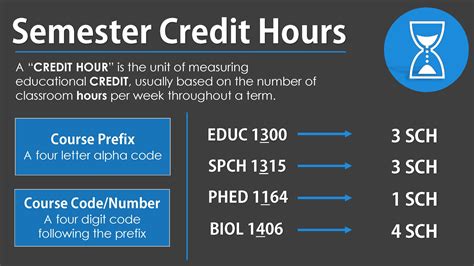
When it comes to higher education, understanding the terminology is essential. Two common terms you’ll encounter are “semester hours” and “credits.” Are they interchangeable? Let’s delve into the nuances of these concepts.

Defining Semester Hours and Credits
Semester Hours
- A unit of measurement for the amount of time spent studying a course during a semester.
- Typically, a semester hour represents one hour of lecture or two to three hours of lab work per week.
- In the United States, most colleges and universities use a semester system, which spans around 15 weeks.
Credits
- A broader term used to describe the academic workload associated with a course.
- Credits usually represent the number of semester hours, but not always.
- Some institutions may award credits for fieldwork, research, or other non-classroom activities.
The Interchangeability of Semester Hours and Credits
In general, semester hours and credits can be used interchangeably. However, there are some exceptions:
- Courses with Variable Credit: Some courses may offer a range of credits, such as 1-3 credits or 3-6 credits. In these cases, the actual number of credits earned depends on the amount of work completed.
- Independent Study: Independent study courses may award credits without being tied to a specific number of semester hours.
- Non-Traditional Institutions: Non-traditional institutions, such as online universities, may have different credit systems that do not align directly with semester hours.
Credits vs. Grade Points
It’s important to note that credits are different from grade points. Grade points are assigned based on the letter grade received in a course and are used to calculate a student’s grade point average (GPA).
Practical Implications
Understanding the relationship between semester hours and credits is crucial for several reasons:
- Course Planning: When registering for courses, students need to know how many semester hours or credits they are taking to ensure they meet the requirements for their degree.
- Transferability: When transferring credits from one institution to another, it’s essential to understand how semester hours are converted to credits at the receiving institution.
- Financial Aid: Some financial aid programs are based on the number of credits earned each semester.
Tables for Reference
Table 1: Typical Credit Equivalencies
| Semester Hours | Credits |
|---|---|
| 1 | 3 |
| 2 | 6 |
| 3 | 9 |
| 4 | 12 |
Table 2: Credit Systems for Different Institutions
| Institution | Credit System |
|---|---|
| Most U.S. Colleges and Universities | Semester Hours |
| Quarter System Institutions | Quarter Units |
| European Higher Education Area | European Credit Transfer and Accumulation System (ECTS) |
| Australian Universities | Credit Points |
Table 3: Credit Requirements for Common Degrees
| Degree | Typical Credit Requirements |
|---|---|
| Associate’s Degree | 60-75 credits |
| Bachelor’s Degree | 120-130 credits |
| Master’s Degree | 30-60 credits |
| Doctorate Degree | 90-120 credits |
Table 4: Credit and Semester Hour Conversion
| Semester Hours | Credits |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1.5 |
| 2 | 3 |
| 3 | 4.5 |
| 4 | 6 |
Conclusion
While semester hours and credits are generally interchangeable, it’s important to be aware of the potential exceptions. By understanding the relationship between these two terms, students can make informed decisions about their course load, transferability of credits, and financial aid eligibility.