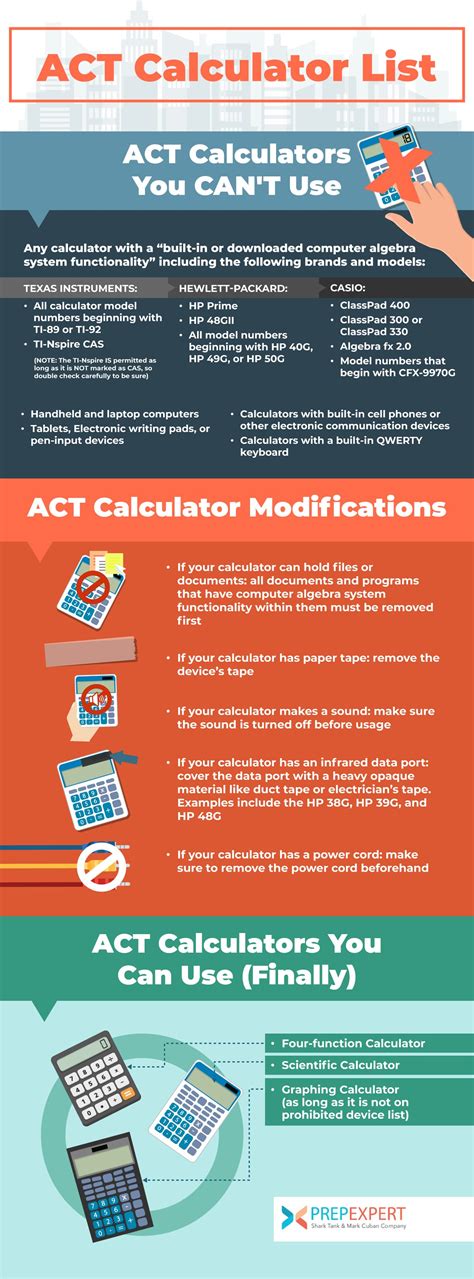
Navigating the Permitted Calculator Landscape

The ACT, a standardized test widely used for college admissions, presents a unique set of requirements for calculators. Understanding the permitted models and their capabilities is crucial for test-takers who wish to maximize their scores. This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth analysis of ACT test permitted calculators, empowering students with the knowledge they need to succeed.
Approved Models and Features
The ACT only permits specific calculator models that meet their stringent criteria. These models are designed to provide basic functionality without the distractions of advanced features. The following models are currently approved by the ACT:
Table 1: List of Permitted Calculator Models
| Manufacturer | Model |
|---|---|
| Casio | fx-260, fx-300, fx-350 |
| Hewlett-Packard | HP 33s, HP 35s |
| Sharp | EL-531X, EL-510R |
| Texas Instruments | TI-30XS MultiView, TI-30XS MultiView Explorer |
Essential Calculator Functions
The ACT test requires students to have access to certain basic functions on their calculators. These include:
- Arithmetic operations: Addition, subtraction, multiplication, division
- Order of operations: Parentheses, exponents, roots
- Trigonometric functions: Sine, cosine, tangent (not required for ACT Math section)
- Logarithms: Common (base 10) logarithms (not required for ACT Math section)
- Fractions and decimals: Converting between fractions, decimals, and percentages
Forbidden Calculator Capabilities
Calculators with advanced capabilities are prohibited on the ACT. These include:
- Graphing: Creating and manipulating graphs
- Symbolic manipulation: Solving algebraic equations symbolically
- Differentiation and integration: Calculus functions
- Statistical calculations: Advanced statistical analyses
- Memory storage: Storing or retrieving information during the test
Tips and Tricks for Maximizing Calculator Usage
- Choose the right model: Select a calculator from the approved list that matches your skill level and comfort zone.
- Familiarize yourself with the functions: Practice using the permitted functions on your calculator before test day.
- Use scratch paper: Write down calculations and notes on scratch paper to avoid making mistakes on your calculator screen.
- Double-check your answers: Use your calculator to verify your work, but don’t rely solely on its results.
- Don’t overcomplicate: Avoid using complex or time-consuming functions. Stick to the basics and focus on efficiency.
Comparative Analysis of Approved Calculators
Table 2: Comparison of Approved Calculators
| Feature | Casio fx-260 | Hewlett-Packard HP 33s | Sharp EL-531X | Texas Instruments TI-30XS MultiView |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Display size | 10-digit | 13-digit | 8-digit | 10-digit |
| Number of functions | 26 | 52 | 20 | 25 |
| Fraction display | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Scientific notation | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Trigonometry functions | No | Yes | No | No |
| Logarithmic functions | No | No | No | No |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Permitted Calculators
Advantages:
- Easier calculations: Calculators can speed up calculations and reduce errors.
- More efficient problem-solving: Calculators can assist with complex operations, freeing up mental energy for other tasks.
- Improved accuracy: Calculators can provide precise results, reducing the risk of mistakes.
Disadvantages:
- Potential for distractions: Calculators can be a source of distraction if used excessively.
- Reliance on technology: Students may become overly reliant on calculators and lose their mental math skills.
- Malfunctions: Calculators can malfunction or run out of power during the test.
FAQs
1. Can I use a graphing calculator on the ACT?
No, graphing calculators are prohibited on the ACT.
2. What if I forget my calculator on test day?
You will not be allowed to use a calculator that is not on the approved list. It is important to bring your own calculator.
3. Can I share my calculator with another student?
No, sharing calculators is not permitted on the ACT. Each student must have their own calculator.
4. What if my calculator malfunctions during the test?
If your calculator malfunctions, you should raise your hand and ask for assistance from a test administrator.
5. Can I use a scientific calculator on the ACT?
Yes, as long as it meets the required functionality criteria and is not a graphing calculator.
6. What is the best calculator for the ACT?
The best calculator for the ACT is one that is approved by the test, meets your skill level, and allows you to perform the required functions efficiently.
7. Is it necessary to use a calculator on the ACT?
While a calculator can be helpful, it is not mandatory to use one on the ACT. Some students prefer to rely on mental math or perform calculations on scratch paper.
8. How can I improve my calculator skills for the ACT?
Practice using your calculator regularly to become familiar with its features and functions. Focus on the essential operations required for the ACT Math section.
Conclusion
Understanding the ACT test permitted calculators is crucial for students seeking to optimize their performance. By choosing the right calculator, utilizing its essential functions, and adhering to the restrictions, students can enhance their ability to solve math problems accurately and efficiently. The information provided in this guide empowers students to make informed decisions and achieve their desired ACT scores.