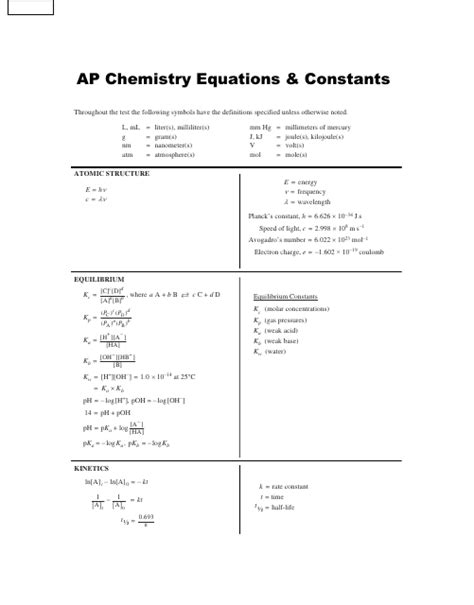
Introduction

AP Chemistry is a rigorous course that requires a strong foundation in the fundamentals of chemistry. To succeed in the AP Chemistry exam, it is crucial to have a comprehensive understanding of the key concepts and equations. This AP Chemistry reference sheet provides a concise overview of the essential information that students need to know for the exam.
Atomic Structure
- Atomic number: Number of protons in the nucleus
- Mass number: Number of protons + neutrons in the nucleus
- Electron configuration: Arrangement of electrons in atomic orbitals
- Periodic trends: Relationships between properties and atomic number
Chemical Bonding
- Ionic bonding: Formation of ions due to electron transfer
- Covalent bonding: Formation of molecules due to electron sharing
- Polarity: Uneven distribution of charge in a molecule
- Molecular geometry: Shape of molecules based on electron-pair repulsion
Gases and Thermodynamics
- Ideal gas law: PV = nRT
- Gas stoichiometry: Calculations involving gases and chemical reactions
- Enthalpy: Heat flow associated with a chemical reaction
- Entropy: Measure of randomness in a system
Kinetics and Equilibrium
- Reaction rate: Rate at which reactants are converted to products
- Equilibrium: State of balance between forward and reverse reactions
- Equilibrium constant: Value that measures the extent of equilibrium
Acids and Bases
- pH: Measure of acidity or basicity
- Strong acids and bases: Completely ionized in water
- Weak acids and bases: Partially ionized in water
- Acid-base reactions: Reactions involving proton transfer
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
- Oxidation: Loss of electrons
- Reduction: Gain of electrons
- Oxidizing agents: Substances that cause oxidation
- Reducing agents: Substances that cause reduction
Gas Laws
- PV = nRT
- P₂V₂ / T₂ = P₁V₁ / T₁ (combined gas law)
Thermodynamics
- ΔH = q – w (enthalpy change)
- ΔS = q / T (entropy change)
- ΔG = ΔH – TΔS (Gibbs free energy change)
Kinetics
- rate = k[A]^m[B]^n (rate law)
- k = Ae^(-Ea/RT) (Arrhenius equation)
Equilibrium
- Keq = [products] / [reactants] (equilibrium constant)
Common Elements and Their Symbols
| Element | Symbol |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen | H |
| Helium | He |
| Lithium | Li |
| Beryllium | Be |
| Boron | B |
Common Polyatomic Ions
| Ion | Formula |
|---|---|
| Nitrate | NO₃⁻ |
| Sulfate | SO₄²⁻ |
| Carbonate | CO₃²⁻ |
| Phosphate | PO₄³⁻ |
| Hydroxide | OH⁻ |
Electrochemical Data
| Element | Reduction Potential (V) |
|---|---|
| Li | -3.05 |
| Na | -2.93 |
| K | -2.71 |
| Mg | -2.37 |
| Al | -1.66 |
Solubility Rules
| Rule | Description |
|---|---|
| Rule 1 | All Group 1 cations are soluble. |
| Rule 2 | All Group 2 cations are soluble, except for BaSO₄. |
| Rule 3 | All ammonium (NH₄⁺) cations are soluble. |
| Rule 4 | All nitrate (NO₃⁻) anions are soluble. |
- Confusing enthalpy and entropy
- Forgetting to balance equations before calculating equilibrium constants
- Using the wrong sign conventions for enthalpy and entropy
- Neglecting the temperature dependence of equilibrium constants
- Assuming that strong acids and bases are always completely ionized
-
What is the most important thing I need to know for the AP Chemistry exam?
– A strong understanding of the key concepts and equations is essential. -
How much time should I spend studying for the exam?
– It is recommended to dedicate several months to studying for the exam. -
What is the best way to prepare for the free-response questions?
– Practice solving problems using the reference table and equations. -
Can I use a calculator on the exam?
– Yes, a scientific calculator is allowed on the exam. -
How many points do I need to earn to get a passing grade on the exam?
– The passing score varies from year to year, but it typically ranges from 65-70%. -
What resources can I use to help me study for the exam?
– There are numerous textbooks, online resources, and practice exams available. -
Is it possible to get a perfect score on the AP Chemistry exam?
– Yes, but it is extremely difficult to achieve. -
What are some of the most challenging topics on the AP Chemistry exam?
– Thermodynamics, kinetics, and equilibrium are often considered to be the most challenging topics.
The AP Chemistry reference sheet can be used in various innovative ways to enhance understanding and application of chemistry concepts. Some potential applications include:
- Creating concept maps: Students can use the reference sheet to create visual representations of key concepts and their relationships.
- Developing simulations: Using the equations and data provided in the reference sheet, students can design computer simulations to model chemical reactions and processes.
- Designing experiments: The reference sheet can provide guidance for students when designing and conducting chemistry experiments.
- Developing real-world applications: Students can use the information in the reference sheet to develop practical applications of chemistry in fields such as medicine, materials science, and environmental science.