Introduction

Babysitting is a crucial service that provides children with essential care and attention when their parents or guardians are unavailable. Babysitters play a vital role in the well-being and safety of children, offering a range of duties that cater to their physical, emotional, and educational needs.
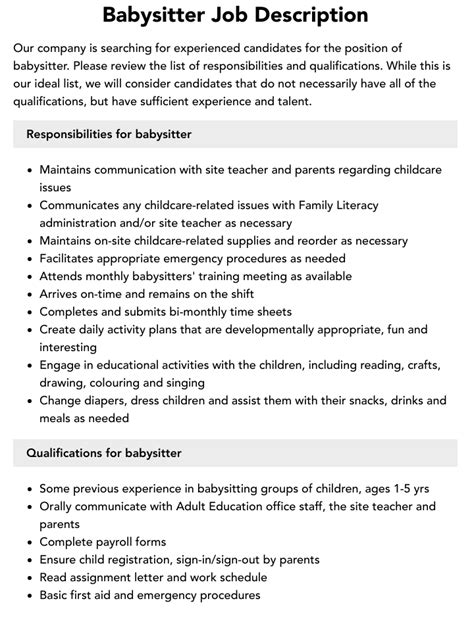
Key Responsibilities
- Childcare: Providing age-appropriate care for children, including feeding, changing diapers, and bathing.
- Safety and Supervision: Ensuring the safety and well-being of children at all times, monitoring their activities and responding to emergencies.
- Play and Stimulation: Engaging children in age-appropriate activities that foster their physical, cognitive, and social development.
- Household Tasks: Assisting with household tasks as requested, such as tidying up toys, preparing snacks, or helping with laundry.
- Communication: Maintaining open and regular communication with parents or guardians about the child’s well-being, activities, and any incidents.
Qualifications and Skills
- Child First Aid and CPR Certification: Essential for handling unexpected medical situations.
- Experience in Childcare: Demonstrated proficiency in providing care for children of different ages.
- Positive Attitude and Patience: Ability to handle challenging situations with grace and maintain a positive outlook.
- Empathy and Sensitivity: Understanding and responding to children’s emotional needs.
- Creativity and Imagination: Engaging children in fun and educational activities that stimulate their development.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Leaving Children Unattended: Never leave children unsupervised, even for a short period.
- Overfeeding or Underfeeding: Follow parents’ instructions carefully regarding feeding schedules and portion sizes.
- Ignoring Safety Hazards: Inspect the environment thoroughly for potential hazards and address them promptly.
- Using Harsh Discipline: Avoid using physical punishment or verbal abuse. Communicate with children in a respectful and age-appropriate manner.
- Ignoring Child’s Emotions: Pay attention to children’s emotional well-being and respond to their cries, fears, or tantrums appropriately.
Step-by-Step Babysitting Approach
- Arrival: Greet the child and parents or guardians warmly. Inquire about any special instructions or routines.
- Care Provision: Attend to the child’s immediate needs, such as feeding, changing diapers, or playing.
- Play and Activities: Engage the child in age-appropriate activities that promote their development.
- Household Tasks: Assist with household tasks as requested, ensuring the child’s safety and comfort.
- Communication: Update parents or guardians regularly about the child’s well-being and activities.
- Departure: Ensure the child is safe and secure before leaving. Inform parents or guardians of any events or concerns.
Why Babysitting Matters
Babysitting provides numerous benefits for children, families, and the wider community:
Benefits for Children
- Secure and Nurturing Environment: Provides a safe and loving environment where children can develop and thrive.
- Intellectual and Emotional Stimulation: Offers activities and interactions that promote cognitive growth, creativity, and social skills.
- Positive Role Models: Exposes children to positive role models who guide and support them in their early development.
Benefits for Families
- Peace of Mind: Enables parents or guardians to attend to their responsibilities or engage in personal activities with peace of mind.
- Flexibility and Convenience: Provides flexible and convenient childcare options that accommodate parents’ schedules and needs.
- Financial Assistance: Reduces childcare expenses for families, making it more affordable to secure quality care for their children.
Benefits for the Community
- Economic Stimulus: Creates employment opportunities and supports the economy by providing childcare services to working parents.
- Social Support: Reduces the burden on extended family members or friends who may be unable to provide regular childcare.
- Improved Child Welfare: Ensures children have access to quality childcare, promoting their well-being and reducing risk factors for developmental issues.
Creative Applications: The “Babysitter as Educator” Model
In addition to traditional childcare responsibilities, babysitters can also play a role as educators by incorporating age-appropriate educational activities into their time with children. This innovative approach has the potential to enhance children’s development and foster a lifelong love of learning.
Babysitter Responsibilities in the “Babysitter as Educator” Model:
- Creating Educational Activities: Developing and implementing activities that align with children’s developmental milestones and interests.
- Incorporating Learning into Play: Integrating educational concepts into playtime, making learning enjoyable and engaging.
- Encouraging Language and Literacy: Reading to children, singing songs, and engaging in conversation to promote language development and literacy skills.
- Fostering Curiosity and Exploration: Providing children with opportunities to explore their surroundings, ask questions, and develop their critical thinking abilities.
Tables
| Table 1: Childcare Activities by Age Group |
|---|
| Age Group |
| 0-6 months |
| 6-12 months |
| 1-2 years |
| 2-3 years |
| 3-5 years |
| Table 2: Safety Hazards to Check for |
|---|
| Hazard |
| Stairs |
| Outlets |
| Sharp Objects |
| Water Sources |
| Electrical Appliances |
| Table 3: Common Behavioral Challenges and Solutions |
|---|
| Challenge |
| Crying |
| Tantrums |
| Aggression |
| Fear or Anxiety |
| Separation Anxiety |
| Table 4: Babysitter Qualities and Expectations |
|---|
| Quality |
| Reliability |
| Punctuality |
| Communication |
| Flexibility |
| Respect for Child’s Boundaries |