’s resources.
-
Step 2: Find Study Sets: Use the search bar to find study sets created by other users or create your own by importing content from textbooks, notes, or other sources.
-
Step 3: Customize Your Study Plan: Set study goals, choose study formats, and tailor your learning experience to suit your needs.
-
Step 4: Practice Regularly: Dedicate time to practice consistently, utilizing spaced repetition to enhance your retention.
-
Step 5: Review and Assess: Monitor your progress and identify areas where you need further study. Adjust your study plan accordingly to maximize your preparation.
-
Passive Studying: Avoid simply reading through the material on Quizlet. Engage actively by answering questions, writing summaries, and creating flashcards to enhance your comprehension.
-
Over-reliance on Quizlet: While Quizlet is a valuable tool, it should not be your sole source of study material. Supplement your preparation with textbooks, class notes, and other resources.
-
Ignoring Spaced Repetition: Resist the temptation to cram all the material at once. Spaced repetition is crucial for long-term retention.
Familiarize yourself with these essential concepts, as they are heavily tested on the AP Psychology exam:
-
Research Methods: Understand experimental and non-experimental methods, research designs, and validity.
-
Biological Bases of Behavior: Study the brain, nervous system, and their role in psychological processes.
-
Sensation and Perception: Explore the different senses, perception processes, and sensory illusions.
-
States of Consciousness: Define sleep, dreaming, hypnosis, and altered states of consciousness.
-
Learning and Memory: Understand classical conditioning, operant conditioning, cognitive theories of learning, and memory processes.
-
Motivation and Emotion: Explain the different theories of motivation, the nature of emotions, and emotional regulation.
-
Development: Trace the stages of human development from infancy to adulthood, focusing on cognitive, social, and personality development.
-
Personality: Study different theories of personality, personality assessment, and the concept of self.
-
Social Psychology: Examine social influence, conformity, aggression, and interpersonal relationships.
-
Clinical Psychology: Understand mental disorders, their causes and treatments, and the role of psychological assessment.
-
Neuroplasticity: Ongoing research explores the brain’s ability to change and adapt throughout life, challenging traditional views of brain development.
-
Positive Psychology: This emerging field focuses on strengths, well-being, and flourishing, rather than solely on mental illness.
-
Technology and Psychology: Technological advancements, such as virtual reality and artificial intelligence, are revolutionizing psychological research and interventions.
Table 1: Cognitive Disorders Tested on the AP Psychology Exam
| Disorder | Symptoms | Causes | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alzheimer’s Disease | Memory loss, confusion, impaired judgment | Genetics, age | Medication, behavioral therapy |
| Parkinson’s Disease | Tremors, rigidity, slow movement | Brain damage | Medication, physical therapy |
| Schizophrenia | Hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thinking | Genetics, environmental factors | Antipsychotic medication, psychotherapy |
| Autism Spectrum Disorder | Social difficulties, repetitive behaviors, communication challenges | Genetics, environmental factors | Behavioral therapy, special education |
Table 2: Key Terms for States of Consciousness
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| REM Sleep | Rapid eye movement sleep associated with dreaming |
| NREM Sleep | Non-rapid eye movement sleep characterized by deep sleep |
| Hypnosis | A state of focused attention and increased suggestibility |
| Meditation | A practice involving focused attention and relaxation techniques |
Table 3: Major Theories of Learning
| Theory | Key Principles |
|---|---|
| Classical Conditioning | Learning based on associations between stimuli |
| Operant Conditioning | Learning based on consequences of behavior |
| Cognitive Theories | Learning based on mental processes and cognitive structures |
| Social Learning Theory | Learning based on observing and imitating others |
Table 4: Factors Influencing Motivation and Emotion
| Factor | Influence |
|---|---|
| Intrinsic Factors | Internal drives, such as curiosity and achievement |
| Extrinsic Factors | External rewards and punishments |
| Emotional Intelligence | Ability to understand and manage emotions |
| Culture | Cultural norms and values can shape motivation and emotions |