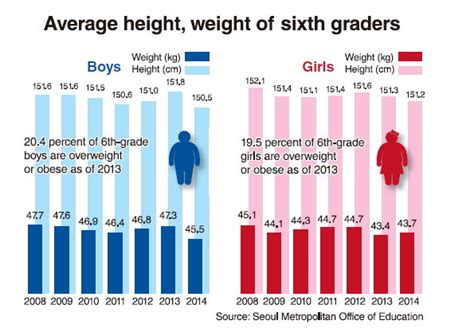
As children enter middle school, their growth patterns become increasingly apparent. Sixth grade is a pivotal year in terms of physical development, and one of the most noticeable changes is an increase in height.

Height Expectations for 6th Graders
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the average height for a 6th grader is:
- Boys: 51.9 inches (132 centimeters)
- Girls: 51.5 inches (131 centimeters)
However, there is considerable variation in height among children of the same age. Some children may be significantly taller or shorter than the average.
Factors Influencing Height
Several factors can influence a child’s height, including:
- Genetics: The genes inherited from parents account for a significant portion of a child’s height.
- Nutrition: A healthy diet rich in essential nutrients, such as protein, calcium, and vitamin D, is crucial for bone growth.
- Sleep: Adequate sleep is essential for the release of growth hormone, which promotes bone growth.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise can stimulate bone growth and help maintain a healthy weight.
- Health Conditions: Certain health conditions, such as growth hormone deficiency or certain medications, can affect height growth.
Signs of Precocious or Delayed Growth
Understanding the average height for a 6th grader can help parents identify any potential growth concerns. Signs of precocious growth include:
- Consistently taller than peers of the same age
- Rapid growth spurts
- Early puberty
Signs of delayed growth include:
- Consistently shorter than peers of the same age
- Slow or no growth spurts
- Late puberty
Tips and Tricks
- Monitor Growth Regularly: Track your child’s height using a growth chart or stadiometer to ensure they are growing at an appropriate rate.
- Encourage a Healthy Diet: Provide your child with a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Promote Adequate Sleep: Ensure your child gets around 9-11 hours of sleep each night.
- Facilitate Physical Activity: Encourage your child to engage in regular physical activity, such as sports, dancing, or outdoor play.
- Consult a Healthcare Professional: If you have concerns about your child’s growth, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional for evaluation.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Assuming Short Children Will Always Be Short: While genetics play a role, environmental factors can also significantly impact height. Providing optimal nutrition and encouraging physical activity can help maximize growth potential.
- Pushing Growth: Attempting to force a child to grow through supplements or excessive exercise can have negative consequences. Focus on creating a healthy environment that supports natural growth.
- Ignoring Signs of Precocious or Delayed Growth: If you notice any signs of precocious or delayed growth, seeking medical attention is crucial for prompt diagnosis and intervention.
- Comparing Children to the Average: Every child grows at their own pace. Avoid comparing your child to the average height for a 6th grader. Instead, focus on their individual growth trajectory.
FAQs
1. Is there a difference in height between boys and girls in 6th grade?
Answer: Yes, boys are typically taller than girls in 6th grade.
2. What is the best way to predict a child’s adult height?
Answer: A doctor can use a child’s height and growth history to estimate their adult height.
3. Can diet affect height growth?
Answer: Yes, a healthy diet rich in essential nutrients can contribute to optimal height growth.
4. What should I do if my child is significantly shorter or taller than their peers?
Answer: Consult a healthcare professional to discuss growth monitoring and potential causes.
5. Is it possible to change a child’s height?
Answer: While genetics significantly influence height, adequate nutrition, sleep, and physical activity can help maximize growth potential. However, it is not possible to significantly alter a child’s height beyond their genetic limits.
6. What are the signs of growth hormone deficiency?
Answer: Signs of growth hormone deficiency include slow or no growth spurts, short stature, delayed puberty, and low energy levels.
7. Can exercise stunt growth?
Answer: Excessive exercise or weightlifting can potentially affect growth if it results in insufficient nutrition or hormonal imbalances. However, moderate exercise is beneficial for bone growth.
8. Is it important to monitor growth after puberty?
Answer: Yes, while growth peaks during puberty, it continues at a slower rate until adolescence.