Introduction

The Advanced Placement Physics exam is a challenging assessment that requires a deep understanding of physics concepts and a mastery of mathematical formulas. To succeed on the exam, it is essential to have a comprehensive formula sheet that you can reference throughout the test. This article provides a comprehensive AP Physics formula sheet that covers all the key topics tested on the exam.
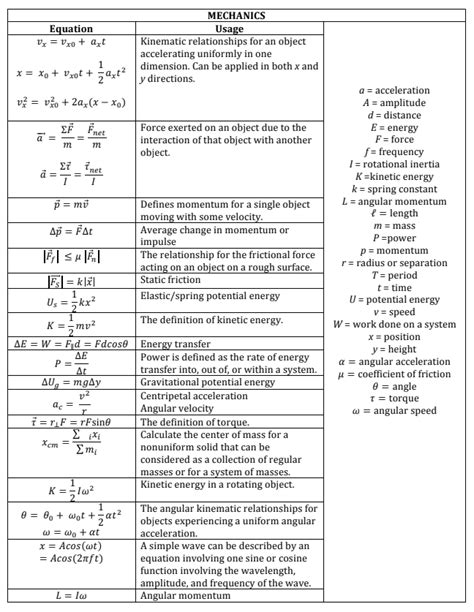
Mechanics
1. Kinematics
- Velocity: v = Δx/Δt
- Acceleration: a = Δv/Δt
- Position: x = x0 + vt + 1/2at^2
- Velocity: v = v0 + at
- Displacement: Δx = v0t + 1/2at^2
2. Dynamics
- Newton’s second law: F = ma
- Weight: W = mg
- Impulse: J = Δp
- Work: W = Fd
- Power: P = W/t
3. Circular Motion and Gravity
- Centripetal acceleration: a = v^2/r
- Gravitational force: Fg = Gm1m2/r^2
- Gravitational acceleration: g = Gm/r^2
Electricity and Magnetism
1. Electric Fields
- Electric field: E = F/q
- Coulomb’s law: F = kq1q2/r^2
- Electric potential: V = W/q
2. Circuits
- Ohm’s law: V = IR
- Power: P = IV
- Kirchhoff’s loop rule: ΣV = 0
- Kirchhoff’s junction rule: ΣI = 0
3. Magnetism
- Magnetic field: B = F/qV
- Magnetic force: F = qvB
- Ampere’s law: ΣB = μ0I
Waves and Optics
1. Waves
- Wave speed: v = fλ
- Frequency: f = 1/T
- Wavelength: λ = v/f
2. Optics
- Snell’s law: n1sinθ1 = n2sinθ2
- Lens equation: 1/f = 1/do + 1/di
- Magnification: M = -di/do
Atomic and Nuclear Physics
1. Atomic Physics
- Rydberg formula: 1/λ = R(1/n1^2 – 1/n2^2)
- Bohr model: E = -13.6eV/n^2
2. Nuclear Physics
- Mass-energy equivalence: E = mc^2
- Radioactive decay: A = A0e-λt
Thermal Physics
1. Thermodynamics
- First law of thermodynamics: ΔU = Q – W
- Ideal gas law: PV = nRT
- Specific heat: c = Q/mΔT
2. Heat Transfer
- Conduction: Q = kAΔT/L
- Convection: Q = hAΔT
- Radiation: Q = σA(T^4 – T0^4)
Tables
Table 1: Kinematic Equations
| Equation | Description |
|---|---|
| v = Δx/Δt | Velocity |
| a = Δv/Δt | Acceleration |
| x = x0 + vt + 1/2at^2 | Position |
| v = v0 + at | Velocity |
| Δx = v0t + 1/2at^2 | Displacement |
Table 2: Dynamics Equations
| Equation | Description |
|---|---|
| F = ma | Newton’s second law |
| W = mg | Weight |
| J = Δp | Impulse |
| W = Fd | Work |
| P = W/t | Power |
Table 3: Electric and Magnetic Equations
| Equation | Description |
|---|---|
| E = F/q | Electric field |
| F = kq1q2/r^2 | Coulomb’s law |
| V = W/q | Electric potential |
| V = IR | Ohm’s law |
| P = IV | Power |
| B = F/qV | Magnetic field |
| F = qvB | Magnetic force |
| ΣB = μ0I | Ampere’s law |
Table 4: Wave and Optics Equations
| Equation | Description |
|---|---|
| v = fλ | Wave speed |
| f = 1/T | Frequency |
| λ = v/f | Wavelength |
| n1sinθ1 = n2sinθ2 | Snell’s law |
| 1/f = 1/do + 1/di | Lens equation |
| M = -di/do | Magnification |
Tips and Tricks
- Study the formula sheet regularly and make sure you understand the concepts behind each formula.
- Use the formula sheet as a reference during practice problems and exams.
- Organize the formula sheet in a way that makes sense to you.
- Create flashcards with the formulas and definitions.
- Use the formula sheet to help you solve problems and check your work.
Conclusion
The AP Physics formula sheet is an essential tool for success on the AP Physics exam. By studying the formula sheet and practicing its use, students can improve their understanding of physics concepts and increase their chances of earning a high score on the exam.