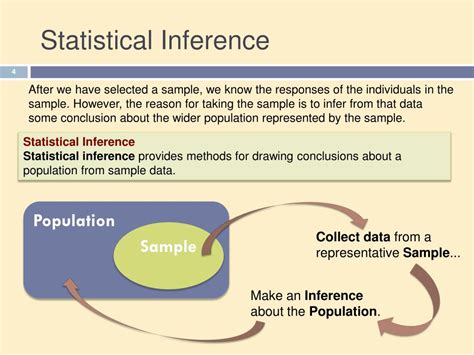
In the realm of statistics, understanding the concept of a population is paramount. In AP Statistics, the population definition lays the foundation for drawing meaningful conclusions from data.

What is a Population in AP Stats?
A population, in the context of AP Stats, refers to the entire collection of individuals or objects under investigation. It represents the complete set of data from which samples are drawn. Populations can vary in size and complexity, ranging from small, finite groups to infinite, theoretical populations.
Key Characteristics of a Population
- Size: Populations can be finite (with a definite number of individuals) or infinite (e.g., the population of all possible measurements).
- Heterogeneity: Populations often consist of individuals or objects with varying characteristics.
- Accessibility: In practice, researchers may not have access to the entire population and must rely on samples.
- Representativeness: Samples should accurately represent the characteristics of the population to ensure valid inferences.
Importance of Population Definition
The accurate definition of the population is crucial for several reasons:
- Sampling: Sampling techniques rely on knowing the population size and characteristics to determine sample size and representativeness.
- Generalizability: Statistical inferences drawn from samples are only generalizable to the population from which they were drawn.
- Hypothesis Testing: Hypothesis tests help determine whether observed differences between samples indicate real differences in population parameters.
- Predictive Analytics: Population data is used to develop models for predicting future outcomes and making informed decisions.
Examples of Populations
- Population of all students in a school district
- Population of all defective products produced by a factory
- Population of all possible test scores on an AP Statistics exam
- Population of all households in a particular ZIP code
- Population of all websites on the Internet
How to Define a Population in AP Stats
- Identify the research question or problem.
- Determine the specific individuals or objects of interest.
- Specify the relevant characteristics and boundaries of the population.
- Consider the size and accessibility of the population.
- Ensure that the definition is clear and unambiguous.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Overly broad or vague definitions: Avoid defining populations that are too large or too general to be useful.
- Sampling bias: Ensure that samples are not biased towards specific subgroups within the population.
- Unrepresentative samples: Avoid drawing conclusions from samples that do not adequately represent the population.
- Confusing population with sample: Remember that samples are only a subset of the population and may not perfectly represent its characteristics.
- Ignoring population variability: Recognize that populations often exhibit variability, which should be considered in statistical analyses.
Step-by-Step Approach to Defining a Population
- Identify the research question: Start by clearly defining the research question or problem you aim to address.
- Consider the scope: Determine the specific individuals or objects that are relevant to the research question.
- Define boundaries: Specify the characteristics and limitations that define the boundaries of the population. This includes age, gender, location, or other relevant factors.
- Assess size and accessibility: Determine the size and accessibility of the population to inform sampling strategies.
- Define clearly: Write a concise and clear definition of the population, ensuring it is specific and unambiguous.
Effective Strategies for Defining a Population
- Use specific parameters: Narrow down the population by specifying precise characteristics, such as age range, income level, or geographic location.
- Consult experts: Seek input from knowledgeable individuals or researchers in the field to ensure the accuracy and relevance of the population definition.
- Review existing data: Utilize existing data sources, such as census records or industry reports, to inform the population definition.
- Conduct pilot studies: Conduct small-scale studies to gather preliminary data and refine the population definition.
- Be flexible: Populations can change over time, so be prepared to adjust the definition as needed.
Applications of Population Definition
The concept of population definition has numerous applications in various fields:
- Market research: Identifying target populations for marketing campaigns and product development.
- Healthcare: Defining patient populations for clinical trials and medical studies.
- Education: Determining the population of students for educational assessments and interventions.
- Data analysis: Selecting relevant populations for data collection and statistical modeling.
- Decision-making: Using population data to inform policy decisions and strategic planning.
Conclusion
The AP Stats population definition serves as the cornerstone for statistical inference and hypothesis testing. By clearly defining the population under investigation, researchers can ensure that their findings are accurate, relevant, and generalizable. Understanding the key characteristics and considerations involved in defining a population is essential for effective data analysis and informed decision-making.