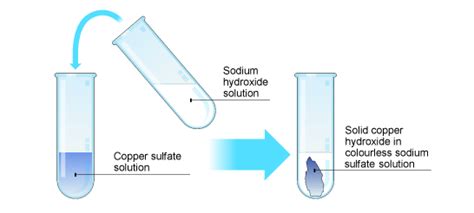
Sodium metal is a soft, silvery-white metal that is highly reactive. It is the sixth most abundant element in the Earth’s crust and is found in a variety of minerals, including halite (rock salt) and cryolite.

Physical Properties
Sodium metal has a melting point of 97.6°C (207.7°F) and a boiling point of 892°C (1638°F). It is a good conductor of heat and electricity and has a density of 0.97 g/cm3.
Chemical Properties
Sodium metal is a highly reactive metal that reacts with water, oxygen, and many other elements. It is a strong reducing agent and can be used to reduce other metals from their oxides.
Applications
Sodium metal is used in a variety of applications, including:
- Production of sodium hydroxide: Sodium metal is used to produce sodium hydroxide, which is a widely used chemical in the manufacture of paper, glass, and soap.
- Production of sodium carbonate: Sodium metal is used to produce sodium carbonate, which is a chemical used in the manufacture of glass, soap, and detergents.
- Production of sodium bicarbonate: Sodium metal is used to produce sodium bicarbonate, which is a chemical used in the manufacture of baking powder, antacids, and toothpaste.
- Production of sodium chloride: Sodium metal is used to produce sodium chloride, which is common table salt.
- Production of sodium metal: Sodium metal is used to produce sodium metal, which is used in a variety of applications, including the production of other chemicals, the manufacture of batteries, and the purification of metals.
Safety
Sodium metal is a hazardous material and should be handled with care. It can react violently with water and can cause burns and explosions. It is important to wear appropriate personal protective equipment when working with sodium metal.
Tips and Tricks
- When handling sodium metal, always wear appropriate personal protective equipment, including gloves, safety glasses, and a lab coat.
- Sodium metal should be stored in a cool, dry place away from water and other sources of moisture.
- Sodium metal should be cut with a sharp knife or scalpel.
- Never use your bare hands to handle sodium metal.
- If sodium metal comes into contact with your skin, wash the area immediately with soap and water.
- If sodium metal gets into your eyes, flush them immediately with water for at least 15 minutes.
- If you ingest sodium metal, seek medical attention immediately.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Do not use water to extinguish a sodium metal fire.
- Do not use a fire extinguisher to extinguish a sodium metal fire.
- Do not attempt to handle sodium metal if you are not properly trained.
- Do not store sodium metal in a humid environment.
- Do not store sodium metal near other chemicals.
How to Step-by-Step Approach
- Gather your materials. You will need a piece of sodium metal, a sharp knife or scalpel, and a pair of gloves.
- Put on your gloves.
- Cut the sodium metal into small pieces.
- Place the sodium metal in a dry container.
- Store the sodium metal in a cool, dry place away from water and other sources of moisture.
Innovative Applications
Sodium metal can be used to generate hydrogen, which is a clean-burning fuel. This could be a potential way to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels.
Useful Tables
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Melting point | 97.6°C (207.7°F) |
| Boiling point | 892°C (1638°F) |
| Density | 0.97 g/cm3 |
| Electrical conductivity | 20.1 x 106 S/m |
| Thermal conductivity | 140 W/m·K |
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Production of sodium hydroxide | Sodium metal is used to produce sodium hydroxide, which is a widely used chemical in the manufacture of paper, glass, and soap. |
| Production of sodium carbonate | Sodium metal is used to produce sodium carbonate, which is a chemical used in the manufacture of glass, soap, and detergents. |
| Production of sodium bicarbonate | Sodium metal is used to produce sodium bicarbonate, which is a chemical used in the manufacture of baking powder, antacids, and toothpaste. |
| Production of sodium chloride | Sodium metal is used to produce sodium chloride, which is common table salt. |
| Safety Precaution | Description |
|---|---|
| Wear appropriate personal protective equipment | When handling sodium metal, always wear appropriate personal protective equipment, including gloves, safety glasses, and a lab coat. |
| Store in a cool, dry place | Sodium metal should be stored in a cool, dry place away from water and other sources of moisture. |
| Cut with a sharp knife or scalpel | Sodium metal should be cut with a sharp knife or scalpel. |
| Common Mistake | Description |
|---|---|
| Using water to extinguish a sodium metal fire | Do not use water to extinguish a sodium metal fire. |
| Using a fire extinguisher to extinguish a sodium metal fire | Do not use a fire extinguisher to extinguish a sodium metal fire. |
| Attempting to handle sodium metal if you are not properly trained | Do not attempt to handle sodium metal if you are not properly trained. |