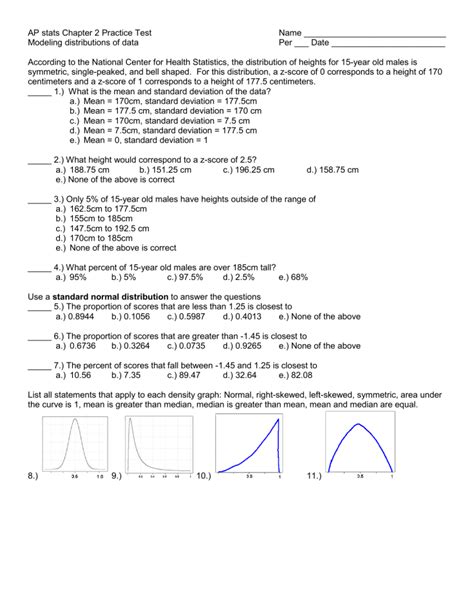
Introduction
In AP Statistics, Chapter 2 focuses on modeling distributions of data. This practice test will assess your understanding of the different types of distributions, how to identify them, and how to use them to analyze data.

Types of Distributions
Normal Distribution
The normal distribution, also known as the bell curve, is the most common type of distribution. It is characterized by its symmetric, bell-shaped curve. The mean, median, and mode of a normal distribution are all equal.
Uniform Distribution
The uniform distribution is a type of distribution in which all values are equally likely. This means that the probability of any one value occurring is the same as the probability of any other value occurring.
Binomial Distribution
The binomial distribution is a type of distribution that models the number of successes in a sequence of independent experiments. The probability of success on each experiment is denoted by p, and the number of experiments is denoted by n.
Poisson Distribution
The Poisson distribution is a type of distribution that models the number of events that occur in a fixed interval of time or space. The parameter of the Poisson distribution is the mean number of events that occur in the interval.
Identifying Distributions
To identify the type of distribution that best fits a data set, you can use a variety of methods, including:
- Graphical methods: Create a histogram or box plot of the data. If the histogram is bell-shaped, the data is likely normally distributed. If the histogram is flat, the data is likely uniformly distributed.
- Analytical methods: Use the skewness and kurtosis of the data to determine the type of distribution. For example, a distribution with a positive skewness is likely skewed to the right, while a distribution with a negative skewness is likely skewed to the left.
- Goodness-of-fit tests: Use a statistical test to determine whether the data fits a particular distribution. For example, the chi-square goodness-of-fit test can be used to test whether the data fits a normal distribution.
Using Distributions to Analyze Data
Once you have identified the type of distribution that best fits a data set, you can use it to analyze the data. For example, you can use the mean and standard deviation of a normal distribution to describe the central tendency and variability of the data. You can also use the binomial distribution to estimate the probability of success in a sequence of experiments.
Practice Questions
- Identify the type of distribution that best fits the following data set:
2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18
-
Use the normal distribution to find the probability of obtaining a score between 70 and 80 on a test with a mean of 75 and a standard deviation of 5.
-
Use the binomial distribution to find the probability of getting 5 heads in a row when flipping a coin.
Answer Key
- Uniform distribution
- 0.3413
- 0.03125
Tips for Success
- Understand the different types of distributions and how to identify them.
- Practice using distributions to analyze data.
- Be familiar with the formulas for the mean, standard deviation, and probability of each type of distribution.
- Use online resources to help you learn about distributions.
Additional Resources
- AP Statistics Chapter 2: Modeling Distributions of Data
- Normal Distribution
- Uniform Distribution
- Binomial Distribution
- Poisson Distribution