Introduction
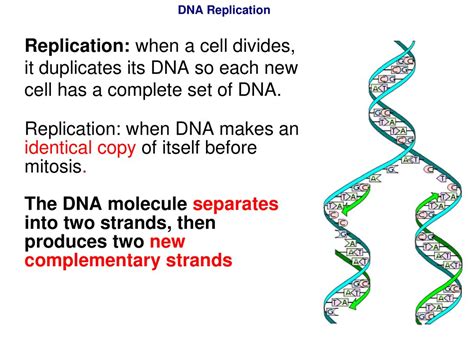
Cell division is a fundamental process in all living organisms. It allows organisms to grow, repair themselves, and reproduce. Before a cell can divide, it must first duplicate its DNA. This process is essential for ensuring that each new cell receives a complete copy of the genetic material.

The Process of DNA Replication
DNA replication is a complex process that involves many enzymes and proteins. It begins with the unwinding of the DNA double helix. This is followed by the separation of the two strands of DNA. Each strand then serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand. The process of DNA replication is highly accurate, and it ensures that each new cell receives an identical copy of the genetic material.
The Importance of DNA Replication
DNA replication is essential for cell division. It ensures that each new cell receives a complete copy of the genetic material. This is important for several reasons. First, it allows organisms to grow and repair themselves. Second, it allows organisms to reproduce. Third, it ensures that genetic information is passed on from one generation to the next.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
There are a number of common mistakes that can occur during DNA replication. These mistakes can lead to mutations, which can have a variety of negative consequences. Some of the most common mistakes include:
- Base misincorporation: This occurs when a wrong nucleotide is inserted into the new strand of DNA.
- Frameshift mutations: These occur when the reading frame of the DNA is shifted, which can lead to the production of non-functional proteins.
- Deletions: These occur when a section of DNA is lost from the new strand of DNA.
- Insertions: These occur when a section of DNA is added to the new strand of DNA.
Conclusion
DNA replication is a complex process that is essential for cell division. It ensures that each new cell receives a complete copy of the genetic material. This is important for growth, repair, reproduction, and the inheritance of genetic information. By understanding the process of DNA replication, we can better understand the fundamental processes of life.
Additional Resources
Tables
| Stage of Cell Cycle | Description |
|---|---|
| Interphase | The cell grows and prepares for division. |
| Prophase | The chromosomes become visible and the nuclear envelope breaks down. |
| Metaphase | The chromosomes line up in the center of the cell. |
| Anaphase | The chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. |
| Telophase | Two new nuclear envelopes form around the chromosomes and the cell membrane pinches in the middle, dividing the cell into two new cells. |
| Type of DNA Replication Error | Description |
|---|---|
| Base misincorporation | A wrong nucleotide is inserted into the new strand of DNA. |
| Frameshift mutation | The reading frame of the DNA is shifted, which can lead to the production of non-functional proteins. |
| Deletion | A section of DNA is lost from the new strand of DNA. |
| Insertion | A section of DNA is added to the new strand of DNA. |
| Consequence of DNA Replication Error | Description |
|---|---|
| Cancer | Mutations in genes that control cell growth can lead to cancer. |
| Birth defects | Mutations in genes that are essential for development can lead to birth defects. |
| Genetic diseases | Mutations in genes that are responsible for specific functions can lead to genetic diseases. |
| Application of DNA Replication | Description |
|---|---|
| Gene therapy | DNA replication can be used to deliver genes to cells that are missing or have damaged genes. |
| Forensic science | DNA replication can be used to identify individuals from DNA samples. |
| Paternity testing | DNA replication can be used to determine the father of a child. |