Introduction
Electrical circuits play a fundamental role in modern society, enabling the operation of countless devices and systems. Understanding the behavior of circuits is essential for engineers, hobbyists, and anyone interested in electronics. This article explores a circuit constructed with four resistors and one capacitor, examining its characteristics, functionality, and practical applications.

Circuit Configuration
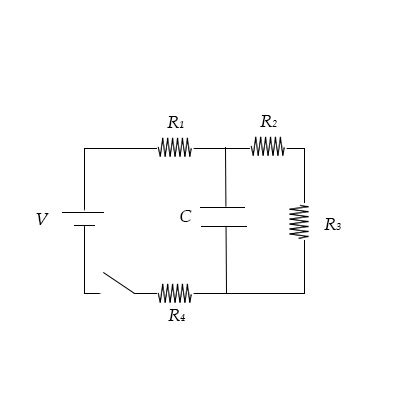
The circuit in question consists of four resistors (R1, R2, R3, R4) connected in series with a capacitor (C). The resistors are arranged in such a way that the current flows through them in sequence. The capacitor is placed in parallel with the last resistor (R4).
Component Analysis
Resistors
Resistors are electronic components that impede the flow of current in an electrical circuit. Their resistance, measured in ohms (Ω), determines the amount of current that flows through them. Resistors can be used to control voltage, current, and power in circuits.
Capacitor
A capacitor is an electronic component that stores electrical energy in an electric field. Its capacitance, measured in farads (F), determines the amount of charge it can store. Capacitors can be used to smooth voltage, filter out noise, and provide a reservoir of energy for electronic circuits.
Circuit Functionality
The four resistors and the capacitor in this circuit work together to create a variety of effects, including:
- Voltage Division: The resistors divide the voltage across the circuit in proportion to their resistances. This allows for precise control of voltage levels in different parts of the circuit.
- Current Limitation: The resistors limit the current flowing through the circuit. This protects sensitive components from damage and prevents excessive current draw.
- Capacitive Reactance: The capacitor introduces capacitive reactance into the circuit, which opposes the flow of alternating current (AC). This can be used to tune circuits to specific frequencies or to filter out unwanted harmonics.
Applications
The circuit constructed with four resistors and one capacitor has numerous applications in electronics, including:
- Voltage Regulators: Used to maintain a constant voltage level in electronic devices, such as power supplies and amplifiers.
- Filters: Used to remove unwanted noise and harmonics from signals in audio, video, and communication systems.
- Timing Circuits: Used to create time delays or to generate pulses in electronic circuits.
- Energy Storage: Used to store electrical energy for short periods of time, such as in camera flashes and portable electronics.
Benefits of Using Four Resistors and One Capacitor
Employing four resistors and one capacitor in a circuit offers several advantages:
- Versatility: The circuit can be configured in various ways to achieve different functionalities, such as voltage regulation, filtering, and timing.
- Cost-effectiveness: The components used in the circuit are relatively inexpensive, making it a cost-effective solution.
- Simplicity: The circuit is relatively simple to design and implement, requiring only a few basic components.
- Reliability: The circuit is robust and reliable, providing consistent performance over time.
Effective Strategies for Circuit Design
When designing a circuit with four resistors and one capacitor, consider these effective strategies:
- Use the correct resistor values: Calculate the appropriate resistor values based on the desired voltage and current levels.
- Choose a suitable capacitor: Select a capacitor with the appropriate capacitance value for the desired effect.
- Consider the frequency response: Take into account the frequency range of the input signal when selecting resistors and capacitors.
- Optimize the circuit layout: Arrange the components in a way that minimizes noise and ensures proper signal flow.
Step-by-Step Approach to Circuit Construction
Follow these steps to construct the circuit:
- Gather the components: Acquire four resistors, a capacitor, and a breadboard or prototyping board.
- Connect the resistors in series: Connect the resistors in sequence, from one end of the circuit to the other.
- Connect the capacitor in parallel: Place the capacitor in parallel with the last resistor in the series.
- Apply voltage to the circuit: Connect a voltage source (e.g., battery) to the input of the circuit.
- Test the circuit: Use a multimeter or oscilloscope to verify the voltage and current levels in the circuit.
Why Circuit Construction Matters
Understanding the principles behind the construction of a circuit is essential for several reasons:
- Troubleshooting: Enables the diagnosis and repair of electronic devices by identifying and resolving circuit issues.
- System design: Empowers engineers to design and develop complex electronic systems by incorporating appropriate circuits.
- Educational value: Provides a foundation for understanding electrical circuits and their applications in various fields.
Conclusion
A circuit constructed with four resistors and one capacitor offers a versatile and cost-effective solution for a wide range of applications in electronics. By understanding the functionality and benefits of this circuit, engineers, hobbyists, and electronics enthusiasts can leverage its capabilities to design and build innovative devices and systems.
Additional Resources
- Resistors: Basics and Applications
- Capacitors: Basics and Applications
- Circuit Construction Techniques
- Circuit Troubleshooting Guide
Tables
| Component | Symbol | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Resistor | R | Ω |
| Capacitor | C | F |
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Versatility | Can be configured for different functionalities |
| Cost-effectiveness | Inexpensive components |
| Simplicity | Easy to design and implement |
| Reliability | Robust and consistent performance |
| Application | Function |
|---|---|
| Voltage Regulator | Maintain constant voltage level |
| Filter | Remove unwanted noise and harmonics |
| Timing Circuit | Create time delays or generate pulses |
| Energy Storage | Store electrical energy |
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Gather components |
| 2 | Connect resistors in series |
| 3 | Connect capacitor in parallel |
| 4 | Apply voltage to circuit |
| 5 | Test circuit |