Understanding Absolute Location
Absolute location refers to the exact, fixed position of a place on Earth’s surface. Unlike relative location, which defines a place in relation to surrounding features, absolute location provides a precise point of reference for geographical identification.

Key Characteristics:
- A unique, unchanging point on the globe
- Determined by a combination of latitude and longitude
- Expressed as coordinates in degrees, minutes, and seconds
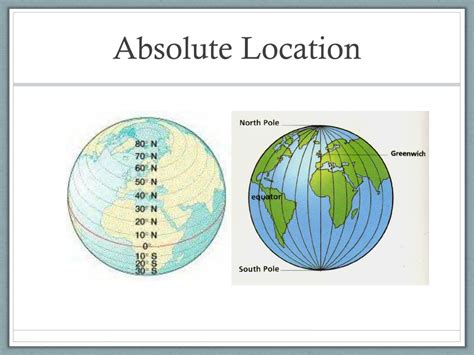
Latitude and Longitude: The Cornerstones of Absolute Location
Latitude:
- Measures the angular distance north or south of the Equator
- Ranges from 0° at the Equator to 90° at the North and South Poles
- Represented by a horizontal line on a map
Longitude:
- Measures the angular distance east or west of the Prime Meridian (0° longitude)
- Ranges from 0° at the Prime Meridian to 180° at the International Date Line
- Represented by a vertical line on a map
Example Usage
Example coordinates: (40° 42′ 51.6″ N, 74° 00′ 21.4″ W) indicate the absolute location of the Empire State Building in New York City.
Importance of Absolute Location
Absolute location is crucial for understanding the following aspects of geography:
- Spatial Relationships: Pinpointing a place’s exact location allows for accurate comparisons with other places.
- Distance and Direction Calculations: Coordinates enable the calculation of distances and directions between different locations.
- Navigation: Global Positioning Systems (GPS) and other navigation technologies rely on precise absolute location information.
- Time Zones: The Earth’s time zones are determined based on longitude, with each 15° of longitude corresponding to a one-hour difference in time.
- Climate and Weather Patterns: Absolute location influences climatic conditions, as it determines the amount of sunlight, precipitation, and wind patterns received in a particular area.
Applications of Absolute Location
Beyond its fundamental geographical applications, absolute location has various practical uses, including:
- Land Surveying and Mapping: Precisely locating land boundaries, roads, and other features.
- Natural Resource Exploration: Identifying potential areas for mining, drilling, and other resource extraction.
- Disaster Management: Tracking the movement and impact of natural disasters such as hurricanes and earthquakes.
- Environmental Conservation: Monitoring changes in land use, deforestation, and other environmental indicators.
Conclusion
Absolute location is a fundamental concept in AP Human Geography, providing a precise and objective way to locate places on Earth’s surface. By understanding latitude, longitude, and their significance, students can develop a comprehensive understanding of the geographical relationships and spatial distributions that shape our world.